# Chatling
> ## Documentation Index
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/knowledge-base/add-data-source.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Add data source
> A guide on adding data sources to the Knowledge Base.
 ## How to add data to the knowledge base
To add data to the Knowledge Base, follow these steps:
1. From the dashboard, go to `Knowledge Base`.
## How to add data to the knowledge base
To add data to the Knowledge Base, follow these steps:
1. From the dashboard, go to `Knowledge Base`.
 2. Click on the `Add new` or `New Data Source` button.
2. Click on the `Add new` or `New Data Source` button.
 3. Select the type of data source you want to add.
3. Select the type of data source you want to add.
 4. Follow the on-screen instructions to add the data source to the knowledge base.
Once added, it will take a few minutes for the data to be processed. The status of the data source will be displayed in the Knowledge Base page and will change to "Processed" once the AI has extracted the information.
4. Follow the on-screen instructions to add the data source to the knowledge base.
Once added, it will take a few minutes for the data to be processed. The status of the data source will be displayed in the Knowledge Base page and will change to "Processed" once the AI has extracted the information.
 ---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/api-reference/v2/knowledge-base/add-faq.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Add FAQ
> Add new FAQ data sources to the knowledge base.
## Request parameters
### Path
The chatbot ID.
### Body
Array of FAQs to add to the knowledge base.
The question of the FAQ.
The answer of the FAQ.
## Response
The status of the request. Will be `success` if the request was successful, otherwise `error`.
The number of FAQs that were added successfully.
```json Response theme={null}
{
"status": "success",
"data": {
"faqs_added": 45
}
}
```
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/web-widget/add-footer-text.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Add disclaimer, privacy notice, or custom text to footer
> Learn how to display custom text in the chatbot's footer.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/api-reference/v2/knowledge-base/add-faq.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Add FAQ
> Add new FAQ data sources to the knowledge base.
## Request parameters
### Path
The chatbot ID.
### Body
Array of FAQs to add to the knowledge base.
The question of the FAQ.
The answer of the FAQ.
## Response
The status of the request. Will be `success` if the request was successful, otherwise `error`.
The number of FAQs that were added successfully.
```json Response theme={null}
{
"status": "success",
"data": {
"faqs_added": 45
}
}
```
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/web-widget/add-footer-text.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Add disclaimer, privacy notice, or custom text to footer
> Learn how to display custom text in the chatbot's footer.
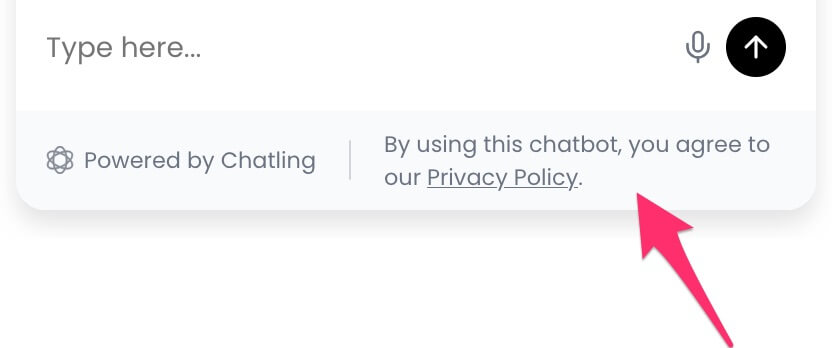 Often times, you may want to display a text in the chatbot's footer, such as a disclaimer, privacy notice, or any other text. Here's how you can do that.
1. Open the `Deploy` page.
Often times, you may want to display a text in the chatbot's footer, such as a disclaimer, privacy notice, or any other text. Here's how you can do that.
1. Open the `Deploy` page.
 2. Under the `Website Widget` option, click the brush icon to open the widget editor.
2. Under the `Website Widget` option, click the brush icon to open the widget editor.
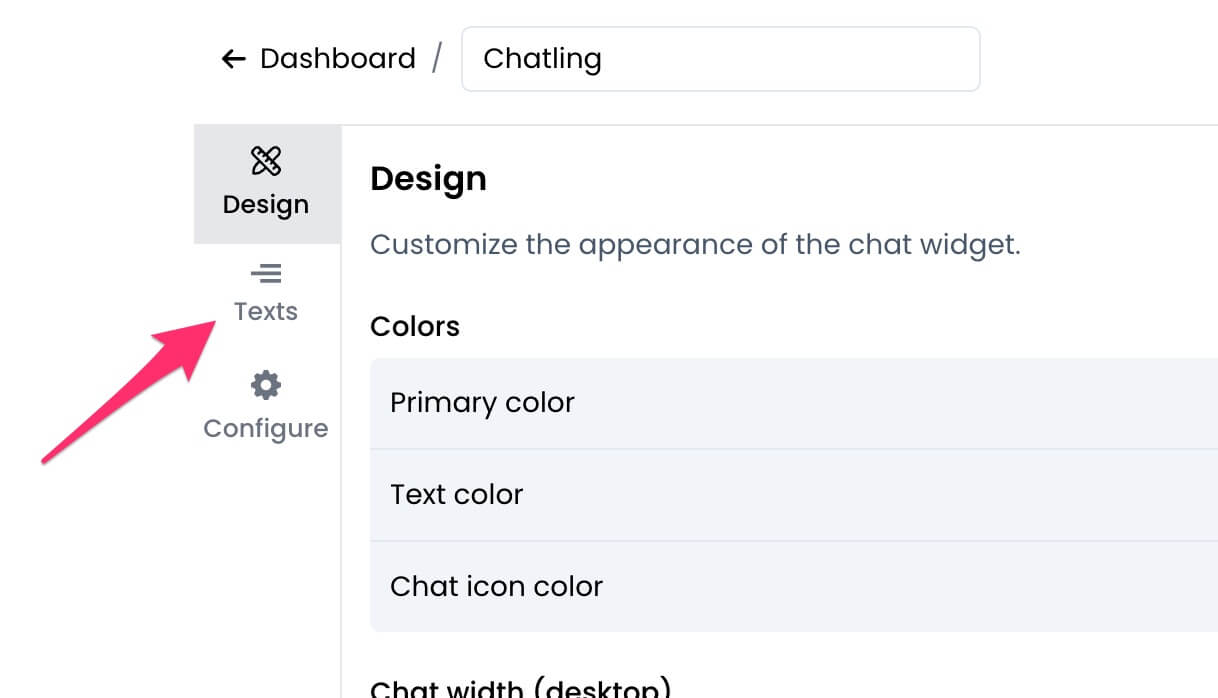
 3. Click on `Texts` from the sidebar.
3. Click on `Texts` from the sidebar.
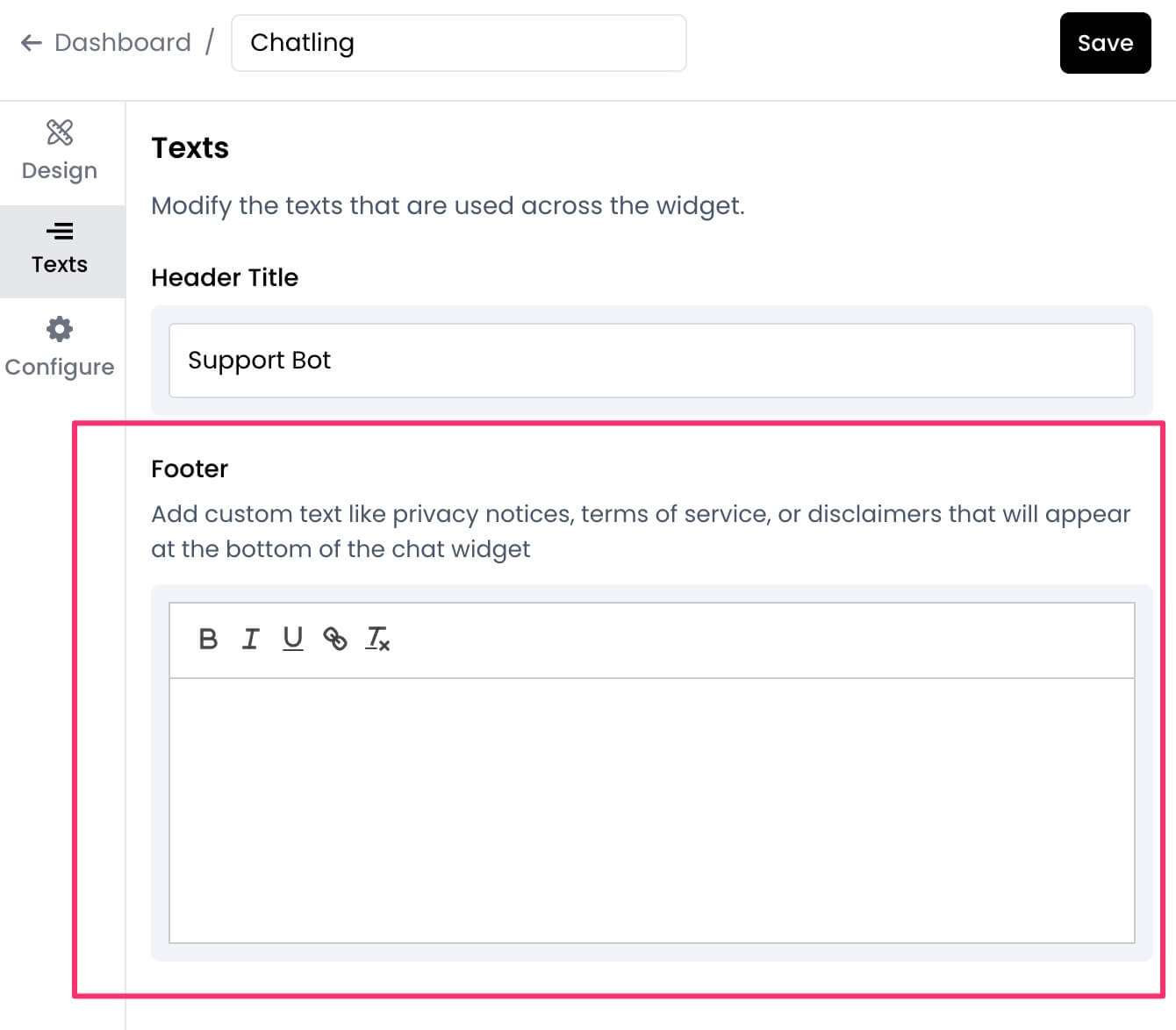
 4. Under the `Footer` section, you can enter the text you want to display.
4. Under the `Footer` section, you can enter the text you want to display.
 5. Click `Save` to apply the changes.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/api-reference/v2/knowledge-base/add-link.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Add link
> Add new link data sources to the knowledge base.
## Request parameters
### Path
The chatbot ID.
### Body
Array of webpage links to add to the knowledge base.
Exclude sections of webpages based on their HTML class names.
Exclude sections of webpages based on their HTML IDs.
Exclude `header` tags.
Exclude `footer` tags.
Exclude `nav` tags.
## Response
The status of the request. Will be `success` if the request was successful, otherwise `error`.
The number of links that were added successfully.
An array of duplicate links that were removed.
```json Response theme={null}
{
"status": "success",
"data": {
"links_added": 105,
"duplicate_links_removed": []
}
}
```
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/api-reference/v2/knowledge-base/add-text.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Add text
> Add new text data sources to the knowledge base.
## Request parameters
### Path
The chatbot ID.
### Body
Array of texts to add to the knowledge base.
## Response
The status of the request. Will be `success` if the request was successful, otherwise `error`.
The number of texts that were added successfully.
```json Response theme={null}
{
"status": "success",
"data": {
"texts_added": 45
}
}
```
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/api-reference/v2/usage/ai-credits.md
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/ai/ai-credits.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# AI credits
> Understanding AI credits and how they are consumed
AI credits are used to manage and track AI usage. These credits are consumed each time a chatbot or AI agent generates an AI response.
The number of credits consumed per response varies based on the AI model you use. Below's a breakdown of credit usage by model.
For chatbots, credits are not consumed for normal messages sent and received by users. It is only used when the chatbot uses AI to generate responses (such as when you use the [AI block](/chatbot/builder/blocks/ai/ai-response)).
## Credits usage by AI model
* Claude Sonnet 4.5: 3 credits
* Claude Haiku 4.5: 2 credits
* Claude Sonnet 4: 3 credits
* Claude Opus 4: 15 credits
* Claude Haiku 3.5: 2 credits
* Gemini 2.5 Pro: 1.5 credit
* Gemini 2.5 Flash: 0.5 credit
* Gemini 2.0 Flash: 0.5 credit
* GPT-5.1: 2 credits
* GPT-5: 2 credits
* GPT-5 Mini: 1 credit
* GPT-5 Nano: 1 credit
* GPT-4.1: 2.5 credits
* GPT-4.1 Mini: 1 credit
* GPT-4.1 Nano: 0.5 credit
* GPT-4o: 2.5 credits
* GPT-4o mini: 0.5 credit
* o3 Mini: 2 credits
* o4 Mini: 3.5 credits
## How to check your AI credits usage
1. Log in to your account.
2. Click the `Billing & usage` menu in the sidebar.
3. Click the `Usage` tab.
4. The usage will be displayed under the `Monthly usage` section.
5. Click `Save` to apply the changes.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/api-reference/v2/knowledge-base/add-link.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Add link
> Add new link data sources to the knowledge base.
## Request parameters
### Path
The chatbot ID.
### Body
Array of webpage links to add to the knowledge base.
Exclude sections of webpages based on their HTML class names.
Exclude sections of webpages based on their HTML IDs.
Exclude `header` tags.
Exclude `footer` tags.
Exclude `nav` tags.
## Response
The status of the request. Will be `success` if the request was successful, otherwise `error`.
The number of links that were added successfully.
An array of duplicate links that were removed.
```json Response theme={null}
{
"status": "success",
"data": {
"links_added": 105,
"duplicate_links_removed": []
}
}
```
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/api-reference/v2/knowledge-base/add-text.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Add text
> Add new text data sources to the knowledge base.
## Request parameters
### Path
The chatbot ID.
### Body
Array of texts to add to the knowledge base.
## Response
The status of the request. Will be `success` if the request was successful, otherwise `error`.
The number of texts that were added successfully.
```json Response theme={null}
{
"status": "success",
"data": {
"texts_added": 45
}
}
```
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/api-reference/v2/usage/ai-credits.md
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/ai/ai-credits.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# AI credits
> Understanding AI credits and how they are consumed
AI credits are used to manage and track AI usage. These credits are consumed each time a chatbot or AI agent generates an AI response.
The number of credits consumed per response varies based on the AI model you use. Below's a breakdown of credit usage by model.
For chatbots, credits are not consumed for normal messages sent and received by users. It is only used when the chatbot uses AI to generate responses (such as when you use the [AI block](/chatbot/builder/blocks/ai/ai-response)).
## Credits usage by AI model
* Claude Sonnet 4.5: 3 credits
* Claude Haiku 4.5: 2 credits
* Claude Sonnet 4: 3 credits
* Claude Opus 4: 15 credits
* Claude Haiku 3.5: 2 credits
* Gemini 2.5 Pro: 1.5 credit
* Gemini 2.5 Flash: 0.5 credit
* Gemini 2.0 Flash: 0.5 credit
* GPT-5.1: 2 credits
* GPT-5: 2 credits
* GPT-5 Mini: 1 credit
* GPT-5 Nano: 1 credit
* GPT-4.1: 2.5 credits
* GPT-4.1 Mini: 1 credit
* GPT-4.1 Nano: 0.5 credit
* GPT-4o: 2.5 credits
* GPT-4o mini: 0.5 credit
* o3 Mini: 2 credits
* o4 Mini: 3.5 credits
## How to check your AI credits usage
1. Log in to your account.
2. Click the `Billing & usage` menu in the sidebar.
3. Click the `Usage` tab.
4. The usage will be displayed under the `Monthly usage` section.
 ---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/blocks/ai/ai-response.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# AI Response Block
> Learn about the AI Response block and how to set it up in the Builder.
The AI Response block is used for generating responses to user input using AI. It can provide answers based on the information you have added to the [Knowledge Base](/knowledge-base/overview) or from the AI's pretrained data.
The AI uses natural language processing (NLP) to understand the user's input and generate relevant responses.
## What is the "Response Source"?
The Response Source determines where the AI will look for answers to user queries. You can choose from the following options:
* **Knowledge Base**: The AI will search the data you've uploaded to the Knowledge Base for the relevant information and return the corresponding answer.
* **AI Model**: The AI will use its pretrained data to generate a response based on the user's query. This is ideal for a general-purpose AI that can answer a wide range of questions without limiting its responses to the data in the knowledge base.
## Configurations for Knowledge Base Response Source
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/blocks/ai/ai-response.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# AI Response Block
> Learn about the AI Response block and how to set it up in the Builder.
The AI Response block is used for generating responses to user input using AI. It can provide answers based on the information you have added to the [Knowledge Base](/knowledge-base/overview) or from the AI's pretrained data.
The AI uses natural language processing (NLP) to understand the user's input and generate relevant responses.
## What is the "Response Source"?
The Response Source determines where the AI will look for answers to user queries. You can choose from the following options:
* **Knowledge Base**: The AI will search the data you've uploaded to the Knowledge Base for the relevant information and return the corresponding answer.
* **AI Model**: The AI will use its pretrained data to generate a response based on the user's query. This is ideal for a general-purpose AI that can answer a wide range of questions without limiting its responses to the data in the knowledge base.
## Configurations for Knowledge Base Response Source
 When you select the "Knowledge Base" as the Response Source, you can configure the following settings:
* **Question**: The user's input or query that the AI will process to generate a response. You can use variables to make the question dynamic. For example, you can capture the user's input using a Text input block and store it in a variable called `user_input`. Then, you can use this variable in the "Question" field to make the AI response dynamic.
* **Store response in variable**: You can store the AI response in a variable to use it in other blocks.
* **Stream**: When enabled, the AI response will be streamed to the user in real-time as it is generated. This provides a more interactive experience for the user.
* When Stream is enabled, some features that require post-processing, such as "Not Found path" will be disabled.
* **Not Found path**: The path to follow if the AI does not find a relevant answer in the Knowledge Base.
* **Model**: The AI model to use for generating responses.
* **Language**: The language in which the AI will respond to the user. If you set it to "Auto," the AI will detect the language of the user's input and respond in the same language.
* If you want the AI to respond in a certain dialect or accent, you can specify it in Instructions section of the [AI Configuration](/chatbot/builder/sidebar#ai-configuration).
* **Temperature**: The randomness of the AI's responses. A higher temperature value will result in more diverse and creative responses, while a lower value will produce more accurate responses.
### What does "Use global AI settings" mean?
When you set an option, such as the AI model, language, or temperature to "Use global AI settings", the AI will use the settings defined in the [AI Configuration](/chatbot/builder/sidebar#ai-configuration) menu in the [sidebar](/chatbot/builder/sidebar). This allows you to define global settings that will be applied to all AI blocks in your bot.
## Configurations for AI Model Response Source
When you set the Response Source to "AI Model", you can configure the following settings:
* **Prompt**: The message or query that the AI will use to generate a response. You can use variables to make the prompt dynamic.
* **Store response in variable**: You can store the AI response in a variable to use it in other blocks.
* **Instructions**: Additional instructions for the AI to follow when generating a response. For example, you can specify its personality, tone, or style, or provide specific context for the response.
* **Model**: The AI model to use for generating responses.
* **Max Length**: Maximum number of tokens to generate, shared between the prompt and the response. One token is roughly 4 characters.
* **Temperature**: Randomness of the AI's responses. A higher temperature value will result in more diverse and creative responses, while a lower value will produce more focused and deterministic responses.
* **Top P**: Controls diversity via nucleus sampling: 0.5 means half of all likelihood-weighted options are considered.
* **Frequency Penalty**: How much to penalize new tokens based on their existing frequency in the text so far. Decreases the model's likelihood to repeat the same line verbatim.
* **Presence Penalty**: How much to penalize new tokens based on whether they appear in the text so far. Increases the model's likelihood to talk about new topics.
## How to set up the AI block to respond from the knowledge base?
Here's a high level overview of how the AI generates responses using the knowledge base:
* The user inputs a question or query, which is saved in a variable of your choice.
* The stored input is passed to the AI which uses natural language processing (NLP) to understand the user's query and the context of the conversation.
* The AI searches the knowledge base for relevant information.
* The AI generates the response and displays it to the user.
To set up the AI block, follow these steps:
1. Add a Text input block to the canvas. We'll use this block to capture the user's input and store it in a variable so it can be passed to the AI block.
When you select the "Knowledge Base" as the Response Source, you can configure the following settings:
* **Question**: The user's input or query that the AI will process to generate a response. You can use variables to make the question dynamic. For example, you can capture the user's input using a Text input block and store it in a variable called `user_input`. Then, you can use this variable in the "Question" field to make the AI response dynamic.
* **Store response in variable**: You can store the AI response in a variable to use it in other blocks.
* **Stream**: When enabled, the AI response will be streamed to the user in real-time as it is generated. This provides a more interactive experience for the user.
* When Stream is enabled, some features that require post-processing, such as "Not Found path" will be disabled.
* **Not Found path**: The path to follow if the AI does not find a relevant answer in the Knowledge Base.
* **Model**: The AI model to use for generating responses.
* **Language**: The language in which the AI will respond to the user. If you set it to "Auto," the AI will detect the language of the user's input and respond in the same language.
* If you want the AI to respond in a certain dialect or accent, you can specify it in Instructions section of the [AI Configuration](/chatbot/builder/sidebar#ai-configuration).
* **Temperature**: The randomness of the AI's responses. A higher temperature value will result in more diverse and creative responses, while a lower value will produce more accurate responses.
### What does "Use global AI settings" mean?
When you set an option, such as the AI model, language, or temperature to "Use global AI settings", the AI will use the settings defined in the [AI Configuration](/chatbot/builder/sidebar#ai-configuration) menu in the [sidebar](/chatbot/builder/sidebar). This allows you to define global settings that will be applied to all AI blocks in your bot.
## Configurations for AI Model Response Source
When you set the Response Source to "AI Model", you can configure the following settings:
* **Prompt**: The message or query that the AI will use to generate a response. You can use variables to make the prompt dynamic.
* **Store response in variable**: You can store the AI response in a variable to use it in other blocks.
* **Instructions**: Additional instructions for the AI to follow when generating a response. For example, you can specify its personality, tone, or style, or provide specific context for the response.
* **Model**: The AI model to use for generating responses.
* **Max Length**: Maximum number of tokens to generate, shared between the prompt and the response. One token is roughly 4 characters.
* **Temperature**: Randomness of the AI's responses. A higher temperature value will result in more diverse and creative responses, while a lower value will produce more focused and deterministic responses.
* **Top P**: Controls diversity via nucleus sampling: 0.5 means half of all likelihood-weighted options are considered.
* **Frequency Penalty**: How much to penalize new tokens based on their existing frequency in the text so far. Decreases the model's likelihood to repeat the same line verbatim.
* **Presence Penalty**: How much to penalize new tokens based on whether they appear in the text so far. Increases the model's likelihood to talk about new topics.
## How to set up the AI block to respond from the knowledge base?
Here's a high level overview of how the AI generates responses using the knowledge base:
* The user inputs a question or query, which is saved in a variable of your choice.
* The stored input is passed to the AI which uses natural language processing (NLP) to understand the user's query and the context of the conversation.
* The AI searches the knowledge base for relevant information.
* The AI generates the response and displays it to the user.
To set up the AI block, follow these steps:
1. Add a Text input block to the canvas. We'll use this block to capture the user's input and store it in a variable so it can be passed to the AI block.
 2. Click on the Text block to open the editor. In the `Store answer in variable` field, enter a variable where the user's input will be stored. In this example, we'll create and use a variable called `user_query`.
2. Click on the Text block to open the editor. In the `Store answer in variable` field, enter a variable where the user's input will be stored. In this example, we'll create and use a variable called `user_query`.
 3. Next, drag and drop the AI Response block onto the canvas.
3. Next, drag and drop the AI Response block onto the canvas.
 4. Connect the Text input block to the AI block by dragging the connector from the Text block to the AI block.
4. Connect the Text input block to the AI block by dragging the connector from the Text block to the AI block.
 5. Click the AI Response block to open the editor. In the `Question` field, enter the variable where the user's input is stored. In step 2, we used the `user_query` variable, so we'll enter `{user_query}` in the Question field.
5. Click the AI Response block to open the editor. In the `Question` field, enter the variable where the user's input is stored. In step 2, we used the `user_query` variable, so we'll enter `{user_query}` in the Question field.
 6. Set up the global AI settings by going to the `AI Configuration` in the sidebar. You can define settings such as the AI model, instructions, language, and business name.
7. Lastly, set up the block connections accordingly. For example, a setup like below will allow the user to continually ask questions and receive responses from the AI.
6. Set up the global AI settings by going to the `AI Configuration` in the sidebar. You can define settings such as the AI model, instructions, language, and business name.
7. Lastly, set up the block connections accordingly. For example, a setup like below will allow the user to continually ask questions and receive responses from the AI.
 ---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/ai-agent/ai-settings.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# AI settings
To configure the agent's AI settings, click the `Settings` button in the sidebar and select `AI`.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/ai-agent/ai-settings.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# AI settings
To configure the agent's AI settings, click the `Settings` button in the sidebar and select `AI`.
 ## Available settings
### AI Model
The AI model that the agent will use to think, plan, and generate answers to the user queries.
Every model has different capabilities and costs. We recommend testing with different models in the [Playground](/ai-agent/playground) to see which one works best for your agent.
### Temperature
Controls randomness/creativity in the Agent's writing and decision-making.
Lower = more deterministic; Higher = more varied.
* **0.0-0.3 (Precise)**: Best for support, policy-bound replies, data extraction, or when strict adherence to facts and formats is required.
* **0.4-0.6 (Balanced)**: Good general setting for helpful responses with light creativity.
* **0.7-1.0 (Creative)**: Use for brainstorming, marketing copy, or when variety is desirable. Expect less consistency.
**Tips**
* If your Agent must follow exact steps (e.g., collecting parameters for an HTTP Request), keep temperature low.
* Raise temperature only where tone/creativity matters and accuracy isn't compromised.
### Instructions
Define the Agent's role, goals, guardrails, and style (often called the "system prompt").
Here's some of the things you can include in the instructions:
* **Role & purpose**: What the Agent is for and what success looks like.
* **Scope & boundaries**: What it should/shouldn't answer.
* **Tone & language**: Brand voice, formality level, and multilingual behavior (auto-detect language; reply in user's language).
* **Compliance & safety**: Any legal disclaimers, restricted topics, PII handling, and masking sensitive values.
* **Formatting**: Preferred reply structure (short summaries, bullet points, tables).
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/blocks/send/audio.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Audio Block
> Learn about the Audio block and how to set it up in the builder
The Audio block allows you to play an audio file to the user in the conversation. It can be used for various purposes, such as playing a welcome message, providing information, or playing music.
## Adding an audio file
To add an audio file, you can either upload an audio file directly or provide a link to a file hosted online. The supported audio formats are `MP3`, `WAV`, and `OGG`.
## Available settings
### AI Model
The AI model that the agent will use to think, plan, and generate answers to the user queries.
Every model has different capabilities and costs. We recommend testing with different models in the [Playground](/ai-agent/playground) to see which one works best for your agent.
### Temperature
Controls randomness/creativity in the Agent's writing and decision-making.
Lower = more deterministic; Higher = more varied.
* **0.0-0.3 (Precise)**: Best for support, policy-bound replies, data extraction, or when strict adherence to facts and formats is required.
* **0.4-0.6 (Balanced)**: Good general setting for helpful responses with light creativity.
* **0.7-1.0 (Creative)**: Use for brainstorming, marketing copy, or when variety is desirable. Expect less consistency.
**Tips**
* If your Agent must follow exact steps (e.g., collecting parameters for an HTTP Request), keep temperature low.
* Raise temperature only where tone/creativity matters and accuracy isn't compromised.
### Instructions
Define the Agent's role, goals, guardrails, and style (often called the "system prompt").
Here's some of the things you can include in the instructions:
* **Role & purpose**: What the Agent is for and what success looks like.
* **Scope & boundaries**: What it should/shouldn't answer.
* **Tone & language**: Brand voice, formality level, and multilingual behavior (auto-detect language; reply in user's language).
* **Compliance & safety**: Any legal disclaimers, restricted topics, PII handling, and masking sensitive values.
* **Formatting**: Preferred reply structure (short summaries, bullet points, tables).
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/blocks/send/audio.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Audio Block
> Learn about the Audio block and how to set it up in the builder
The Audio block allows you to play an audio file to the user in the conversation. It can be used for various purposes, such as playing a welcome message, providing information, or playing music.
## Adding an audio file
To add an audio file, you can either upload an audio file directly or provide a link to a file hosted online. The supported audio formats are `MP3`, `WAV`, and `OGG`.
 You can enable the `Autoplay` option to automatically play the audio file when the block is displayed to the user.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/knowledge-base/auto-sync-data-sources.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Auto-sync data sources
> Learn how to auto-sync data sources in the Knowledge Base.
Auto-syncing allows you to automatically sync your knowledge base sources at specified intervals, such as daily, weekly, or monthly, to fetch the latest data. This ensures that your knowledge base is always up to date with the latest information.
## How to enable auto-syncing
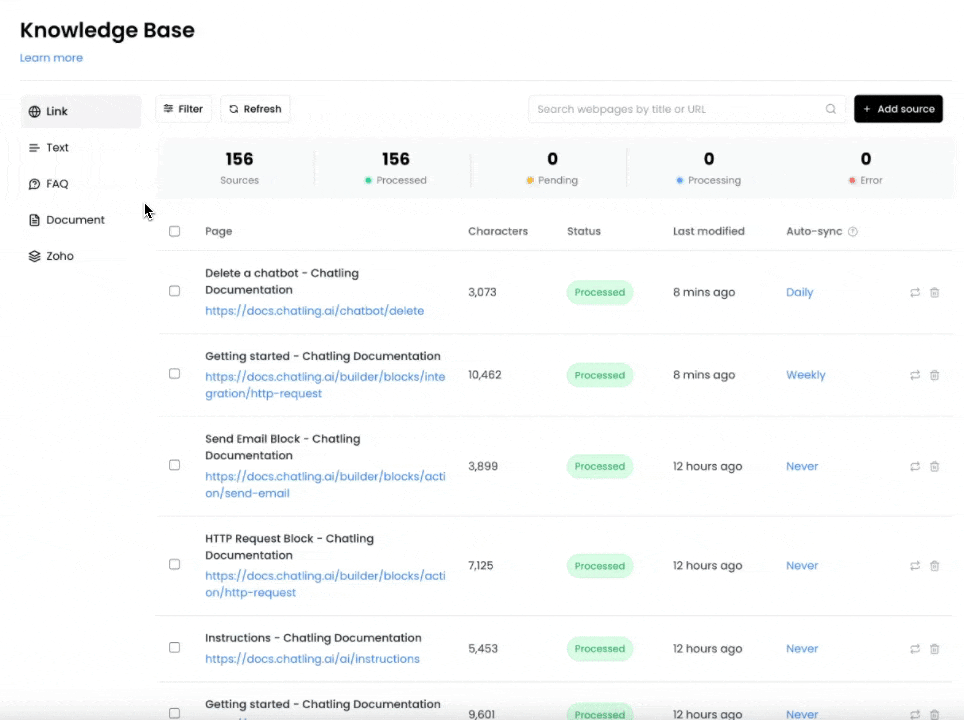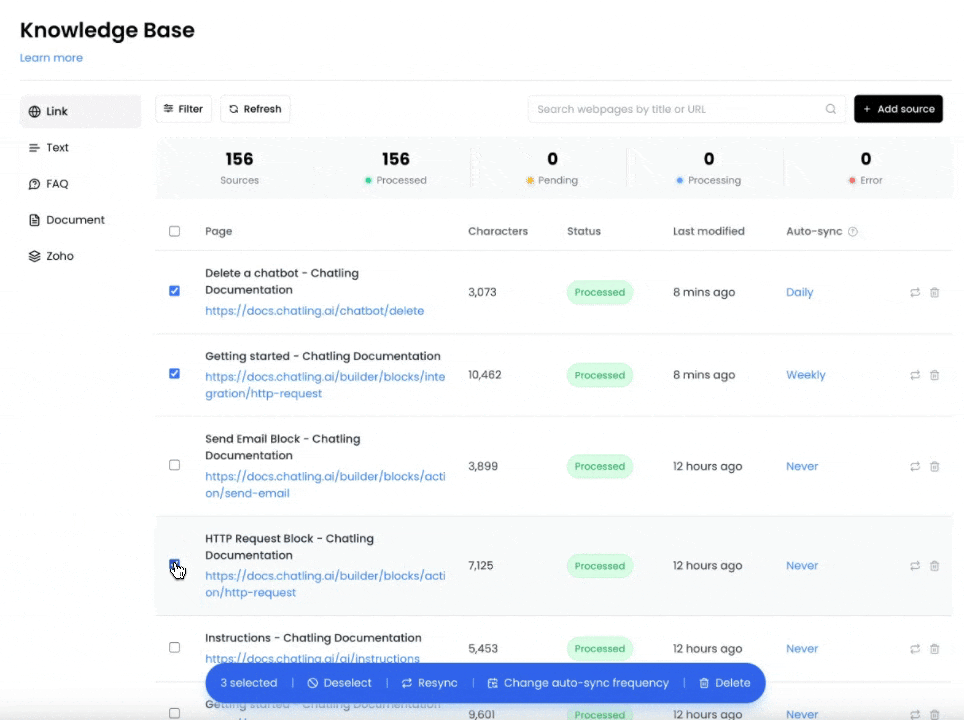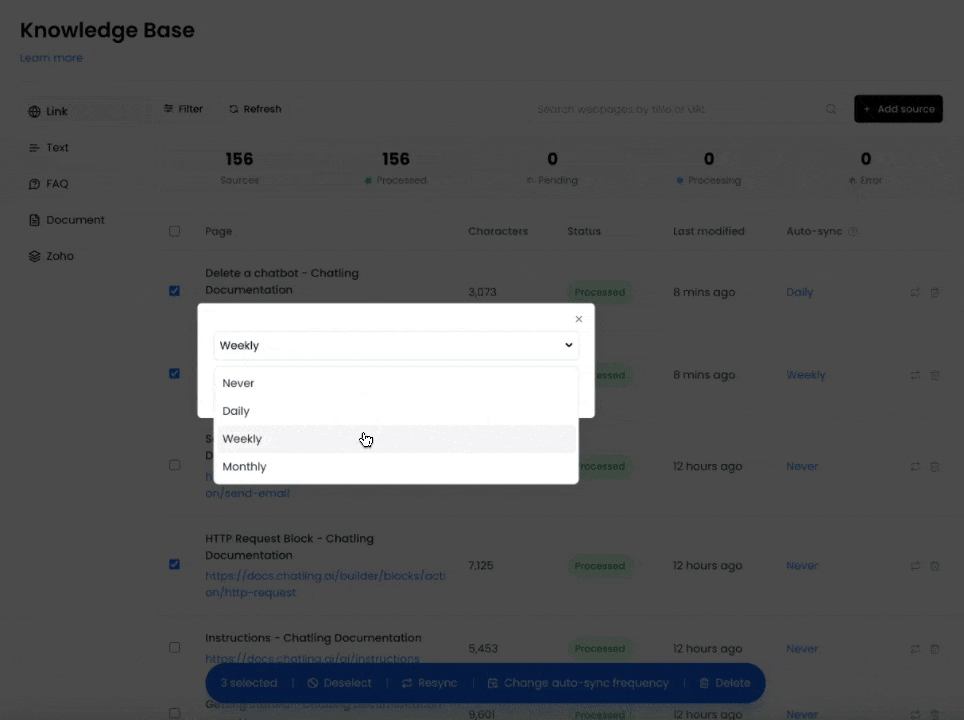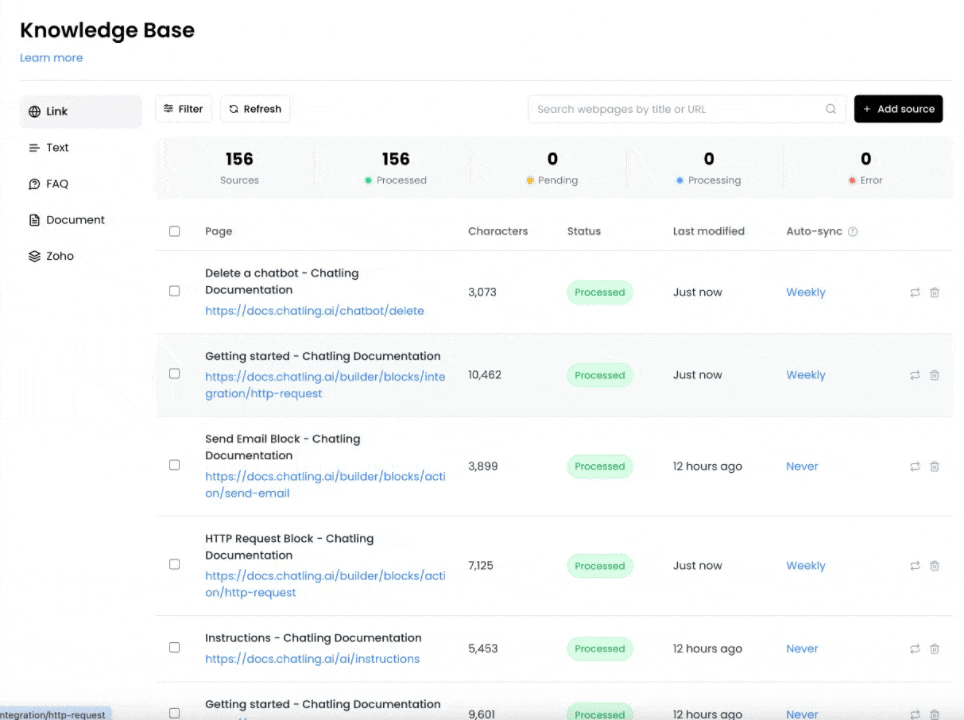
1. Go to the `Knowledge Base` page.
2. From the `Auto-sync` column, you can select an interval for each data source.
You can enable the `Autoplay` option to automatically play the audio file when the block is displayed to the user.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/knowledge-base/auto-sync-data-sources.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Auto-sync data sources
> Learn how to auto-sync data sources in the Knowledge Base.
Auto-syncing allows you to automatically sync your knowledge base sources at specified intervals, such as daily, weekly, or monthly, to fetch the latest data. This ensures that your knowledge base is always up to date with the latest information.
## How to enable auto-syncing
1. Go to the `Knowledge Base` page.
2. From the `Auto-sync` column, you can select an interval for each data source.
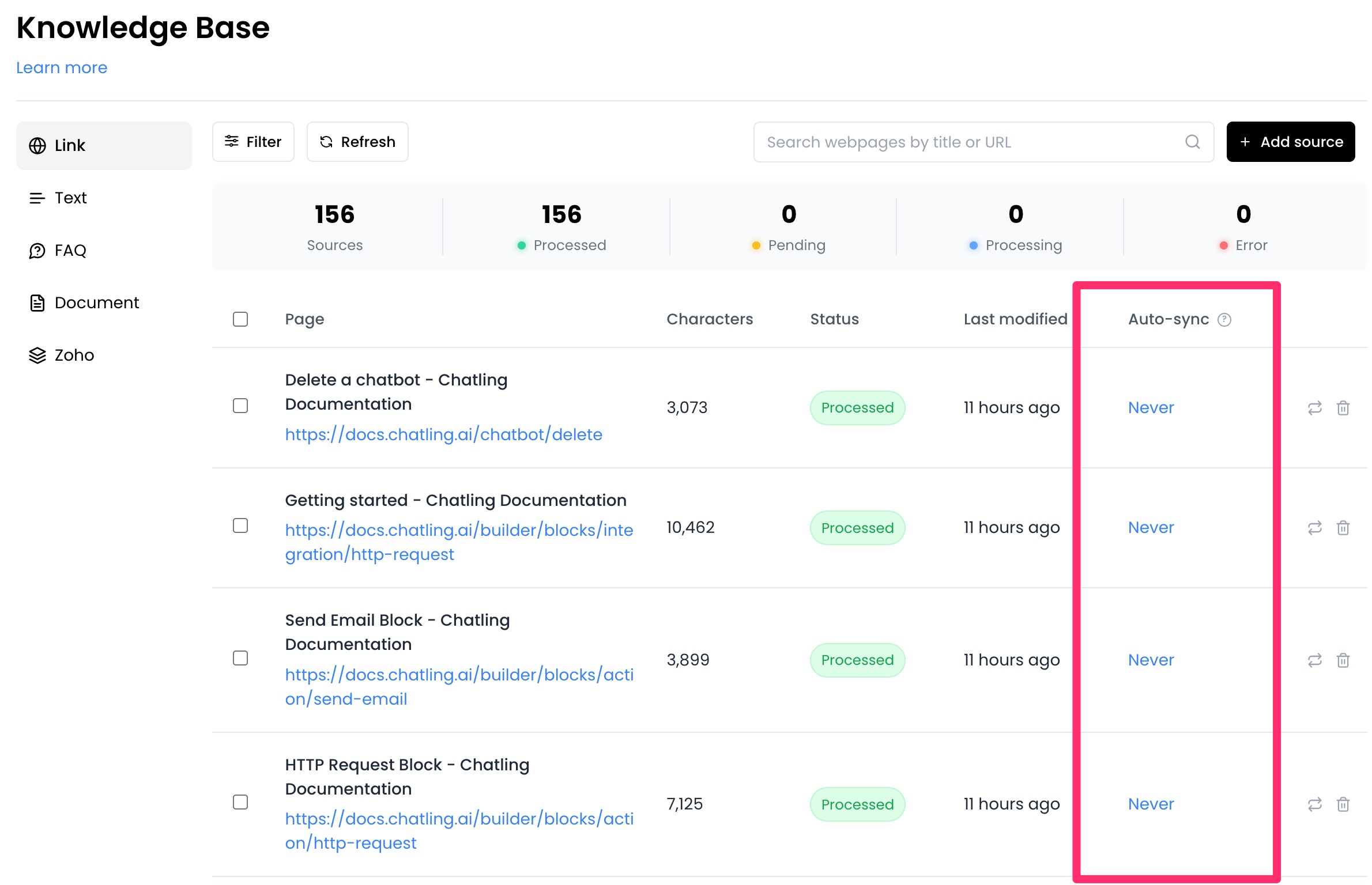 3. Click on the auto-sync value for a specific source and choose an interval.
3. Click on the auto-sync value for a specific source and choose an interval.
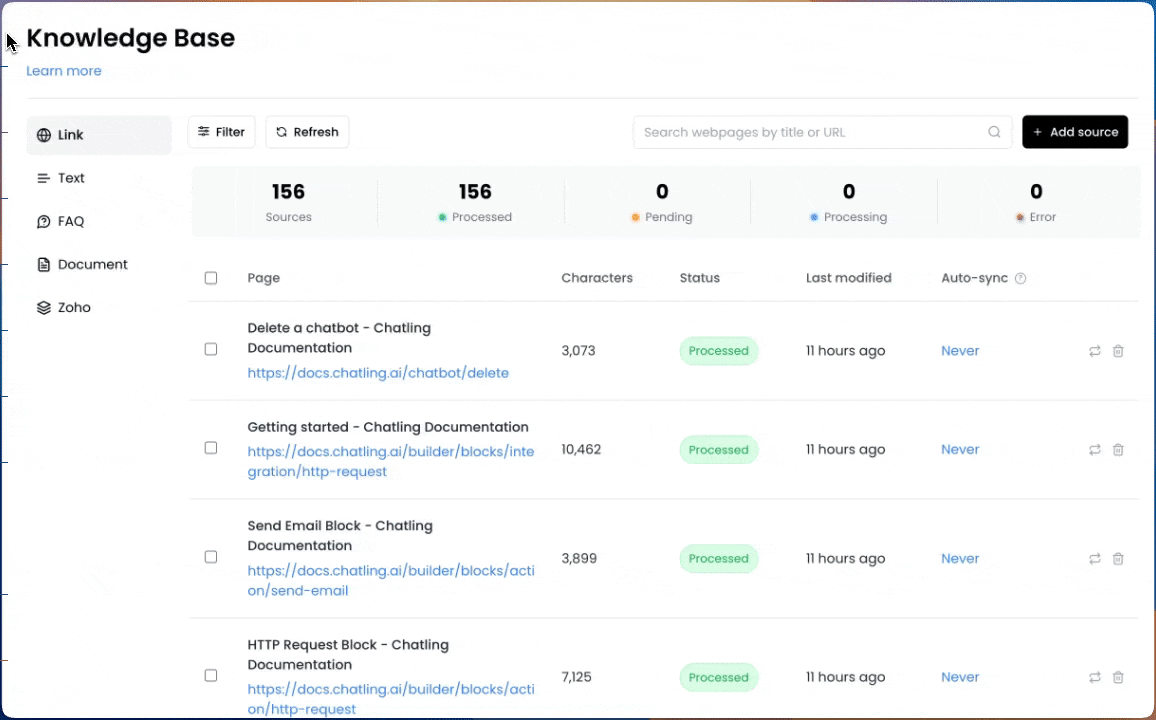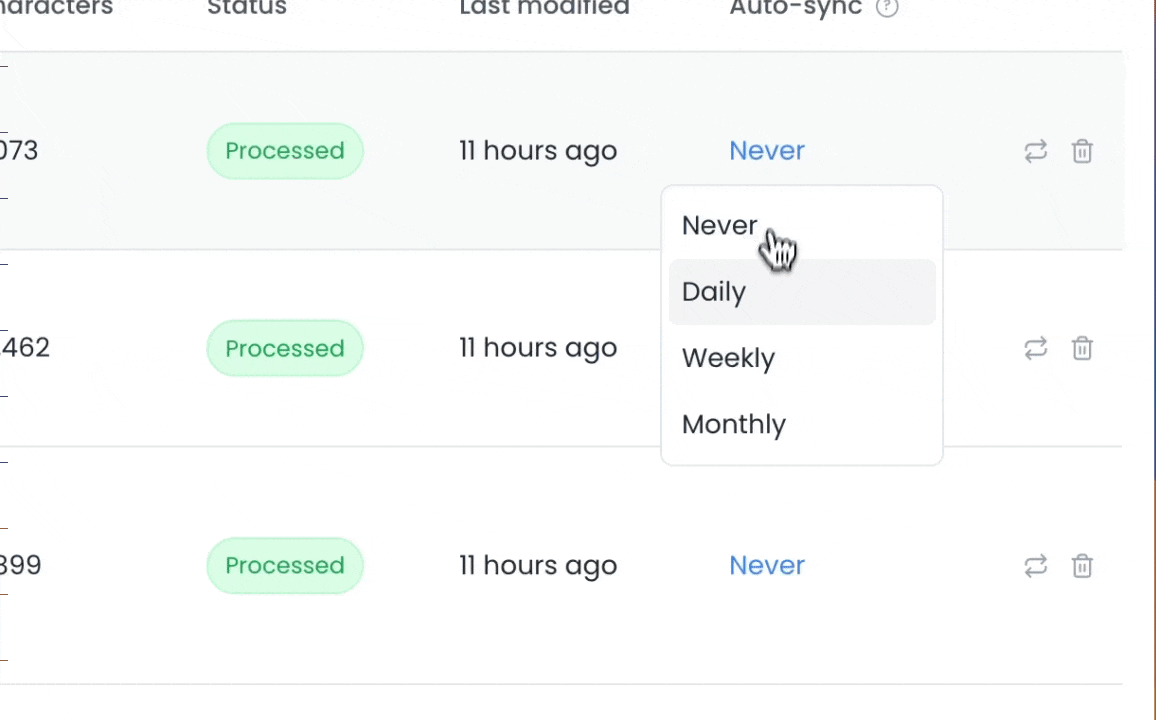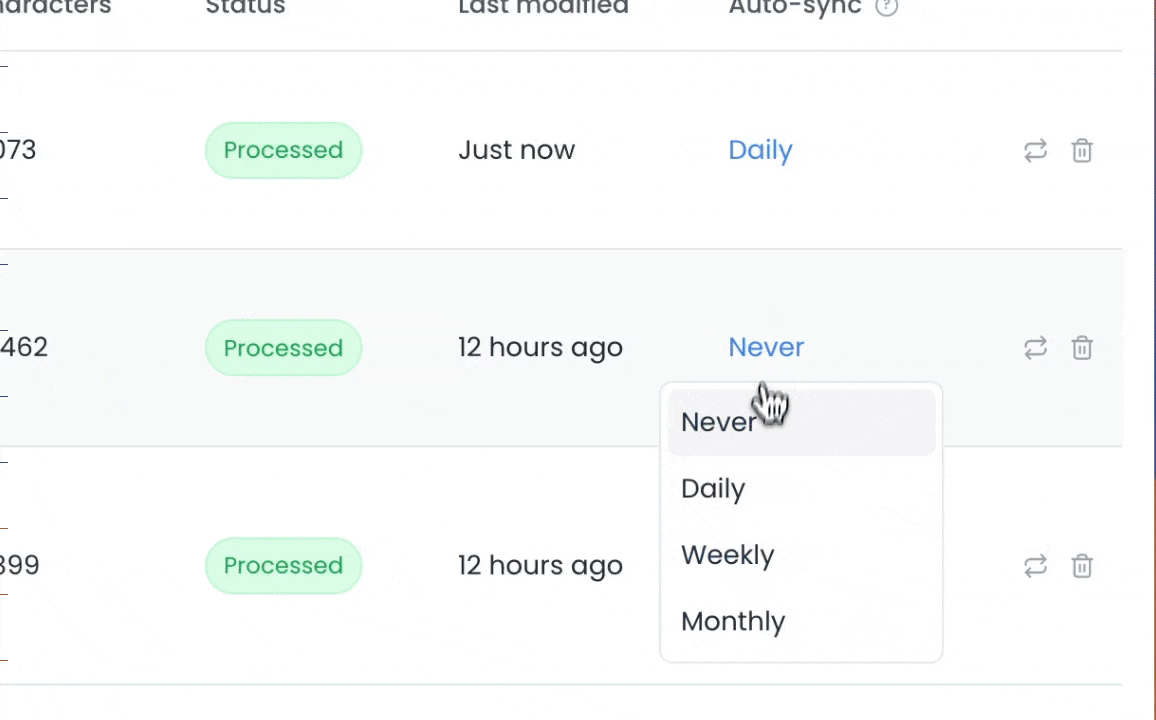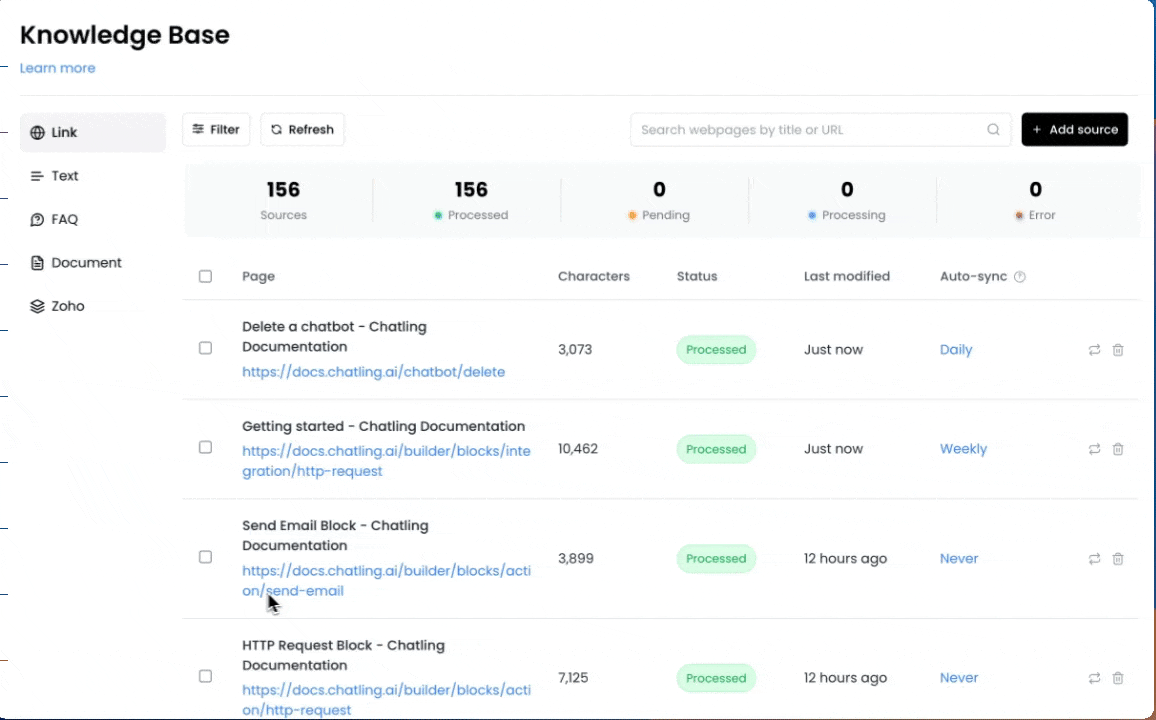 4. If you want to enable auto-syncing for multiple sources, you can select the sources and click the `Change auto-sync frequency` button to update all selected sources at once.
4. If you want to enable auto-syncing for multiple sources, you can select the sources and click the `Change auto-sync frequency` button to update all selected sources at once.
 ---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/variables/available-system-variables.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Available system variables
> List of all the system variables available and what they do.
Here are all the system variables that are available. If a variable is not present in your chatbot, you must [import it](/chatbot/builder/variables/import-system-variables).
`chat_id`
The unique identifier of the chat.
`user_id`
The unique identifier of the user.
`conversation_content`
The chat transcript (recent 25 messages).
`current_date`
The current date in UTC.
`current_time`
The current time in UTC.
`locale`
The user's browser locale, such as en-US, en-CA, fr-FR, pt-BR, etc.
`page_title`
The title of the page the user is currently on.
`page_url`
The URL of the page the user is currently on.
`timestamp`
The UNIX timestamp, which is the number of seconds since January 1, 1970 UTC.
`current_time`
The current time in UTC.
`current_date`
The current date in UTC.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/block-editor.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Block Editor
> Learn how to edit blocks in the Builder.
The Block Editor is where you can configure the settings of a block in the Builder.
The editor appears when you click a block that you've added to the canvas. Every block has its own unique settings that you can configure.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/variables/available-system-variables.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Available system variables
> List of all the system variables available and what they do.
Here are all the system variables that are available. If a variable is not present in your chatbot, you must [import it](/chatbot/builder/variables/import-system-variables).
`chat_id`
The unique identifier of the chat.
`user_id`
The unique identifier of the user.
`conversation_content`
The chat transcript (recent 25 messages).
`current_date`
The current date in UTC.
`current_time`
The current time in UTC.
`locale`
The user's browser locale, such as en-US, en-CA, fr-FR, pt-BR, etc.
`page_title`
The title of the page the user is currently on.
`page_url`
The URL of the page the user is currently on.
`timestamp`
The UNIX timestamp, which is the number of seconds since January 1, 1970 UTC.
`current_time`
The current time in UTC.
`current_date`
The current date in UTC.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/block-editor.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Block Editor
> Learn how to edit blocks in the Builder.
The Block Editor is where you can configure the settings of a block in the Builder.
The editor appears when you click a block that you've added to the canvas. Every block has its own unique settings that you can configure.
 ---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/web-widget/installation/bubble.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Bubble
> Learn how to add Chatling to your Bubble website
1. Go to your dashboard.
2. Click `Deploy` button in the sidebar menu.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/web-widget/installation/bubble.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Bubble
> Learn how to add Chatling to your Bubble website
1. Go to your dashboard.
2. Click `Deploy` button in the sidebar menu.
 3. Click the `Manage` button under the `Website Widget` option.
3. Click the `Manage` button under the `Website Widget` option.
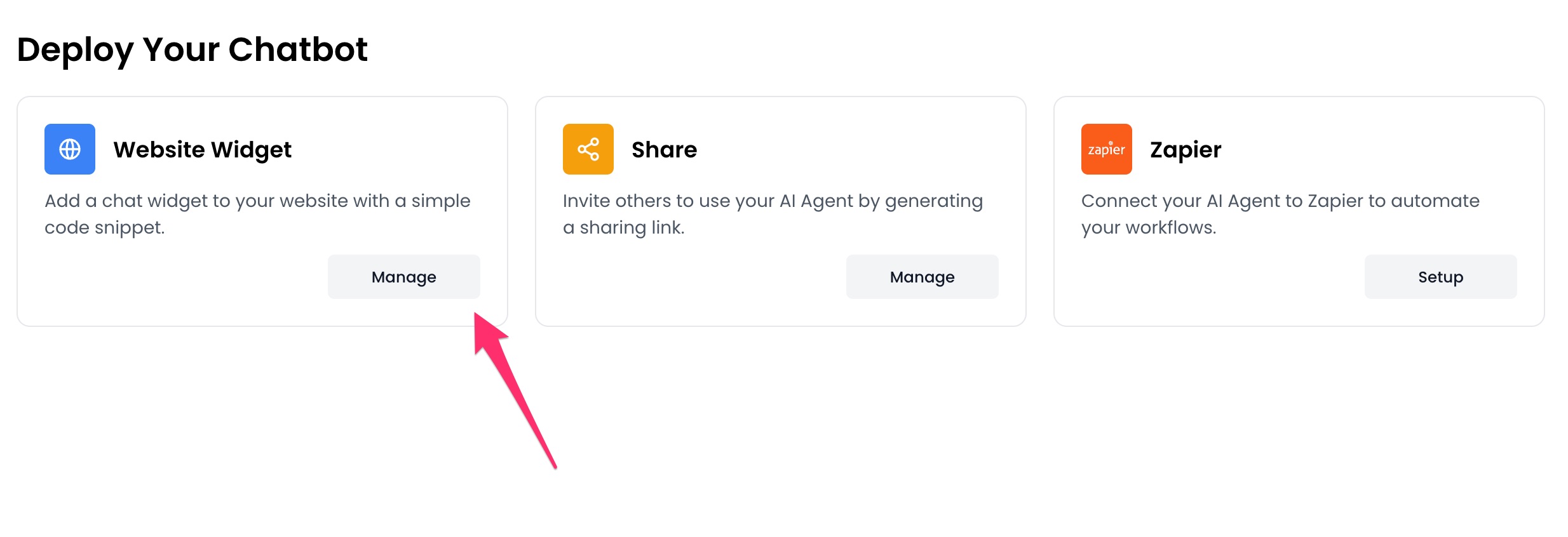 4. Design the appearance of the widget by clicking the `Open widget designer` button.
4. Design the appearance of the widget by clicking the `Open widget designer` button.
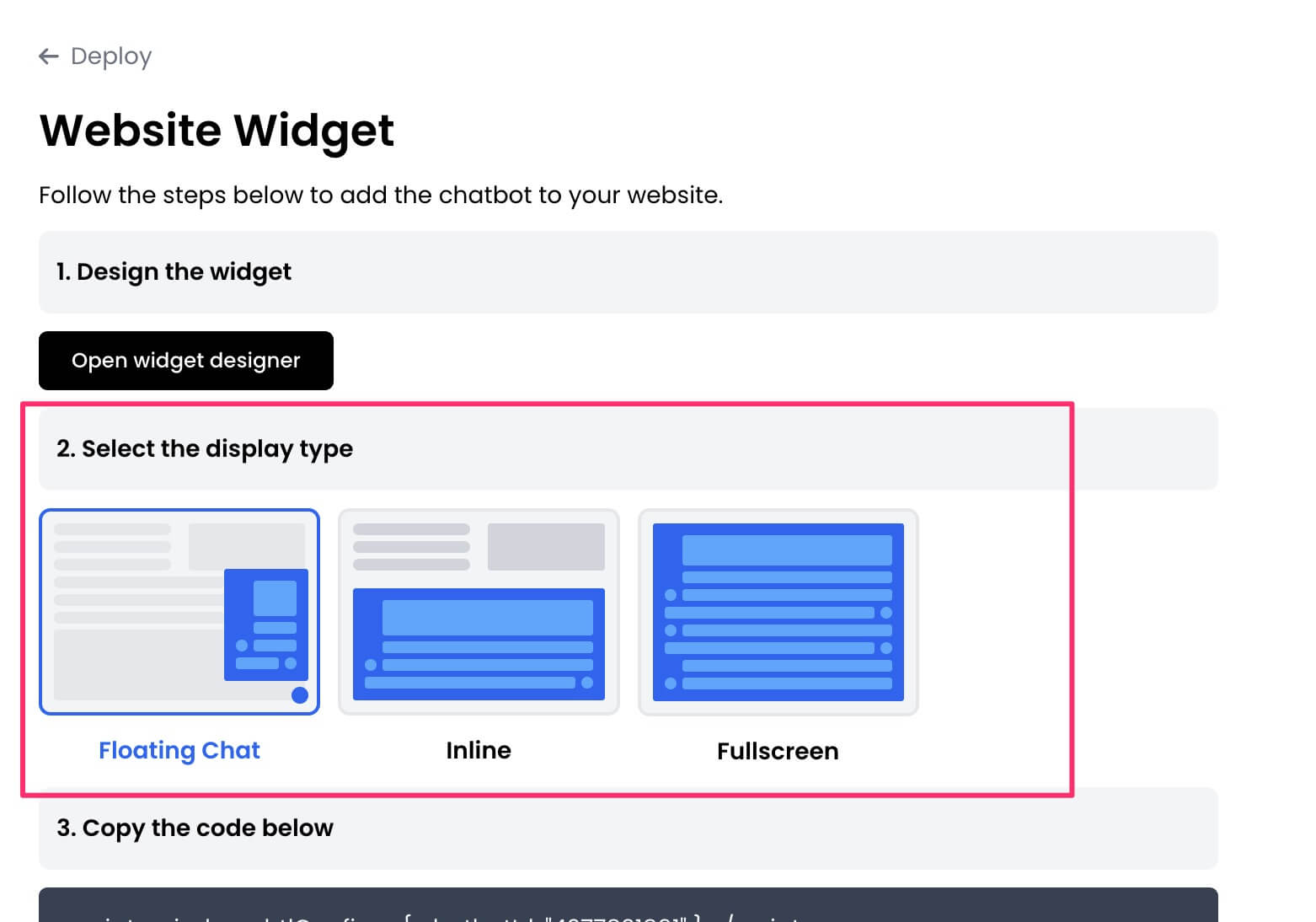
 5. Select the display mode for your chatbot, such as "Floating Chat", "Inline", or "Fullscreen".
5. Select the display mode for your chatbot, such as "Floating Chat", "Inline", or "Fullscreen".
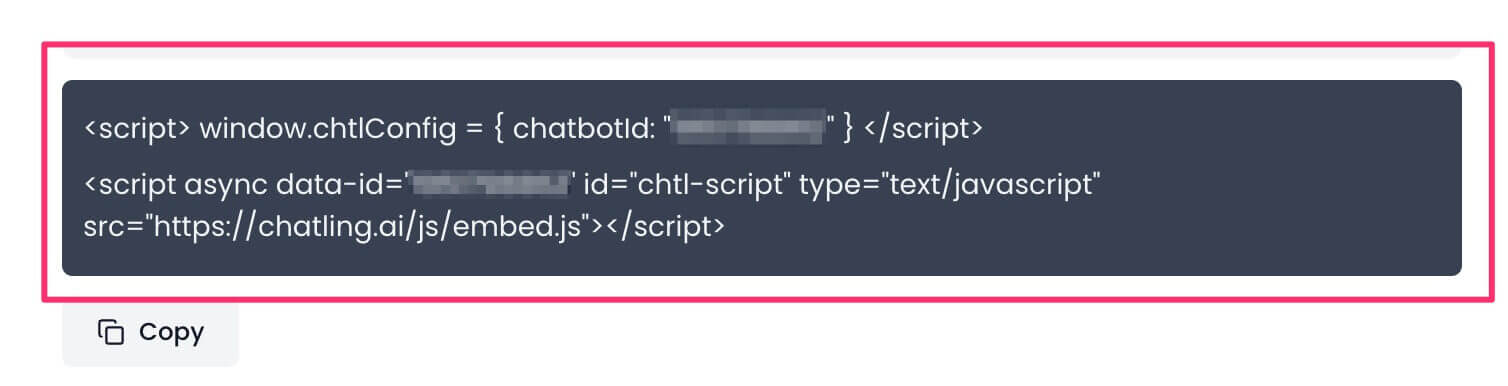
 6. Copy the widget code.
6. Copy the widget code.
 7. Go to your Bubble account and open the app/website where you want to add the widget.
7. Go to your Bubble account and open the app/website where you want to add the widget.
 8. On the side, click the gear icon to open Settings.
8. On the side, click the gear icon to open Settings.
 9. Go to `SEO / metatags`.
9. Go to `SEO / metatags`.
 10. Under the `SEO settings` section, paste the widget code in the header or body textbox.
10. Under the `SEO settings` section, paste the widget code in the header or body textbox.
 11. The settings will be saved automatically. Click the Preview icon to confirm that the widget has been added.
* Note that this method only works on paid plans. If you're on a free account, Bubble doesn't load the widget.
11. The settings will be saved automatically. Click the Preview icon to confirm that the widget has been added.
* Note that this method only works on paid plans. If you're on a free account, Bubble doesn't load the widget.
 ---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/blocks/inputs/buttons.md
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/ai-agent/actions/buttons.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Buttons
Displays a set of buttons in the chat, such as URL buttons to open a webpage or text buttons to send preset replies that keep the flow moving.
## Configuration
### `Action Name`
A short, specific identifier that tells the Agent what this action does (e.g. best\_sellers\_buttons, support\_button).
### `When to Use`
A detailed description of what the action does and when it must be used.
When applicable, you can specify one or more of the following:
* **Positive cues/phrases**: Example utterances and keywords that signal this action (include a few variations).
* **Preconditions**: What must be true before running.
* **Do not use when**: Explicit exclusions to avoid false triggers.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/blocks/inputs/buttons.md
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/ai-agent/actions/buttons.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Buttons
Displays a set of buttons in the chat, such as URL buttons to open a webpage or text buttons to send preset replies that keep the flow moving.
## Configuration
### `Action Name`
A short, specific identifier that tells the Agent what this action does (e.g. best\_sellers\_buttons, support\_button).
### `When to Use`
A detailed description of what the action does and when it must be used.
When applicable, you can specify one or more of the following:
* **Positive cues/phrases**: Example utterances and keywords that signal this action (include a few variations).
* **Preconditions**: What must be true before running.
* **Do not use when**: Explicit exclusions to avoid false triggers.
 ### `Frequency`
Specify how often the Agent can invoke this action to avoid overusing it, e.g `Once per chat` or `Whenever applicable`.
### `Frequency`
Specify how often the Agent can invoke this action to avoid overusing it, e.g `Once per chat` or `Whenever applicable`.
 ### `Buttons`
Add the buttons that you want to display in the chat. Buttons can be of two types:
* **URL button**: Opens a webpage when clicked.
* **Text button**: Sends a message to the AI agent when clicked. If a `Message` is provided, it will be sent as the message. Otherwise, the button label will be used.
To reorder the buttons, click the drag handle next to a button and move it up or down.
### `Buttons`
Add the buttons that you want to display in the chat. Buttons can be of two types:
* **URL button**: Opens a webpage when clicked.
* **Text button**: Sends a message to the AI agent when clicked. If a `Message` is provided, it will be sent as the message. Otherwise, the button label will be used.
To reorder the buttons, click the drag handle next to a button and move it up or down.
 ---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/ai-agent/actions/cal-booking.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Cal.com Booking Widget
The Cal.com Booking Widget action embeds your Cal.com scheduler directly inside the chat, so users can view real-time availability and book without leaving the conversation.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/ai-agent/actions/cal-booking.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Cal.com Booking Widget
The Cal.com Booking Widget action embeds your Cal.com scheduler directly inside the chat, so users can view real-time availability and book without leaving the conversation.
 ## Configuration
### `Action Name`
A short, specific identifier that tells the Agent what this action does (e.g. best\_sellers\_buttons, support\_button).
### `When to Use`
A detailed description of what the action does and when it must be used.
When applicable, you can specify one or more of the following:
* **Positive cues/phrases**: Example utterances and keywords that signal this action (include a few variations).
* **Preconditions**: What must be true before running.
* **Do not use when**: Explicit exclusions to avoid false triggers.
## Configuration
### `Action Name`
A short, specific identifier that tells the Agent what this action does (e.g. best\_sellers\_buttons, support\_button).
### `When to Use`
A detailed description of what the action does and when it must be used.
When applicable, you can specify one or more of the following:
* **Positive cues/phrases**: Example utterances and keywords that signal this action (include a few variations).
* **Preconditions**: What must be true before running.
* **Do not use when**: Explicit exclusions to avoid false triggers.
 ### `Frequency`
Specify how often the Agent can invoke this action to avoid overusing it, e.g `Once per chat` or `Whenever applicable`.
### `Frequency`
Specify how often the Agent can invoke this action to avoid overusing it, e.g `Once per chat` or `Whenever applicable`.
 ### `Widget`
Configure the widget's settings and appearance.
* **Event link**: The link to the Cal.com event page, such as `https://cal.com/rick/get-rick-rolled`.
* **Layout**: The layout of calendar, such as `Month`, `Week`, or `Column`.
* **Hide event type details**: Whether to hide the details of the event.
* **Pre-fill information**: The information to pre-fill in the booking form, such as `Name`, `Email`, and `Phone`.
### `Save Booking Information`
Save the data from the booking in variables to re-use later in the chat, if applicable.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/canvas.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Canvas
> Learn about the canvas and how to navigate and interact with it.

The canvas is where you design the conversational flow of your chatbot. You can add [blocks](/chatbot/builder/blocks/overview), connect them, and define the logic for how the chatbot responds to user inputs.
To move around the canvas, click and drag an empty area. To zoom in or out, use your mouse scroll wheel or the zoom controls in top toolbar.
All chatbots contain a default `Start` block, which is the entry point of the conversation. From there, you can add blocks to create the flow.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/blocks/send/carousel.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Carousel Block
> Learn about the Carousel block and how to set it up in the builder
The Carousel block allows you to display a carousel of cards to the user. Each card can contain an image, title, description, and buttons.
Carousels are a great way to showcase multiple products, services, or information in a visually appealing format.
### `Widget`
Configure the widget's settings and appearance.
* **Event link**: The link to the Cal.com event page, such as `https://cal.com/rick/get-rick-rolled`.
* **Layout**: The layout of calendar, such as `Month`, `Week`, or `Column`.
* **Hide event type details**: Whether to hide the details of the event.
* **Pre-fill information**: The information to pre-fill in the booking form, such as `Name`, `Email`, and `Phone`.
### `Save Booking Information`
Save the data from the booking in variables to re-use later in the chat, if applicable.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/canvas.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Canvas
> Learn about the canvas and how to navigate and interact with it.

The canvas is where you design the conversational flow of your chatbot. You can add [blocks](/chatbot/builder/blocks/overview), connect them, and define the logic for how the chatbot responds to user inputs.
To move around the canvas, click and drag an empty area. To zoom in or out, use your mouse scroll wheel or the zoom controls in top toolbar.
All chatbots contain a default `Start` block, which is the entry point of the conversation. From there, you can add blocks to create the flow.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/blocks/send/carousel.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Carousel Block
> Learn about the Carousel block and how to set it up in the builder
The Carousel block allows you to display a carousel of cards to the user. Each card can contain an image, title, description, and buttons.
Carousels are a great way to showcase multiple products, services, or information in a visually appealing format.
 ## Adding a carousel
To add a carousel, you can create multiple cards within the block editor. For each card, you can set an image, title, description, and buttons.
You can add as many cards as you like to the carousel. Users can swipe through the cards to view the content.
## Adding a carousel
To add a carousel, you can create multiple cards within the block editor. For each card, you can set an image, title, description, and buttons.
You can add as many cards as you like to the carousel. Users can swipe through the cards to view the content.
 ---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/whatsapp/change-language.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Change language
> A guide to change the language of system and error messages in your WhatsApp chatbot.
You can set the language that your chatbot or AI agent will use for system messages, errors, and various other messages.
The steps differ for AI Agents and Chatbots. We've created separate guides for each below.
## How to change the WhatsApp language for a Chatbot
1. From your chatbot's dashboard, click the `Settings` button under the Chatbot menu.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/whatsapp/change-language.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Change language
> A guide to change the language of system and error messages in your WhatsApp chatbot.
You can set the language that your chatbot or AI agent will use for system messages, errors, and various other messages.
The steps differ for AI Agents and Chatbots. We've created separate guides for each below.
## How to change the WhatsApp language for a Chatbot
1. From your chatbot's dashboard, click the `Settings` button under the Chatbot menu.
 2. Under the `General` tab, you will see the `Language` setting. Select the language you want to use.
2. Under the `General` tab, you will see the `Language` setting. Select the language you want to use.
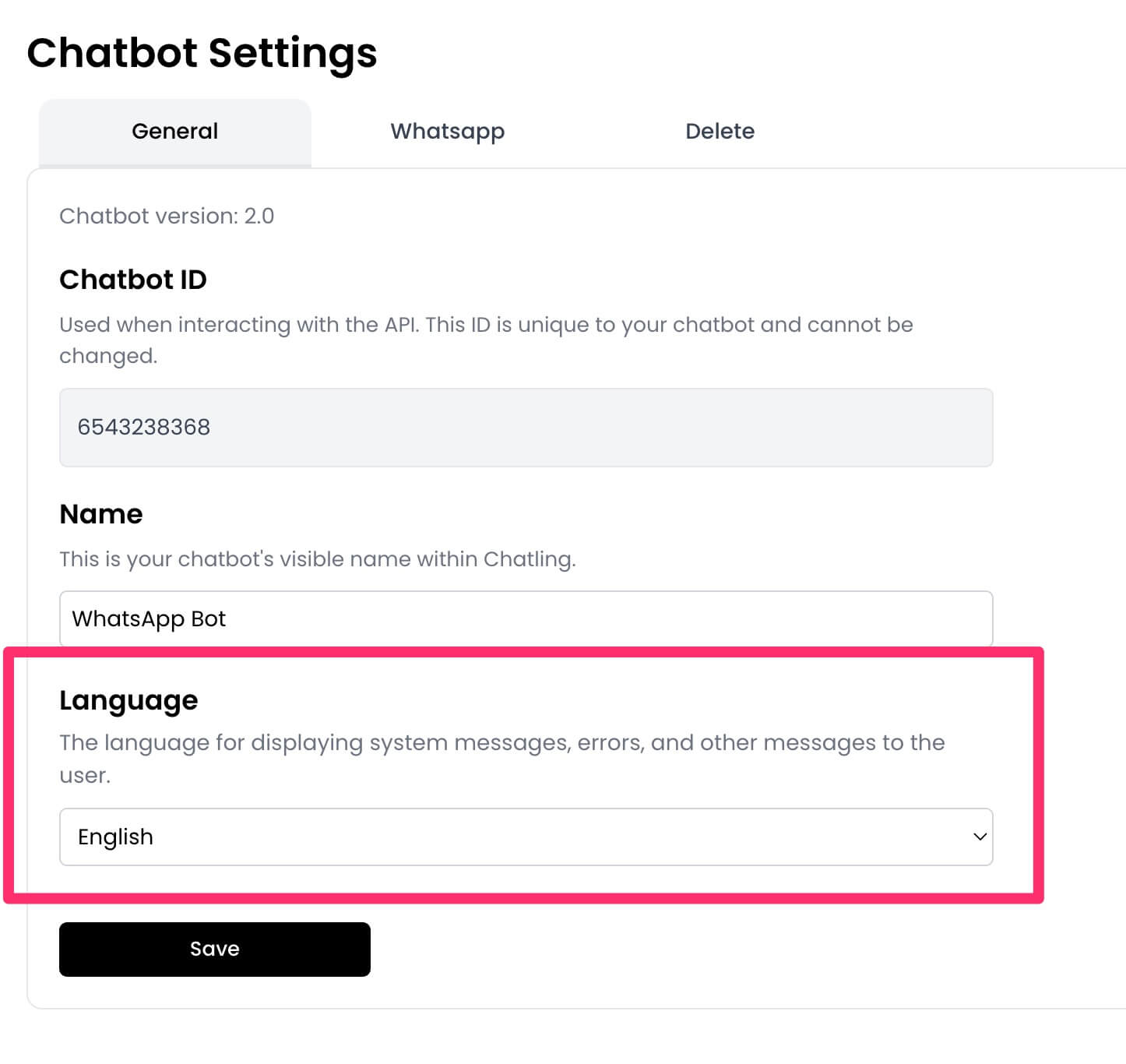 3. Click `Save` to save the changes.
## How to change the WhatsApp language for an AI Agent
1. From your agent's dashboard, click the `Deploy` button in the sidebar.
3. Click `Save` to save the changes.
## How to change the WhatsApp language for an AI Agent
1. From your agent's dashboard, click the `Deploy` button in the sidebar.
 2. Click the settings icon for `WhatsApp`.
2. Click the settings icon for `WhatsApp`.
 3. You will see the `Language` settings. Select the language you want to use.
3. You will see the `Language` settings. Select the language you want to use.
 4. Click `Save` to save the changes.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/api-reference/v2/ai-kb/chat.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Chat with Knowledge Base AI
> Chat with the AI using the knowledge base as the response source.
## Request parameters
### Path
The chatbot ID.
### Body
The message to send to the AI.
The ID of the AI model to use for the response. To get a list of available AI models, use the [List AI models](./list-ai-models) endpoint.
The ID of the conversation. This allows the AI to remember the context of the conversation.
If left blank, a new conversation will be created.
The ID of the contact to associate with the conversation.
The ID of the language to use for the AI response. To get a list of available languages, use the [List languages](./list-ai-languages) endpoint.
The temperature to be used by the AI. The temperature controls the randomness of the response. A lower temperature value, such as 0, will make the outputs more focused and deterministic, whereas a higher temperature, such as 1, will make the responses more diverse and unpredictable.
List of [instructions](/chatbot/ai/instructions) to tailor the AI's response. It can be used to provide additional context to the AI, such as the desired tone or style of the response.
Must be an array of strings.
## Response
The status of the request. Will be `success` if the request was successful, otherwise `error`.
The unique identifier of the conversation.
The response from the AI.
The type of the source, such as `webpage` or `document`.
The title of the source.
The URL of the source if it's a webpage.
```json Response theme={null}
{
"status": "success",
"data": {
"conversation_id": "3154224116",
"response": "We offer a variety of AI models to power your chatbot. Here are the models available:\n\n- **GPT-4o**\n- **GPT-4 Turbo**\n- **GPT-3.5 Turbo**\n- **Claude 3.5 Sonnet**\n- **Claude 3 Opus**\n- **Claude 3 Sonnet**\n- **Claude 3 Haiku**\n\nThese models ensure that you can select the best fit for your specific needs and use cases.",
"sources": [
{
"type": "webpage",
"title": "Supported AI Models - Chatling Documentation",
"url": "https://docs.chatling.ai/ai/supported-ai-models"
},
{
"type": "webpage",
"title": "Pricing | Chatling",
"url": "https://chatling.ai/pricing"
},
]
}
}
```
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/api-reference/v2/usage/chatbots.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Chatbots
> Get the chatbots usage for the project.
## Response
The status of the request. Will be `success` if the request was successful, otherwise `error`.
The number of chatbots created.
The maximum number of chatbots allowed for the project.
```json Response theme={null}
{
"status": "success",
"data": {
"used": 2,
"max": 5
}
}
```
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/whatsapp/create-ai-agent.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Create a WhatsApp AI Agent
> Learn how to create a WhatsApp AI agent in Chatling.
The steps below will guide you through the process of creating and connecting your WhatsApp to your **AI Agent** in Chatling.
1. Login to your [Chatling account](https://app.chatling.ai).
2. From the "My agents" page, click the `Create` button.
4. Click `Save` to save the changes.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/api-reference/v2/ai-kb/chat.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Chat with Knowledge Base AI
> Chat with the AI using the knowledge base as the response source.
## Request parameters
### Path
The chatbot ID.
### Body
The message to send to the AI.
The ID of the AI model to use for the response. To get a list of available AI models, use the [List AI models](./list-ai-models) endpoint.
The ID of the conversation. This allows the AI to remember the context of the conversation.
If left blank, a new conversation will be created.
The ID of the contact to associate with the conversation.
The ID of the language to use for the AI response. To get a list of available languages, use the [List languages](./list-ai-languages) endpoint.
The temperature to be used by the AI. The temperature controls the randomness of the response. A lower temperature value, such as 0, will make the outputs more focused and deterministic, whereas a higher temperature, such as 1, will make the responses more diverse and unpredictable.
List of [instructions](/chatbot/ai/instructions) to tailor the AI's response. It can be used to provide additional context to the AI, such as the desired tone or style of the response.
Must be an array of strings.
## Response
The status of the request. Will be `success` if the request was successful, otherwise `error`.
The unique identifier of the conversation.
The response from the AI.
The type of the source, such as `webpage` or `document`.
The title of the source.
The URL of the source if it's a webpage.
```json Response theme={null}
{
"status": "success",
"data": {
"conversation_id": "3154224116",
"response": "We offer a variety of AI models to power your chatbot. Here are the models available:\n\n- **GPT-4o**\n- **GPT-4 Turbo**\n- **GPT-3.5 Turbo**\n- **Claude 3.5 Sonnet**\n- **Claude 3 Opus**\n- **Claude 3 Sonnet**\n- **Claude 3 Haiku**\n\nThese models ensure that you can select the best fit for your specific needs and use cases.",
"sources": [
{
"type": "webpage",
"title": "Supported AI Models - Chatling Documentation",
"url": "https://docs.chatling.ai/ai/supported-ai-models"
},
{
"type": "webpage",
"title": "Pricing | Chatling",
"url": "https://chatling.ai/pricing"
},
]
}
}
```
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/api-reference/v2/usage/chatbots.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Chatbots
> Get the chatbots usage for the project.
## Response
The status of the request. Will be `success` if the request was successful, otherwise `error`.
The number of chatbots created.
The maximum number of chatbots allowed for the project.
```json Response theme={null}
{
"status": "success",
"data": {
"used": 2,
"max": 5
}
}
```
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/whatsapp/create-ai-agent.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Create a WhatsApp AI Agent
> Learn how to create a WhatsApp AI agent in Chatling.
The steps below will guide you through the process of creating and connecting your WhatsApp to your **AI Agent** in Chatling.
1. Login to your [Chatling account](https://app.chatling.ai).
2. From the "My agents" page, click the `Create` button.
 3. Choose `AI Agent` as the type.
To learn the difference between AI Agents and Chatbots, refer to [this page](/introduction#difference-between-ai-agents-and-ai-chatbots).
3. Choose `AI Agent` as the type.
To learn the difference between AI Agents and Chatbots, refer to [this page](/introduction#difference-between-ai-agents-and-ai-chatbots).
 4. Enter a name for your Agent and click the `Create agent` button.
4. Enter a name for your Agent and click the `Create agent` button.
 5. From your Agent's dashboard, click the `Deploy` button in the sidebar.
5. From your Agent's dashboard, click the `Deploy` button in the sidebar.
 6. Click the `Setup` button under the `WhatsApp` option.
6. Click the `Setup` button under the `WhatsApp` option.
 7. A popup will appear to guide you through the process of connecting your WhatsApp Business account to Chatling.
Before continuing, note that the phone number you connect must not be in use by a WhatsApp account. If it's in use, you must delete the account from WhatsApp before continuing.
Here's how to delete a WhatsApp account:
1. Open the WhatsApp app.
2. Go to `Settings` > `Account` > `Delete my account`.
3. Type in your phone number for confirmation and tap on `Delete my account`.
Once deleted, the phone number can be used to create a WhatsApp Business account.
8. Click the `Login with Facebook` button to continue.
7. A popup will appear to guide you through the process of connecting your WhatsApp Business account to Chatling.
Before continuing, note that the phone number you connect must not be in use by a WhatsApp account. If it's in use, you must delete the account from WhatsApp before continuing.
Here's how to delete a WhatsApp account:
1. Open the WhatsApp app.
2. Go to `Settings` > `Account` > `Delete my account`.
3. Type in your phone number for confirmation and tap on `Delete my account`.
Once deleted, the phone number can be used to create a WhatsApp Business account.
8. Click the `Login with Facebook` button to continue.
 9. The Facebook authentication window will open. Sign in to your Facebook account and click the `Continue` button.
9. The Facebook authentication window will open. Sign in to your Facebook account and click the `Continue` button.
 10. Select `Get started`.
10. Select `Get started`.
 11. Choose or create a new business profile.
11. Choose or create a new business profile.
 12. Choose or create a new WhatsApp Business account and profile.
12. Choose or create a new WhatsApp Business account and profile.
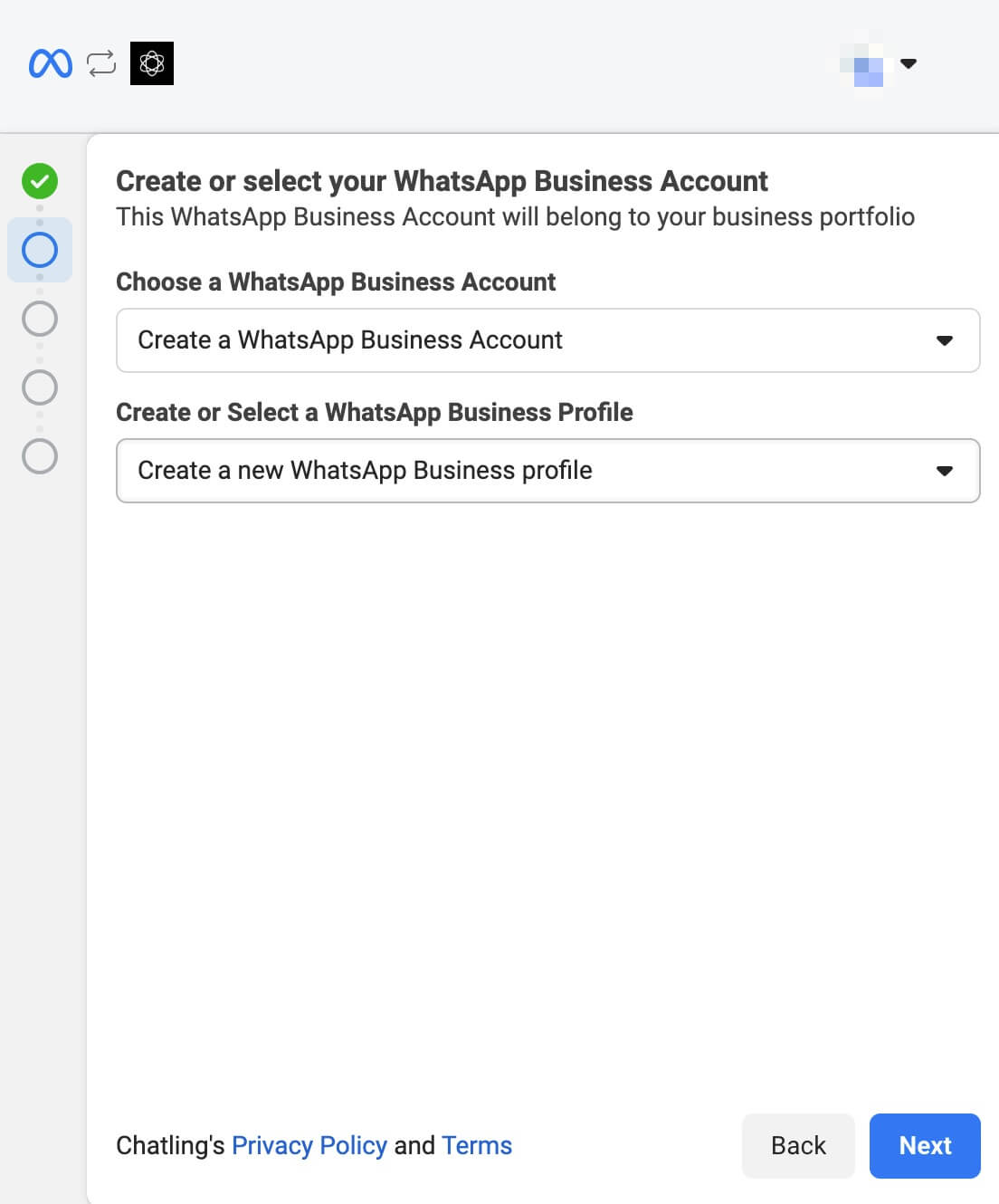 13. If you chose to create a new profile:
* Enter the required information for the profile.
* When prompted to add a phone number, select `Add a new phone number`. Do not select `Get a free WhatsApp number` as it will not work with Chatling.
13. If you chose to create a new profile:
* Enter the required information for the profile.
* When prompted to add a phone number, select `Add a new phone number`. Do not select `Get a free WhatsApp number` as it will not work with Chatling.
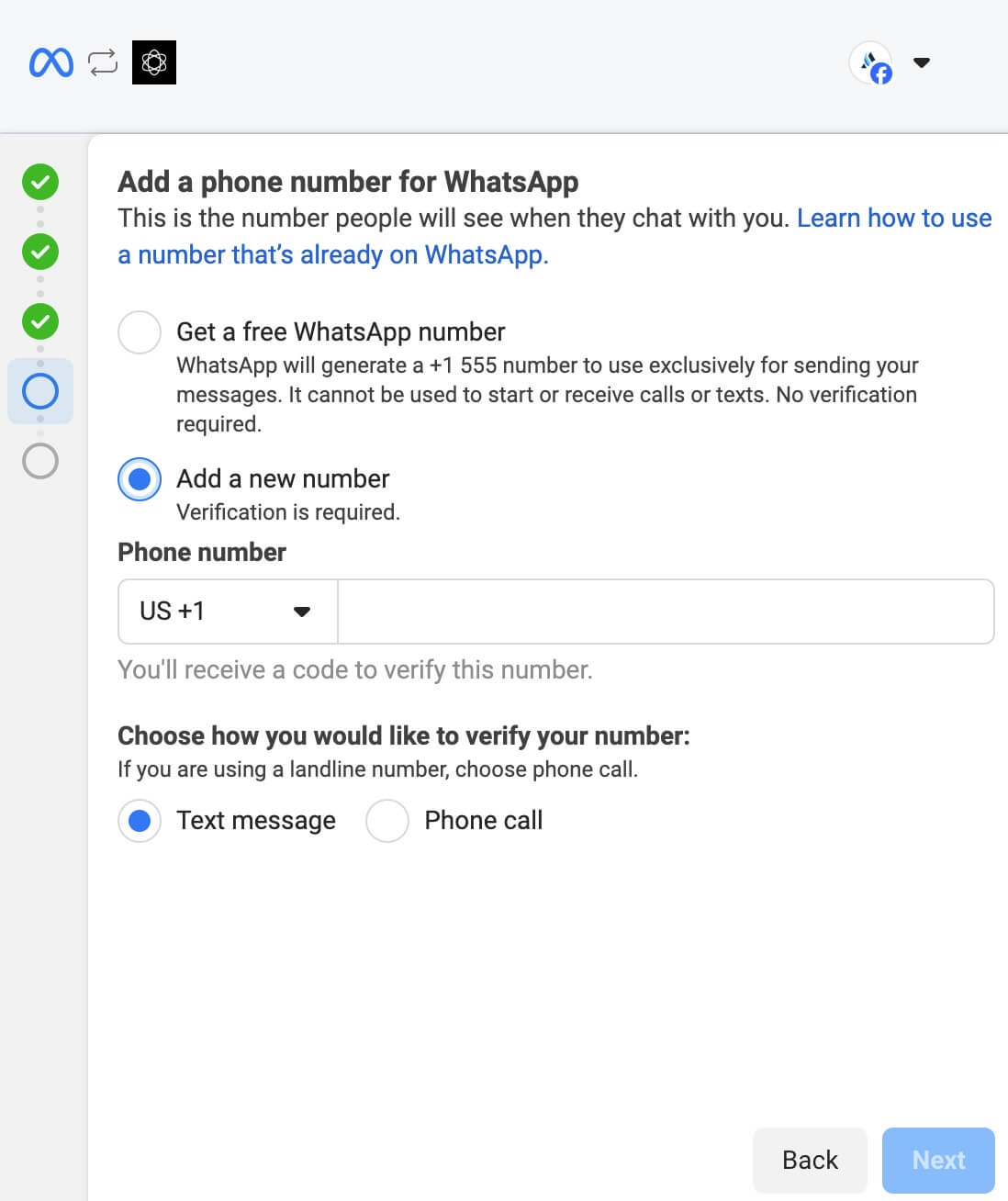 14. Facebook will display the permissions required by Chatling. Review and click the `Continue` or `Confirm` button.
14. Facebook will display the permissions required by Chatling. Review and click the `Continue` or `Confirm` button.
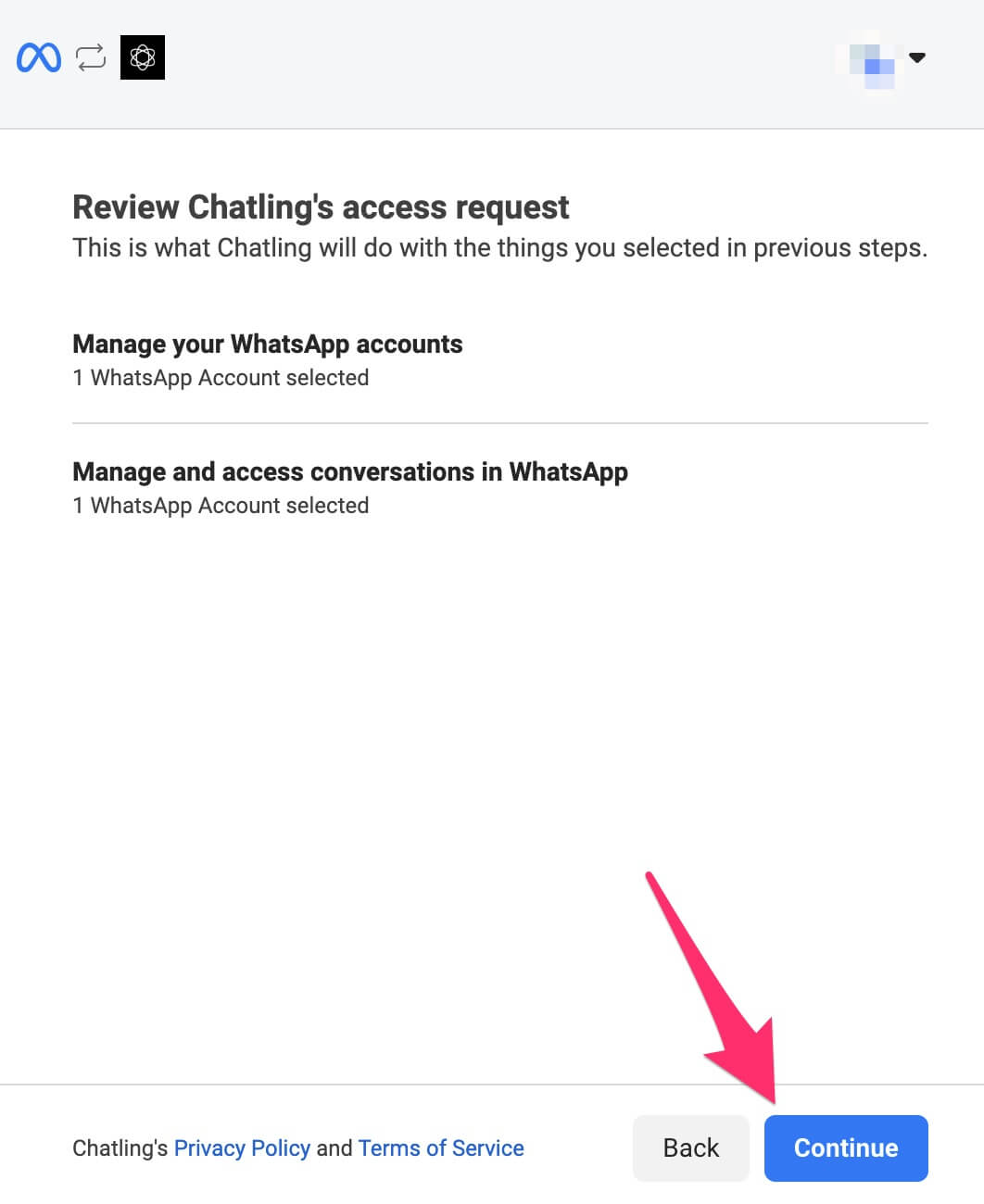 15. Facebook begins verifying the information you provided. Once it's completed successfully, you should see a message similar to below. Click the `Finish` button.
15. Facebook begins verifying the information you provided. Once it's completed successfully, you should see a message similar to below. Click the `Finish` button.
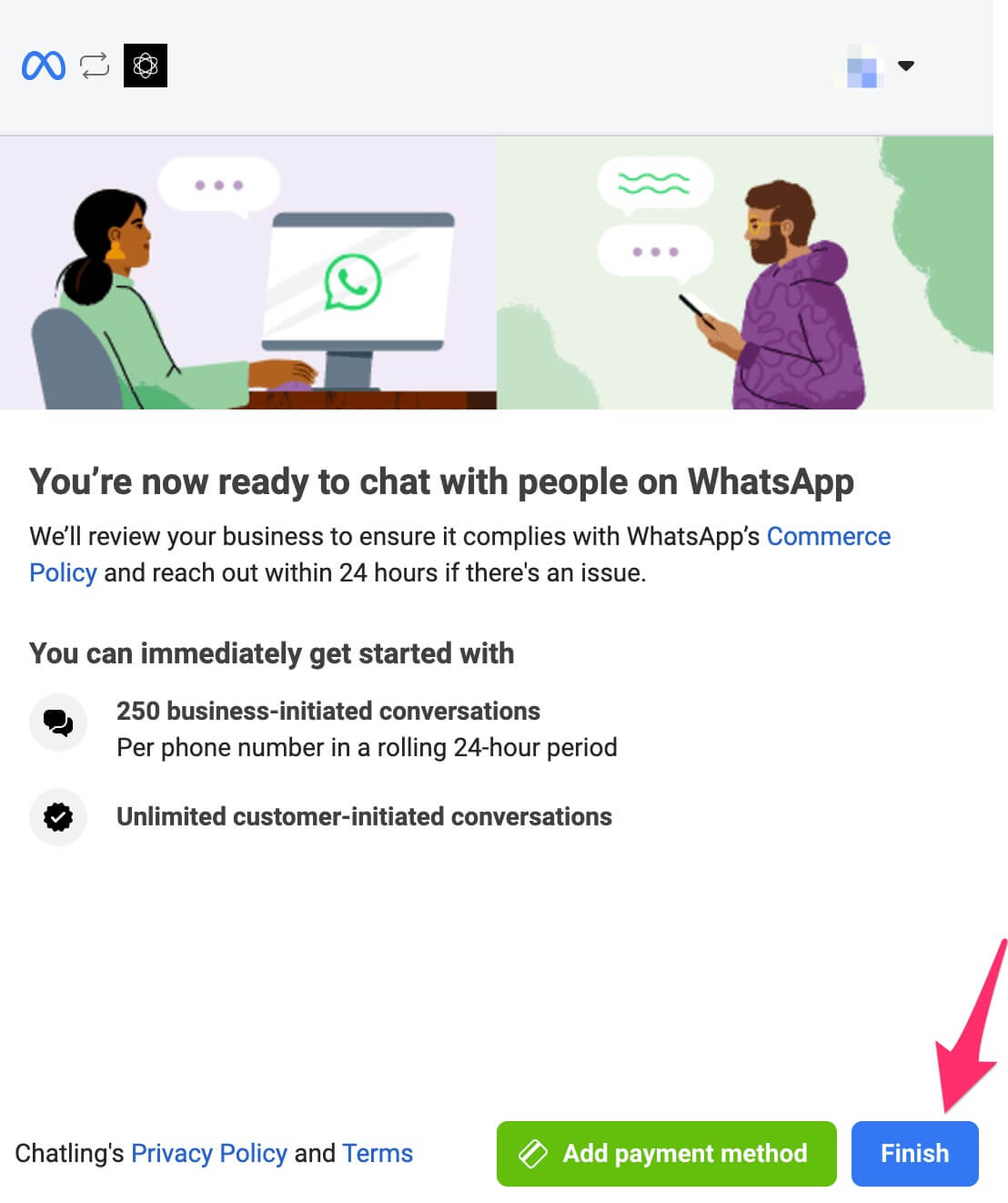 16. Go back to Chatling and a message will be displayed that your authentication is being processed. If successful, you should see a message similar to below.
16. Go back to Chatling and a message will be displayed that your authentication is being processed. If successful, you should see a message similar to below.
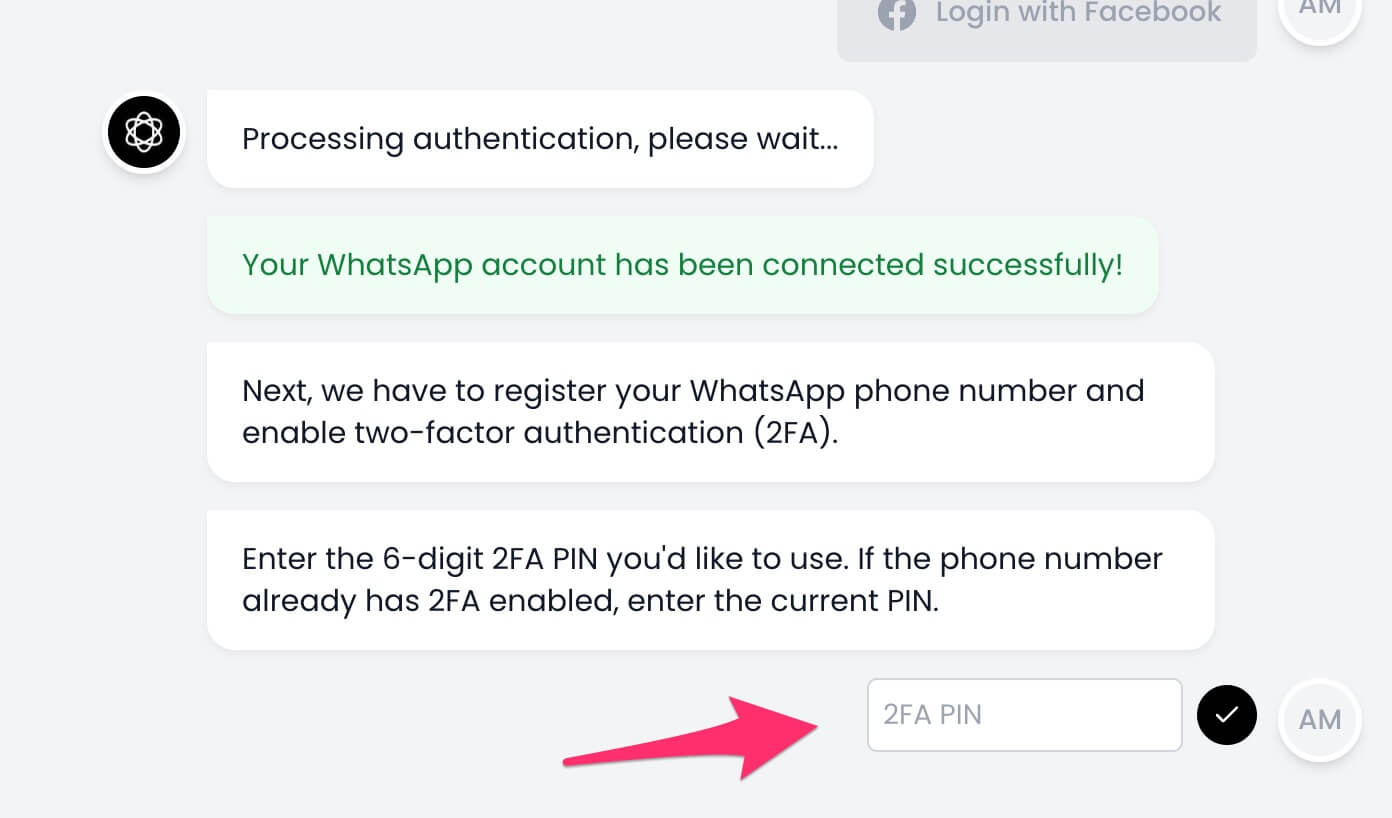
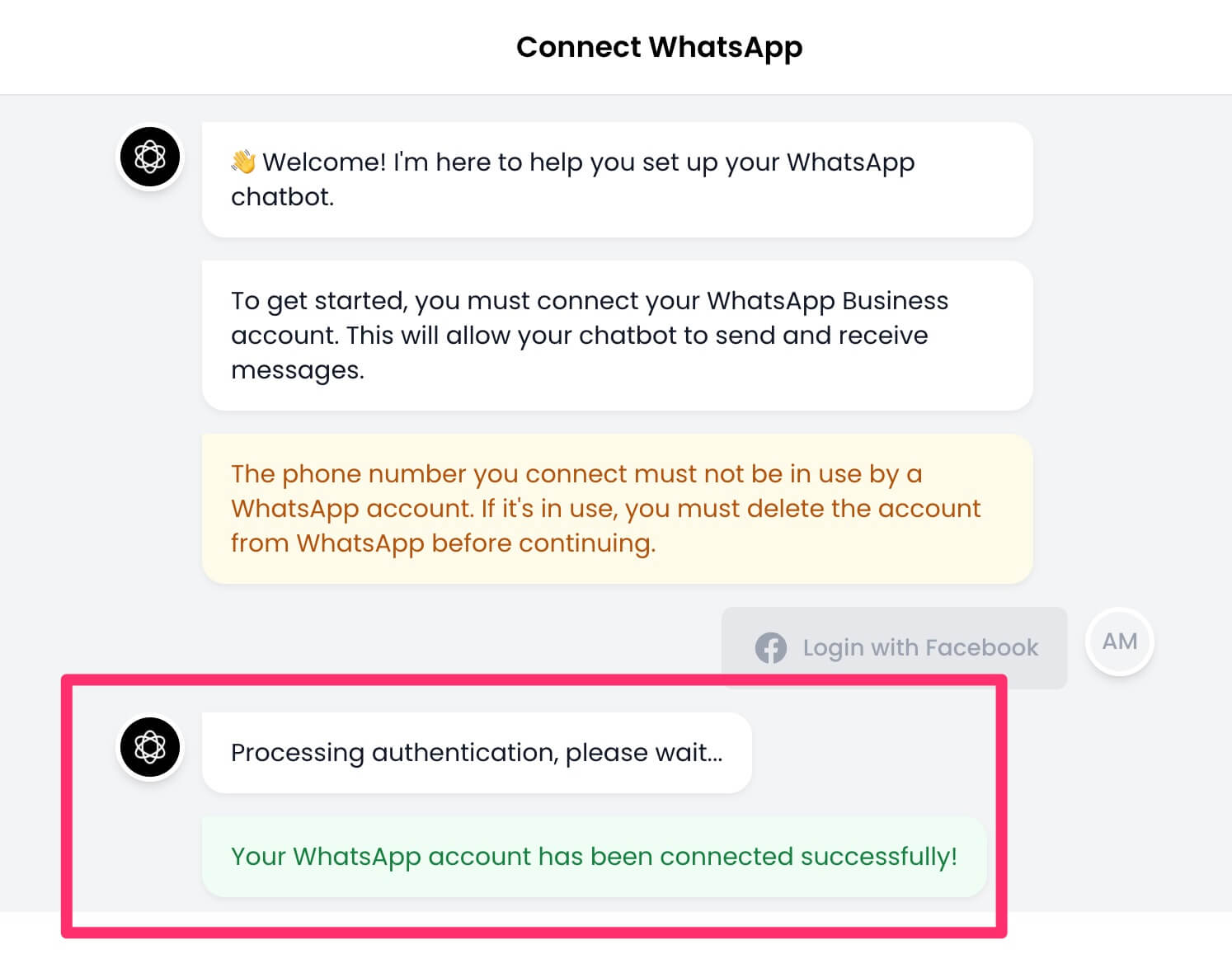 17. Next, you must enter a 6-digit code for two-factor authentication so your phone number can be registered with WhatsApp.
If the number already has 2FA enabled, enter the same code you had set up.
17. Next, you must enter a 6-digit code for two-factor authentication so your phone number can be registered with WhatsApp.
If the number already has 2FA enabled, enter the same code you had set up.
 18. Once the phone number is registered successfully, you're all set and your WhatsApp Business account is connected to Chatling. Click the `Close` button to finish the setup process.
WhatsApp provides 1,000 free conversations per month. If you reach this limit, you must add a payment method in your Facebook Business Manager to continue sending and receiving messages.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/whatsapp/create-ai-chatbot.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Create a WhatsApp AI Chatbot
> Learn how to create a WhatsApp AI chatbot in Chatling.
The steps below will guide you through the process of creating and connecting your WhatsApp to your **AI Chatbot** in Chatling.
1. Login to your [Chatling account](https://app.chatling.ai).
2. From the "My agents" page, click the `Create` button.
18. Once the phone number is registered successfully, you're all set and your WhatsApp Business account is connected to Chatling. Click the `Close` button to finish the setup process.
WhatsApp provides 1,000 free conversations per month. If you reach this limit, you must add a payment method in your Facebook Business Manager to continue sending and receiving messages.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/whatsapp/create-ai-chatbot.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Create a WhatsApp AI Chatbot
> Learn how to create a WhatsApp AI chatbot in Chatling.
The steps below will guide you through the process of creating and connecting your WhatsApp to your **AI Chatbot** in Chatling.
1. Login to your [Chatling account](https://app.chatling.ai).
2. From the "My agents" page, click the `Create` button.
 3. Choose `AI Chatbot` as the type.
To learn the difference between AI Agents and Chatbots, refer to [this page](/introduction#difference-between-ai-agents-and-ai-chatbots).
3. Choose `AI Chatbot` as the type.
To learn the difference between AI Agents and Chatbots, refer to [this page](/introduction#difference-between-ai-agents-and-ai-chatbots).
 4. Select `WhatsApp` as the platform.
4. Select `WhatsApp` as the platform.
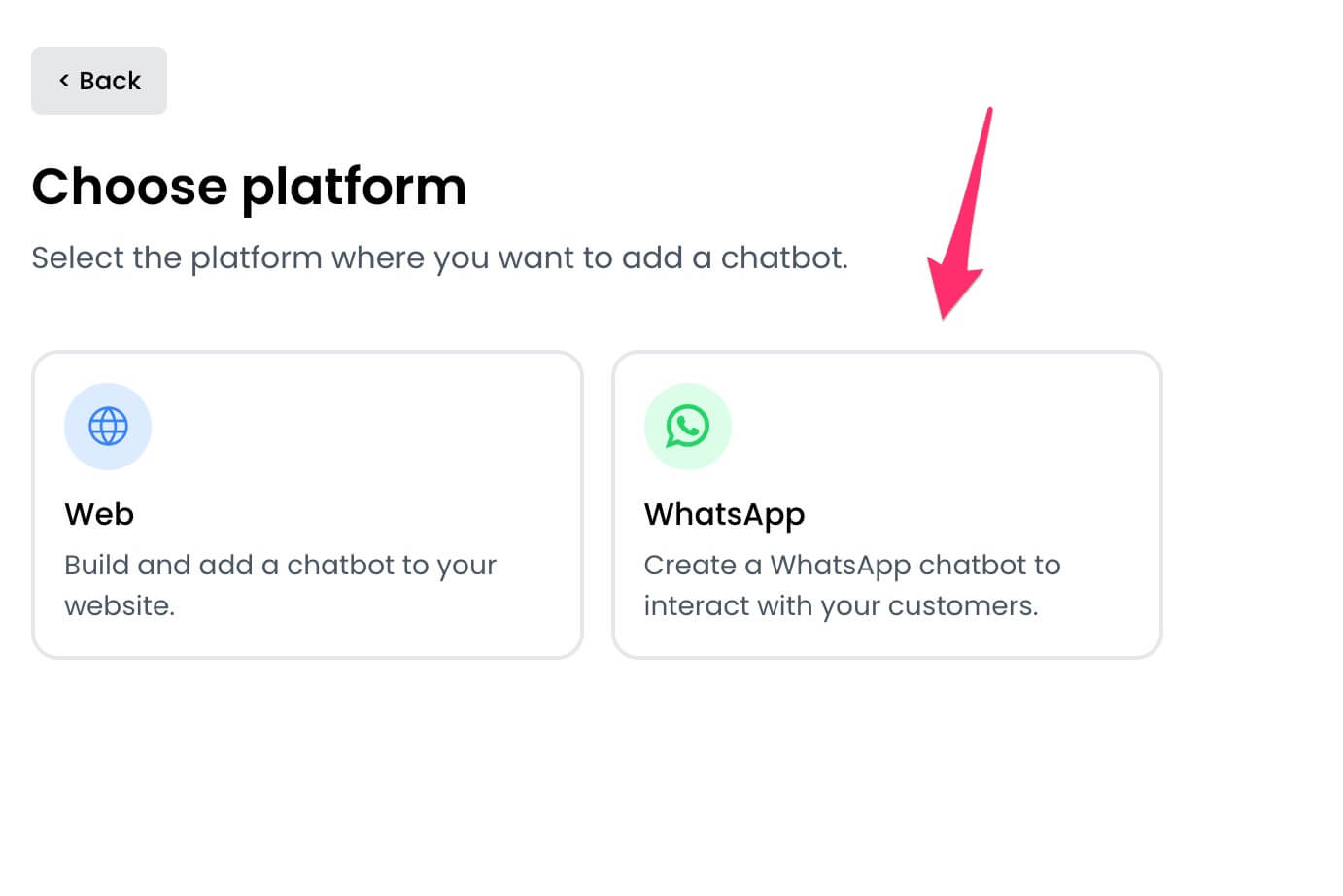 5. You can choose to create a chatbot from scratch or use a template. Templates help you get started quickly with pre-built flows.
6. Enter a name for your chatbot and click the `Create chatbot` button.
5. You can choose to create a chatbot from scratch or use a template. Templates help you get started quickly with pre-built flows.
6. Enter a name for your chatbot and click the `Create chatbot` button.
 7. A setup wizard will open to guide you through connecting your WhatsApp Business account.
Before continuing, note that the phone number you connect must not be in use by a WhatsApp account. If it's in use, you must delete the account from WhatsApp before continuing.
Here's how to delete a WhatsApp account:
1. Open the WhatsApp app.
2. Go to `Settings` > `Account` > `Delete my account`.
3. Type in your phone number for confirmation and tap on `Delete my account`.
Once deleted, the phone number can be used to create a WhatsApp Business account.
8. Click the `Login with Facebook` button to continue.
7. A setup wizard will open to guide you through connecting your WhatsApp Business account.
Before continuing, note that the phone number you connect must not be in use by a WhatsApp account. If it's in use, you must delete the account from WhatsApp before continuing.
Here's how to delete a WhatsApp account:
1. Open the WhatsApp app.
2. Go to `Settings` > `Account` > `Delete my account`.
3. Type in your phone number for confirmation and tap on `Delete my account`.
Once deleted, the phone number can be used to create a WhatsApp Business account.
8. Click the `Login with Facebook` button to continue.
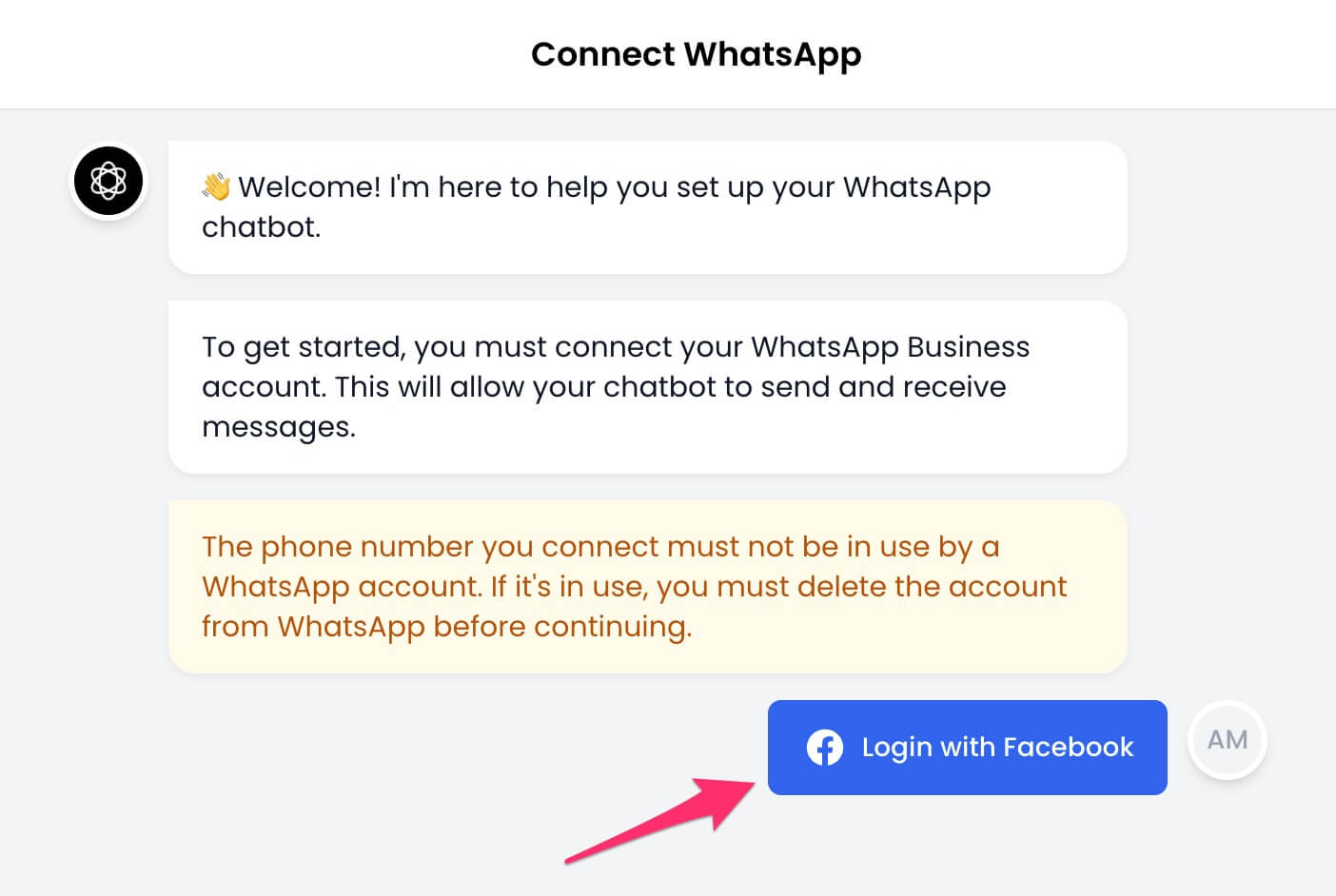 9. The Facebook authentication window will open. Sign in to your Facebook account and click the `Continue` button.
9. The Facebook authentication window will open. Sign in to your Facebook account and click the `Continue` button.
 10. Select `Get started`.
10. Select `Get started`.
 11. Choose or create a new business profile.
11. Choose or create a new business profile.
 12. Choose or create a new WhatsApp Business account and profile.
12. Choose or create a new WhatsApp Business account and profile.
 13. If you chose to create a new profile:
* Enter the required information for the profile.
* When prompted to add a phone number, select `Add a new phone number`. Do not select `Get a free WhatsApp number` as it will not work with Chatling.
13. If you chose to create a new profile:
* Enter the required information for the profile.
* When prompted to add a phone number, select `Add a new phone number`. Do not select `Get a free WhatsApp number` as it will not work with Chatling.
 14. Facebook will display the permissions required by Chatling. Review and click the `Continue` or `Confirm` button.
14. Facebook will display the permissions required by Chatling. Review and click the `Continue` or `Confirm` button.
 15. Facebook begins verifying the information you provided. Once it's completed successfully, you should see a message similar to below. Click the `Finish` button.
15. Facebook begins verifying the information you provided. Once it's completed successfully, you should see a message similar to below. Click the `Finish` button.
 16. Go back to Chatling and a message will be displayed that your authentication is being processed. If successful, you should see a message similar to below.
16. Go back to Chatling and a message will be displayed that your authentication is being processed. If successful, you should see a message similar to below.
 17. Next, you must enter a 6-digit code for two-factor authentication so your phone number can be registered with WhatsApp.
If the number already has 2FA enabled, enter the same code you had set up.
17. Next, you must enter a 6-digit code for two-factor authentication so your phone number can be registered with WhatsApp.
If the number already has 2FA enabled, enter the same code you had set up.
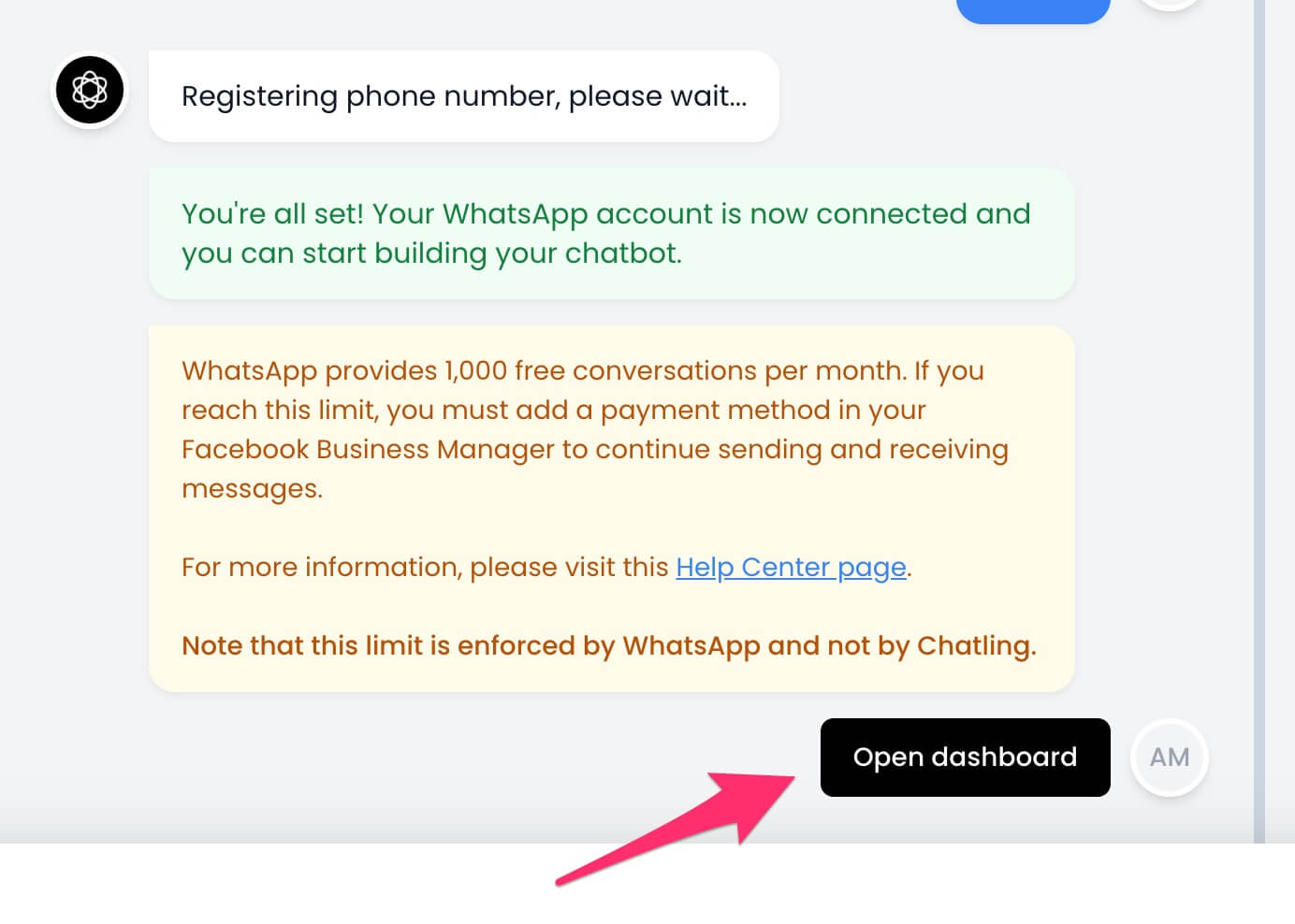
 18. Once the phone number is registered successfully, you're all set and your WhatsApp Business account is connected to Chatling. Click the `Open Dashboard` button to continue.
WhatsApp provides 1,000 free conversations per month. If you reach this limit, you must add a payment method in your Facebook Business Manager to continue sending and receiving messages.
18. Once the phone number is registered successfully, you're all set and your WhatsApp Business account is connected to Chatling. Click the `Open Dashboard` button to continue.
WhatsApp provides 1,000 free conversations per month. If you reach this limit, you must add a payment method in your Facebook Business Manager to continue sending and receiving messages.
 ---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/api-reference/v2/chatbots/create-chatbot.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Create chatbot
> Create a new chatbot using a template or from scratch.
## Request parameters
### Body
The chatbot name.
The ID of the chatbot template to use. You can get the list of available templates using the [List chatbot templates](./list-chatbot-templates) endpoint.
Leave blank to create a chatbot from scratch.
## Response
The status of the request. Will be `success` if the request was successful, otherwise `error`.
The unique identifier of the chatbot.
The name of the chatbot.
The version of the chatbot.
The visibility of the chatbot.
The date and time when the chatbot was created.
```json theme={null}
{
"status": "success",
"data": {
"id": "9761342719",
"name": "My chatbot",
"version": "2.0",
"visibility": "public",
"created_at": "2024-06-17T12:00:00+00:00"
}
}
```
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/blocks/hubspot/create-company.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Create Company
> Create companies in HubSpot from your chatbot.
Easily create new companies in HubSpot through your chatbot to streamline lead capture and keep your CRM up to date automatically.
## Configuration
1. Click the `Connect account` button under the Account field to connect your HubSpot account to Chatling or select an existing connection.
2. Under the `Company details` section, add the properties you want to set for the company. You can enter variables in certain fields for dynamic values.
3. To store the company's ID when the company is created, select a variable for the `Company ID` field under the `Save response` section.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/blocks/hubspot/create-contact.md
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/blocks/action/create-contact.md
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/api-reference/v2/contacts/create-contact.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Create contact
> Create a new contact for the chatbot.
## Request parameters
### Path
The chatbot ID.
### Body
At least one of the following properties is required.
## Response
The status of the request. Will be `success` if the request was successful, otherwise `error`.
The unique identifier of the contact.
```json Response theme={null}
{
"status": "success",
"data": {
"id": "qtr89df0-112d-d197-b541-3f8674663246"
}
}
```
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/blocks/zendesk/create-ticket.md
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/blocks/hubspot/create-ticket.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Create Ticket
> Create tickets in HubSpot from your chatbot.
Create tickets in HubSpot from your chatbot. This is useful for forwarding user queries to your support team or creating tickets for issues that require further investigation.
## Configuration
1. Click the `Connect account` button under the Account field to connect your HubSpot account to Chatling or select an existing connection.
2. Select the `Pipeline` where the ticket should be created.
3. Enter the ticket's details, such as the subject, status, and description. You can enter variables in all fields to make the ticket dynamic.
4. To store the ticket's ID when the ticket is created, select a variable for the `Ticket ID` field under the `Save response` section.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/contacts/create.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Save contacts from chatbot conversations
You can collect user information at any point in your chatbot flow and save it as a contact using the [Create Contact](/chatbot/builder/blocks/action/create-contact) block. The contact is automatically associated with the user and retained across future chat sessions.
The example below shows a flow that collects the user's name, email, and phone number using a form. Once submitted, it is used to create a new contact.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/api-reference/v2/chatbots/create-chatbot.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Create chatbot
> Create a new chatbot using a template or from scratch.
## Request parameters
### Body
The chatbot name.
The ID of the chatbot template to use. You can get the list of available templates using the [List chatbot templates](./list-chatbot-templates) endpoint.
Leave blank to create a chatbot from scratch.
## Response
The status of the request. Will be `success` if the request was successful, otherwise `error`.
The unique identifier of the chatbot.
The name of the chatbot.
The version of the chatbot.
The visibility of the chatbot.
The date and time when the chatbot was created.
```json theme={null}
{
"status": "success",
"data": {
"id": "9761342719",
"name": "My chatbot",
"version": "2.0",
"visibility": "public",
"created_at": "2024-06-17T12:00:00+00:00"
}
}
```
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/blocks/hubspot/create-company.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Create Company
> Create companies in HubSpot from your chatbot.
Easily create new companies in HubSpot through your chatbot to streamline lead capture and keep your CRM up to date automatically.
## Configuration
1. Click the `Connect account` button under the Account field to connect your HubSpot account to Chatling or select an existing connection.
2. Under the `Company details` section, add the properties you want to set for the company. You can enter variables in certain fields for dynamic values.
3. To store the company's ID when the company is created, select a variable for the `Company ID` field under the `Save response` section.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/blocks/hubspot/create-contact.md
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/blocks/action/create-contact.md
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/api-reference/v2/contacts/create-contact.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Create contact
> Create a new contact for the chatbot.
## Request parameters
### Path
The chatbot ID.
### Body
At least one of the following properties is required.
## Response
The status of the request. Will be `success` if the request was successful, otherwise `error`.
The unique identifier of the contact.
```json Response theme={null}
{
"status": "success",
"data": {
"id": "qtr89df0-112d-d197-b541-3f8674663246"
}
}
```
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/blocks/zendesk/create-ticket.md
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/blocks/hubspot/create-ticket.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Create Ticket
> Create tickets in HubSpot from your chatbot.
Create tickets in HubSpot from your chatbot. This is useful for forwarding user queries to your support team or creating tickets for issues that require further investigation.
## Configuration
1. Click the `Connect account` button under the Account field to connect your HubSpot account to Chatling or select an existing connection.
2. Select the `Pipeline` where the ticket should be created.
3. Enter the ticket's details, such as the subject, status, and description. You can enter variables in all fields to make the ticket dynamic.
4. To store the ticket's ID when the ticket is created, select a variable for the `Ticket ID` field under the `Save response` section.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/contacts/create.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Save contacts from chatbot conversations
You can collect user information at any point in your chatbot flow and save it as a contact using the [Create Contact](/chatbot/builder/blocks/action/create-contact) block. The contact is automatically associated with the user and retained across future chat sessions.
The example below shows a flow that collects the user's name, email, and phone number using a form. Once submitted, it is used to create a new contact.
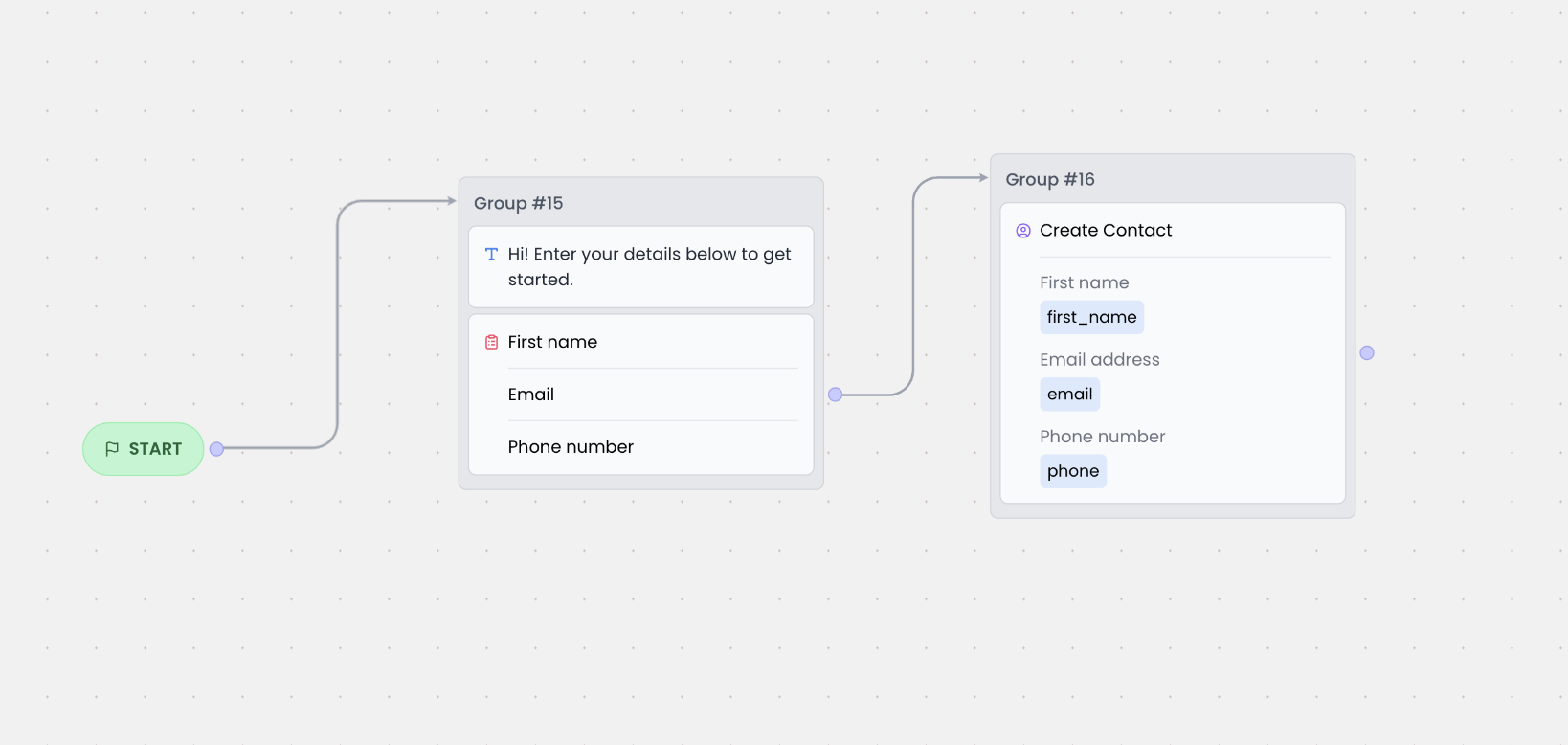 All contacts created by the chatbot are displayed in the `Contacts` page in your dashboard.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/general-settings/custom-domain.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Custom domain
> Learn how to add a custom domain to your chatbot.
You can use a custom subdomain for the chatbot widget and sharing link rather than the default one used by Chatling. This allows you to whitelabel your chatbots to maintain your brand identity or make them look like your team developed them.
## How to set a custom domain
1. Open the chatbot you want to set a custom subdomain for.
2. From the menu, click on `Settings` under the `Chatbot` section.
All contacts created by the chatbot are displayed in the `Contacts` page in your dashboard.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/general-settings/custom-domain.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Custom domain
> Learn how to add a custom domain to your chatbot.
You can use a custom subdomain for the chatbot widget and sharing link rather than the default one used by Chatling. This allows you to whitelabel your chatbots to maintain your brand identity or make them look like your team developed them.
## How to set a custom domain
1. Open the chatbot you want to set a custom subdomain for.
2. From the menu, click on `Settings` under the `Chatbot` section.
 3. Go to the `Custom Domain` tab.
3. Go to the `Custom Domain` tab.
 4. Enter the custom domain you want to use for the chatbot, such as `sample.domain.com`, and click the `Save` button.
4. Enter the custom domain you want to use for the chatbot, such as `sample.domain.com`, and click the `Save` button.
 5. Add the DNS records displayed on the page to your domain provider to activate the custom domain.
5. Add the DNS records displayed on the page to your domain provider to activate the custom domain.
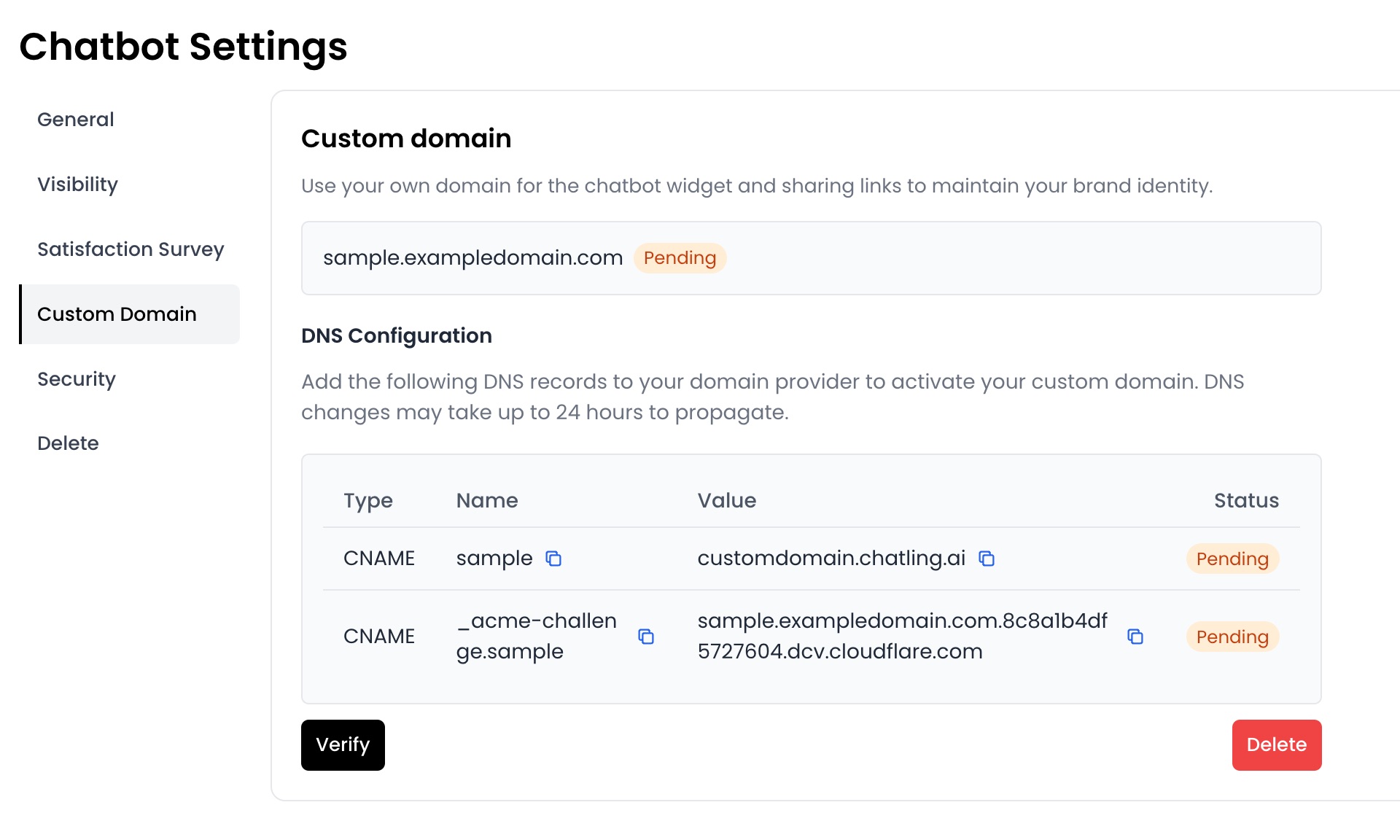 6. Once you add the DNS records, it may take up to 24 hours for the changes to propagate. You can click the `Verify` button to check if the records are active.
7. Once completed and the status is `Active`, the chatbot widget and sharing link will use the custom domain.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/web-widget/installation/custom-website.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Custom Website
> Learn how to add Chatling to your website
You can easily add Chatling to your website by pasting the widget code to your website's header or body section.
1. Go to your dashboard.
2. Click `Deploy` button in the sidebar menu.
6. Once you add the DNS records, it may take up to 24 hours for the changes to propagate. You can click the `Verify` button to check if the records are active.
7. Once completed and the status is `Active`, the chatbot widget and sharing link will use the custom domain.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/web-widget/installation/custom-website.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Custom Website
> Learn how to add Chatling to your website
You can easily add Chatling to your website by pasting the widget code to your website's header or body section.
1. Go to your dashboard.
2. Click `Deploy` button in the sidebar menu.
 3. Click the `Manage` button under the `Website Widget` option.
3. Click the `Manage` button under the `Website Widget` option.
 4. Design the appearance of the widget by clicking the `Open widget designer` button.
4. Design the appearance of the widget by clicking the `Open widget designer` button.
 5. Select the display mode for your chatbot, such as "Floating Chat", "Inline", or "Fullscreen".
5. Select the display mode for your chatbot, such as "Floating Chat", "Inline", or "Fullscreen".
 6. Copy the widget code.
6. Copy the widget code.
 7. Paste the code into the `head` or `body` section of your website's HTML.
* If you selected the `Inline` mode, you must paste the code where you want the chatbot to appear on your website.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/whatsapp/customize-profile.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Customize profile
> Learn how to change your profile picture, name, bio, and more.
You can visit the [WhatsApp Manager](https://business.facebook.com/latest/whatsapp_manager) on Facebook to change your profile picture, display name, and business details such as description, address, email, and website.
## How to customize your WhatsApp Business profile
1. Go to the [WhatsApp Manager](https://business.facebook.com/latest/whatsapp_manager) on Facebook.
2. From the sidebar, click on the `Phone numbers` tab.
7. Paste the code into the `head` or `body` section of your website's HTML.
* If you selected the `Inline` mode, you must paste the code where you want the chatbot to appear on your website.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/whatsapp/customize-profile.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Customize profile
> Learn how to change your profile picture, name, bio, and more.
You can visit the [WhatsApp Manager](https://business.facebook.com/latest/whatsapp_manager) on Facebook to change your profile picture, display name, and business details such as description, address, email, and website.
## How to customize your WhatsApp Business profile
1. Go to the [WhatsApp Manager](https://business.facebook.com/latest/whatsapp_manager) on Facebook.
2. From the sidebar, click on the `Phone numbers` tab.
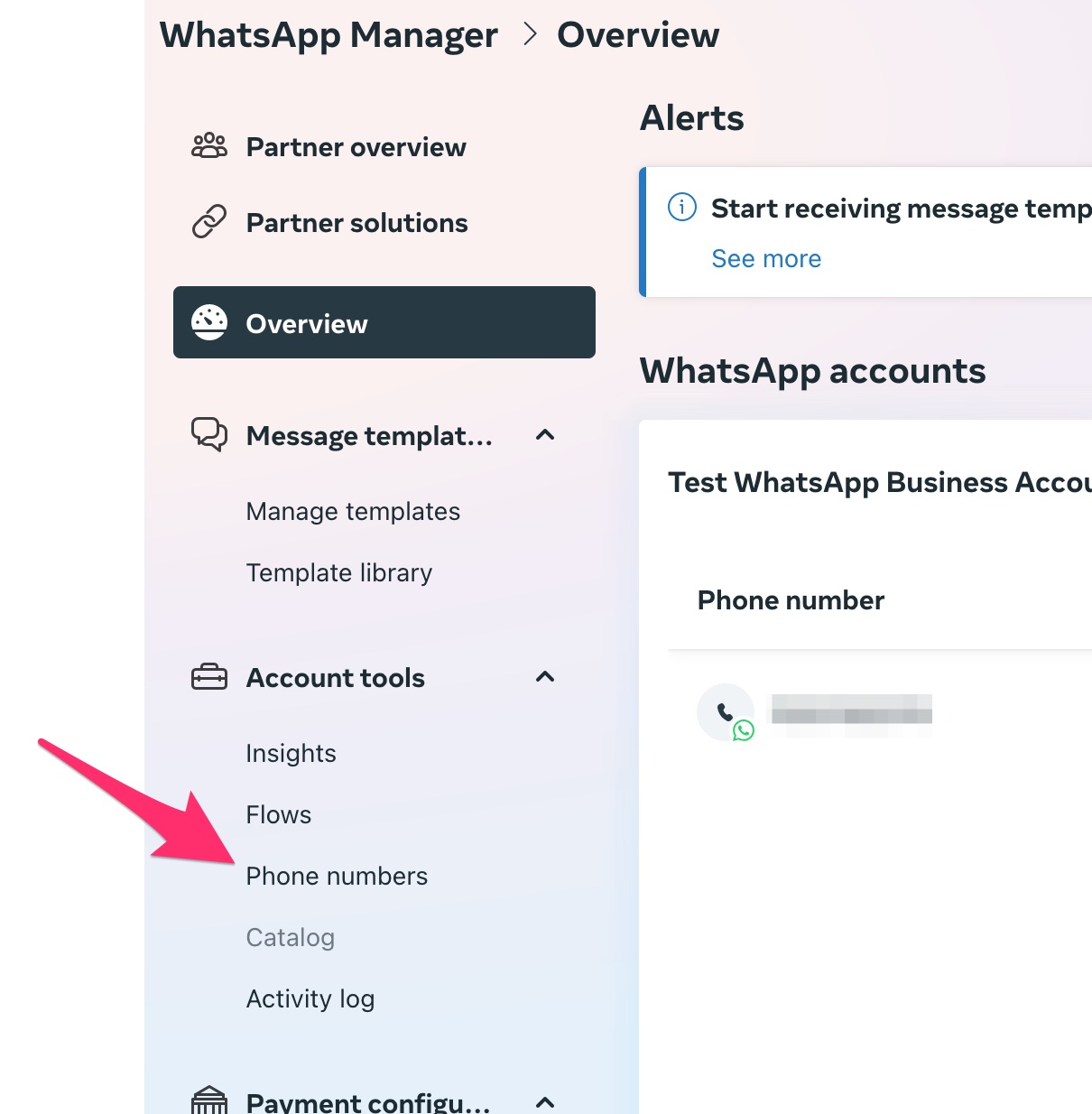 3. Find your phone number from the list and click on the settings icon next to it.
3. Find your phone number from the list and click on the settings icon next to it.
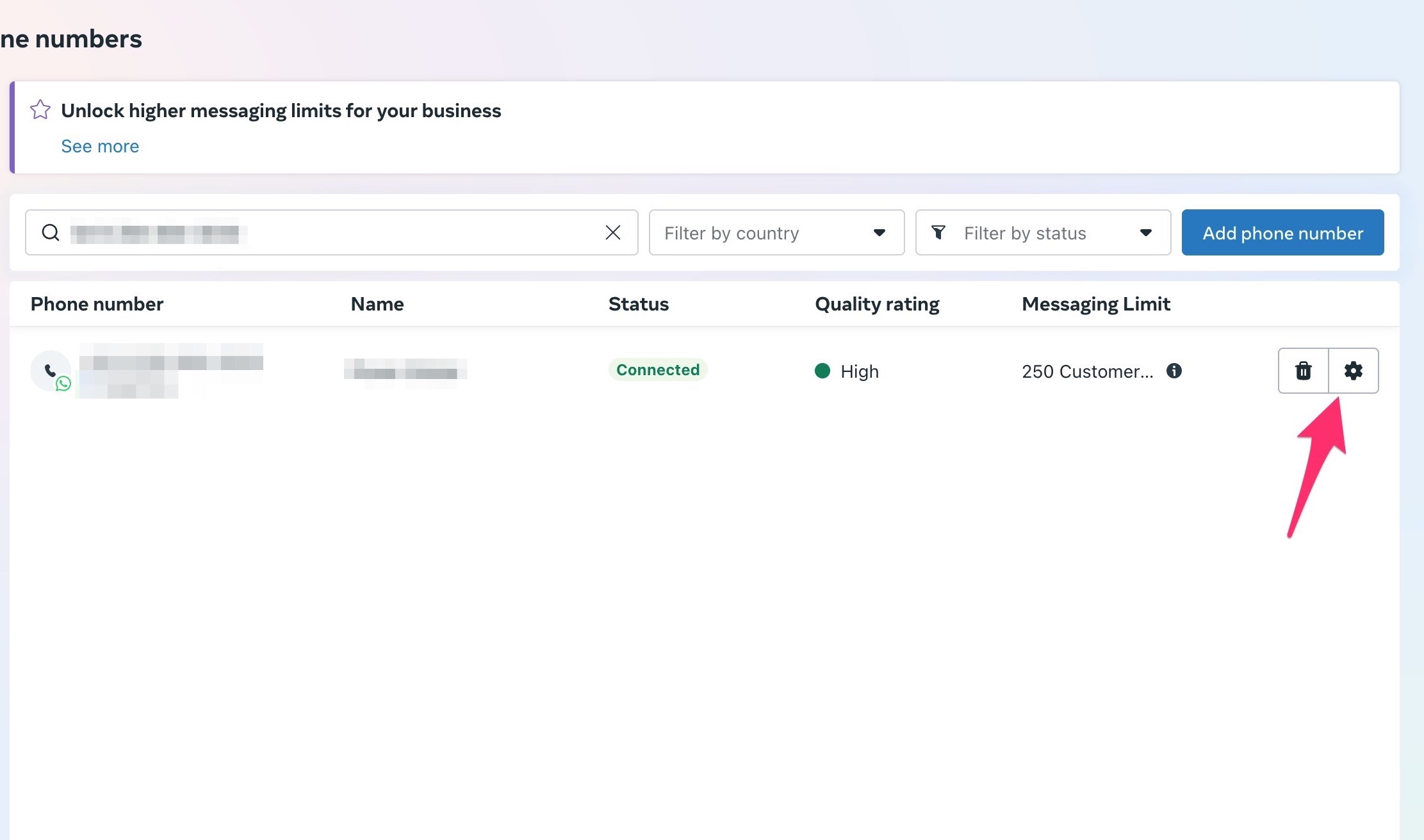 4. From here, you can update the profile information for your WhatsApp Business account.
4. From here, you can update the profile information for your WhatsApp Business account.
 ---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/web-widget/customize.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Design your chatbot widget
> A guide on how to customize the appearance of your website widget and make it match your brand.
You can customize the appearance of your website chat widget to match your brand. Many aspects of the widget, such as the colors, icons, and other design elements can be customized to create a chatbot that fits seamlessly into your website.
## How to customize the widget
1. Go to your chatbot or AI agent's dashboard.
2. Click the `Deploy` button in the sidebar menu.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/web-widget/customize.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Design your chatbot widget
> A guide on how to customize the appearance of your website widget and make it match your brand.

You can customize the appearance of your website chat widget to match your brand. Many aspects of the widget, such as the colors, icons, and other design elements can be customized to create a chatbot that fits seamlessly into your website.
## How to customize the widget
1. Go to your chatbot or AI agent's dashboard.
2. Click the `Deploy` button in the sidebar menu.
 3. Under the `Website Widget` option, click the brush icon to open the widget editor.
3. Under the `Website Widget` option, click the brush icon to open the widget editor.
 # Customization options
Here are some of the available customization options:
* **Colors**: Change the primary, secondary, and chat icon colors.
* **Chat Width**: Set the width of the chat window.
* **Position**: Choose the position where the widget should appear on your website, such as bottom right or bottom left.
* **Bot Icon**: Upload a custom image for the icon that appears next to the bot's messages.
* **Chat Icon**: Upload a custom image for the chat icon that users click to open the chatbot.
* **Header Title**: The title that appears at the top of the chat window, such as "Support Chat" or "Virtual Assistant".
* **Interface Language**: The language of the chatbot's interface. Note that this doesn't affect the language used by the AI.
* **Ask user to rate AI response**: Enabling this will display a thumbs up/down icon after the AI response, allowing users to rate it. This feedback can be used to improve the AI's performance.
* **Hide "Powered by Chatling" text**: At the bottom of the chatbot, there's a "Powered by Chatling" text. You can hide it by enabling this option.
* **Hovering Message**: You can display attention-grabbing messages above the chat icon to encourage users to start a conversation.
* **Show Sources for AI Response**: Enable this option to show the sources of the AI responses when it answers from the Knowledge Base. This helps users understand where the information is coming from.
* **Auto-Open Chat**: Automatically open the chat window when the page loads.
Once you've made the changes, click the `Save` button to apply them to your chatbot.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/knowledge-base/data-source-types.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Types of data sources
> Learn about the different types of data sources you can add to the Knowledge Base.
Data sources are the sources of information you can add to the Knowledge Base. Together, they provide information the AI needs to respond accurately to user queries.
You can add the following types of data sources to the Knowledge Base:
* **Website**: When you add a website, our crawler will visit and extract all the pages from the website. You can then select the pages you want to add to the Knowledge Base.
* The website crawler can extract up to 1,000 pages from a website. If your site contains more pages, you must use the Sitemap data source.
* **Sitemap**: Add a sitemap URL to fetch all the pages of your website. The sitemap is suitable when your website has more than 1,000 pages. Once the sitemap is fetched, you can select the pages to add to the Knowledge Base.
* **URL List**: Add a list of URLs to the Knowledge Base. This is useful when you want to add specific links instead of an entire website.
* **Document**: Upload documents such as PDF, DOCX, and TXT. The AI will extract the text from the document and use it to generate responses.
* **Text**: You can add text directly to the Knowledge Base. This is useful when you want to add custom information that isn't available on your website or documents.
* **FAQs**: You can add a list of questions and answers that users frequently ask. This is useful when the information is not available through other data sources. You can also use it for fine-tuning the AI responses, such as when it responds incorrectly to certain questions.
* **Zoho**: Import all or select articles from your Zoho account into the Chatling knowledge base.
* **Zendesk**: Import all or select articles from your Zendesk account into the Chatling knowledge base.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/blocks/inputs/date.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Date/Time Block
> Learn about the Date/Time input block and how to set it up in the Builder.
The Date/Time block is used to collect the date and time from users. You can use this block to ask users for dates, times, or date-time combinations.
## Configuration
The Date/Time block has the following configuration options:
* **Store answer in variable**: The variable where the user's input will be stored.
* **Input required**: Whether the user's input is mandatory. If disabled, a Skip button will appear, allowing users to skip the input.
* **Format**: The type of input the block will accept. You can choose from the following:
* Date
* Time
* Date & Time
* **Min**: The minimum value the user can input.
* **Max**: The maximum value the user can input.
# Customization options
Here are some of the available customization options:
* **Colors**: Change the primary, secondary, and chat icon colors.
* **Chat Width**: Set the width of the chat window.
* **Position**: Choose the position where the widget should appear on your website, such as bottom right or bottom left.
* **Bot Icon**: Upload a custom image for the icon that appears next to the bot's messages.
* **Chat Icon**: Upload a custom image for the chat icon that users click to open the chatbot.
* **Header Title**: The title that appears at the top of the chat window, such as "Support Chat" or "Virtual Assistant".
* **Interface Language**: The language of the chatbot's interface. Note that this doesn't affect the language used by the AI.
* **Ask user to rate AI response**: Enabling this will display a thumbs up/down icon after the AI response, allowing users to rate it. This feedback can be used to improve the AI's performance.
* **Hide "Powered by Chatling" text**: At the bottom of the chatbot, there's a "Powered by Chatling" text. You can hide it by enabling this option.
* **Hovering Message**: You can display attention-grabbing messages above the chat icon to encourage users to start a conversation.
* **Show Sources for AI Response**: Enable this option to show the sources of the AI responses when it answers from the Knowledge Base. This helps users understand where the information is coming from.
* **Auto-Open Chat**: Automatically open the chat window when the page loads.
Once you've made the changes, click the `Save` button to apply them to your chatbot.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/knowledge-base/data-source-types.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Types of data sources
> Learn about the different types of data sources you can add to the Knowledge Base.
Data sources are the sources of information you can add to the Knowledge Base. Together, they provide information the AI needs to respond accurately to user queries.
You can add the following types of data sources to the Knowledge Base:
* **Website**: When you add a website, our crawler will visit and extract all the pages from the website. You can then select the pages you want to add to the Knowledge Base.
* The website crawler can extract up to 1,000 pages from a website. If your site contains more pages, you must use the Sitemap data source.
* **Sitemap**: Add a sitemap URL to fetch all the pages of your website. The sitemap is suitable when your website has more than 1,000 pages. Once the sitemap is fetched, you can select the pages to add to the Knowledge Base.
* **URL List**: Add a list of URLs to the Knowledge Base. This is useful when you want to add specific links instead of an entire website.
* **Document**: Upload documents such as PDF, DOCX, and TXT. The AI will extract the text from the document and use it to generate responses.
* **Text**: You can add text directly to the Knowledge Base. This is useful when you want to add custom information that isn't available on your website or documents.
* **FAQs**: You can add a list of questions and answers that users frequently ask. This is useful when the information is not available through other data sources. You can also use it for fine-tuning the AI responses, such as when it responds incorrectly to certain questions.
* **Zoho**: Import all or select articles from your Zoho account into the Chatling knowledge base.
* **Zendesk**: Import all or select articles from your Zendesk account into the Chatling knowledge base.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/blocks/inputs/date.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Date/Time Block
> Learn about the Date/Time input block and how to set it up in the Builder.
The Date/Time block is used to collect the date and time from users. You can use this block to ask users for dates, times, or date-time combinations.
## Configuration
The Date/Time block has the following configuration options:
* **Store answer in variable**: The variable where the user's input will be stored.
* **Input required**: Whether the user's input is mandatory. If disabled, a Skip button will appear, allowing users to skip the input.
* **Format**: The type of input the block will accept. You can choose from the following:
* Date
* Time
* Date & Time
* **Min**: The minimum value the user can input.
* **Max**: The maximum value the user can input.
 ---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/blocks/action/delete-contact.md
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/api-reference/v2/contacts/delete-contact.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Delete contact
> Delete a contact by its ID.
## Request parameters
### Path
The chatbot ID.
The contact ID.
## Response
The status of the request. Will be `success` if the request was successful, otherwise `error`.
```json theme={null}
{
"status": "success"
}
```
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/api-reference/v2/conversations/delete-conversation.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Delete conversation
> Delete a conversation.
## Request parameters
### Path
The chatbot ID.
The conversation ID.
## Response
The status of the request. Will be `success` if the request was successful, otherwise `error`.
```json theme={null}
{
"status": "success"
}
```
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/knowledge-base/delete-data-sources.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Delete data sources
> Learn how to delete data sources in the Knowledge Base.
If you no longer need a data source or want to prevent the AI from using it, you can delete it from the Knowledge Base. The information associated with the deleted data source will be purged permanently and cannot be recovered.
## How to delete a data source
1. Go to the `Knowledge Base`.
2. Next to every data source is a delete icon, as shown below. Click on the icon to delete the data source.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/blocks/action/delete-contact.md
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/api-reference/v2/contacts/delete-contact.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Delete contact
> Delete a contact by its ID.
## Request parameters
### Path
The chatbot ID.
The contact ID.
## Response
The status of the request. Will be `success` if the request was successful, otherwise `error`.
```json theme={null}
{
"status": "success"
}
```
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/api-reference/v2/conversations/delete-conversation.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Delete conversation
> Delete a conversation.
## Request parameters
### Path
The chatbot ID.
The conversation ID.
## Response
The status of the request. Will be `success` if the request was successful, otherwise `error`.
```json theme={null}
{
"status": "success"
}
```
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/knowledge-base/delete-data-sources.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Delete data sources
> Learn how to delete data sources in the Knowledge Base.
If you no longer need a data source or want to prevent the AI from using it, you can delete it from the Knowledge Base. The information associated with the deleted data source will be purged permanently and cannot be recovered.
## How to delete a data source
1. Go to the `Knowledge Base`.
2. Next to every data source is a delete icon, as shown below. Click on the icon to delete the data source.
 ## How to delete data sources in bulk
To delete multiple data sources at once, click on the checkbox next to the data sources you want to delete. Then, click the `Bulk action` dropdown and select `Delete`.
## How to delete data sources in bulk
To delete multiple data sources at once, click on the checkbox next to the data sources you want to delete. Then, click the `Bulk action` dropdown and select `Delete`.
 ---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/api-reference/v2/knowledge-base/delete-source.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Delete data source
> Delete a data source from the knowledge base.
## Request parameters
### Path
The chatbot ID.
The data source ID.
## Response
The status of the request. Will be `success` if the request was successful, otherwise `error`.
```json Response theme={null}
{
"status": "success"
}
```
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/general-settings/delete.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# How to delete a chatbot
> Learn how to remove a chatbot permanently from your account.
If you no longer need a chatbot, you can delete it from the dashboard.
Deleting a chatbot will permanently remove it from your account, and you won't be able to recover it. All data associated with the chatbot, including contacts, conversations, and knowledge base will be removed permanently.
## How to delete a chatbot
1. Open the chatbot you want to delete.
2. From the menu, click on `Settings` under the `Chatbot` section.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/api-reference/v2/knowledge-base/delete-source.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Delete data source
> Delete a data source from the knowledge base.
## Request parameters
### Path
The chatbot ID.
The data source ID.
## Response
The status of the request. Will be `success` if the request was successful, otherwise `error`.
```json Response theme={null}
{
"status": "success"
}
```
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/general-settings/delete.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# How to delete a chatbot
> Learn how to remove a chatbot permanently from your account.
If you no longer need a chatbot, you can delete it from the dashboard.
Deleting a chatbot will permanently remove it from your account, and you won't be able to recover it. All data associated with the chatbot, including contacts, conversations, and knowledge base will be removed permanently.
## How to delete a chatbot
1. Open the chatbot you want to delete.
2. From the menu, click on `Settings` under the `Chatbot` section.
 3. Go to the `Delete` tab.
3. Go to the `Delete` tab.
 4. Click the `Delete` button.
4. Click the `Delete` button.
 5. Confirm the deletion by typing `delete permanently` in the text box and click \`Delete\`\`
5. Confirm the deletion by typing `delete permanently` in the text box and click \`Delete\`\`
 ---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/faq/difference-between-ai-agents-and-ai-chatbots.md
# What's the difference between AI Agents and AI Chatbots?
The main difference between an agent and a chatbot is how they handle conversations and tasks:
* **Chatbots** rely on prebuilt flows. This means their responses and actions follow a set, predefined path that you design in advance. They are great for handling straightforward, repetitive tasks where the conversation can be mapped out step by step.
* **AI Agents**, on the other hand, plan steps dynamically based on the context of the conversation and the instructions and actions you set. They do not require a rigid flow design. Instead, they can decide which tasks to carry out while interacting with users, making them more flexible and adaptive to complex or changing situations.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/whatsapp/disconnect-account.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Disconnect WhatsApp account
> Learn how to disconnect your WhatsApp account in Chatling.
The guide below will walk you through the process of disconnecting your WhatsApp account from your chatbot or AI agent in Chatling.
The steps differ for chatbots and AI agents. We've created separate guides for each below.
Disconnecting your WhatsApp account will prevent Chatling from sending and receiving messages from WhatsApp. To restore this functionality, you must reconnect your WhatsApp account.
## How to disconnect WhatsApp from your chatbot
1. From your chatbot's dashboard, click the `Settings` button under the Chatbot menu.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/faq/difference-between-ai-agents-and-ai-chatbots.md
# What's the difference between AI Agents and AI Chatbots?
The main difference between an agent and a chatbot is how they handle conversations and tasks:
* **Chatbots** rely on prebuilt flows. This means their responses and actions follow a set, predefined path that you design in advance. They are great for handling straightforward, repetitive tasks where the conversation can be mapped out step by step.
* **AI Agents**, on the other hand, plan steps dynamically based on the context of the conversation and the instructions and actions you set. They do not require a rigid flow design. Instead, they can decide which tasks to carry out while interacting with users, making them more flexible and adaptive to complex or changing situations.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/whatsapp/disconnect-account.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Disconnect WhatsApp account
> Learn how to disconnect your WhatsApp account in Chatling.
The guide below will walk you through the process of disconnecting your WhatsApp account from your chatbot or AI agent in Chatling.
The steps differ for chatbots and AI agents. We've created separate guides for each below.
Disconnecting your WhatsApp account will prevent Chatling from sending and receiving messages from WhatsApp. To restore this functionality, you must reconnect your WhatsApp account.
## How to disconnect WhatsApp from your chatbot
1. From your chatbot's dashboard, click the `Settings` button under the Chatbot menu.
 2. Go to the `WhatsApp` tab.
2. Go to the `WhatsApp` tab.
 3. Click the `Disconnect` button.
3. Click the `Disconnect` button.
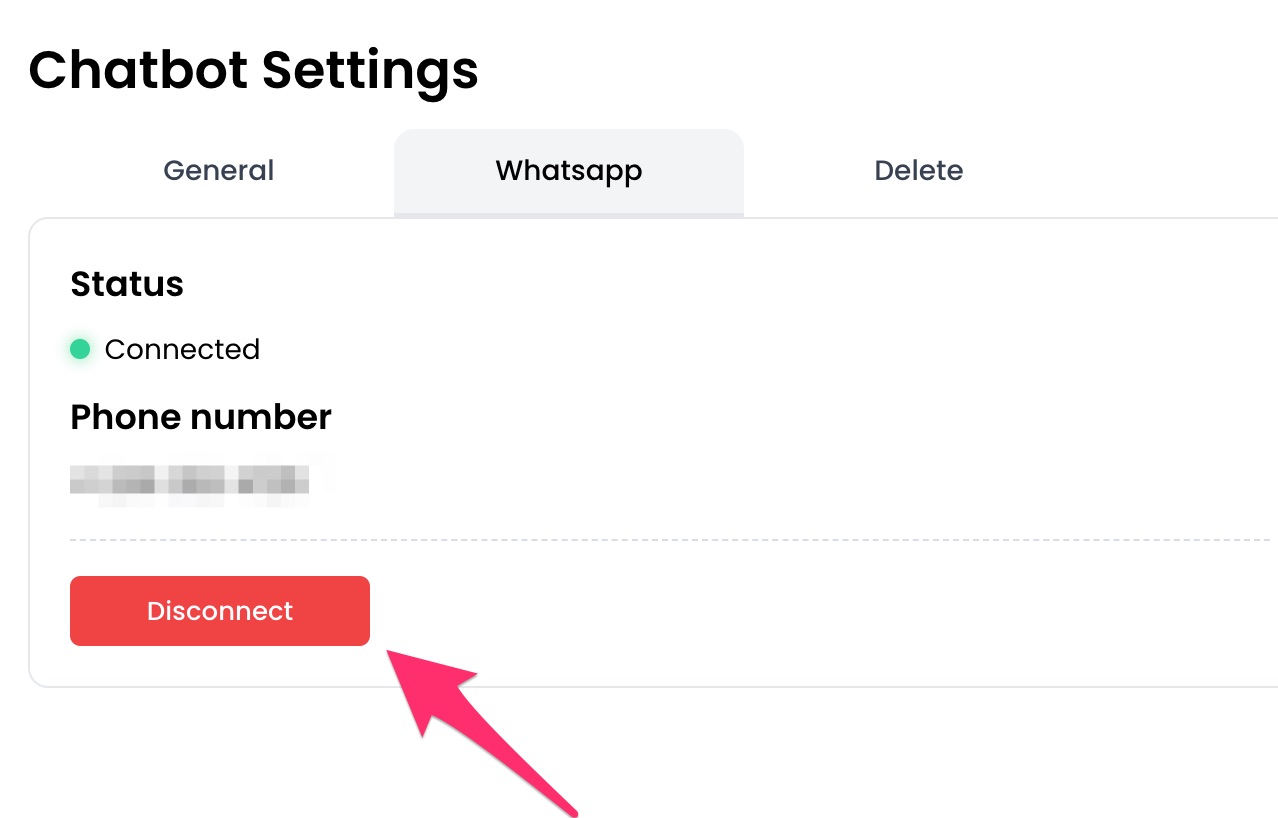 ## How to disconnect WhatsApp from your AI Agent
1. From your agent's dashboard, click the `Deploy` button in the sidebar.
## How to disconnect WhatsApp from your AI Agent
1. From your agent's dashboard, click the `Deploy` button in the sidebar.
 2. Click the settings icon for `WhatsApp`.
2. Click the settings icon for `WhatsApp`.
 3. Click the `Disconnect` button.
3. Click the `Disconnect` button.
 ---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/whatsapp/display-name-approval.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Display name approval
> Learn how to fix issues related to the display name approval for your WhatsApp account.
If you get an error message stating `WhatsApp provided number needs display name approval before messages can be sent`, it means you cannot use the WhatsApp bot until Facebook approves your display name.
This normally happens when you use the free WhatsApp number provided by Facebook when you first connect your WhatsApp account to Chatling.
To fix this issue, you must verify your business in Facebook before they approve your display name.
## How to verify your business in Facebook
1. Go to the [Security Center](https://business.facebook.com/latest/settings/security_center) in your Facebook Business Manager.
2. Under the `Business Verification` section, set the verification use case to `Setting up a WhatsApp Business account`.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/whatsapp/display-name-approval.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Display name approval
> Learn how to fix issues related to the display name approval for your WhatsApp account.
If you get an error message stating `WhatsApp provided number needs display name approval before messages can be sent`, it means you cannot use the WhatsApp bot until Facebook approves your display name.
This normally happens when you use the free WhatsApp number provided by Facebook when you first connect your WhatsApp account to Chatling.
To fix this issue, you must verify your business in Facebook before they approve your display name.
## How to verify your business in Facebook
1. Go to the [Security Center](https://business.facebook.com/latest/settings/security_center) in your Facebook Business Manager.
2. Under the `Business Verification` section, set the verification use case to `Setting up a WhatsApp Business account`.
 3. Click the `Start verification` button.
3. Click the `Start verification` button.
 4. Follow the on-screen instructions to verify your business.
5. Once you complete the process, your business will either be verified immediately or placed under review.
6. After your business is verified, Facebook will begin reviewing your display name. To view the status of the review:
* Go to [WhatsApp Manager](https://business.facebook.com/latest/whatsapp_manager/overview).
* Click `Phone numbers` in the left sidebar.
* You will see the status of the review under the display name as shown below.
4. Follow the on-screen instructions to verify your business.
5. Once you complete the process, your business will either be verified immediately or placed under review.
6. After your business is verified, Facebook will begin reviewing your display name. To view the status of the review:
* Go to [WhatsApp Manager](https://business.facebook.com/latest/whatsapp_manager/overview).
* Click `Phone numbers` in the left sidebar.
* You will see the status of the review under the display name as shown below.
 7. Once the review is complete, you'll receive an email notification from Facebook and you can begin using your WhatsApp bot to send and receive messages.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/web-widget/display-sources.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Display AI sources
> Learn how to enable sources for AI responses.
1. Open the widget designer. To learn how to access it, see [this guide](/web-widget/customize#how-to-customize-the-widget).
2. Go to `Configure`.
7. Once the review is complete, you'll receive an email notification from Facebook and you can begin using your WhatsApp bot to send and receive messages.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/web-widget/display-sources.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Display AI sources
> Learn how to enable sources for AI responses.
1. Open the widget designer. To learn how to access it, see [this guide](/web-widget/customize#how-to-customize-the-widget).
2. Go to `Configure`.
 3. Enable the `Show Sources for AI Response` option. You can customize it by selecting the number and type of sources to display.
3. Enable the `Show Sources for AI Response` option. You can customize it by selecting the number and type of sources to display.
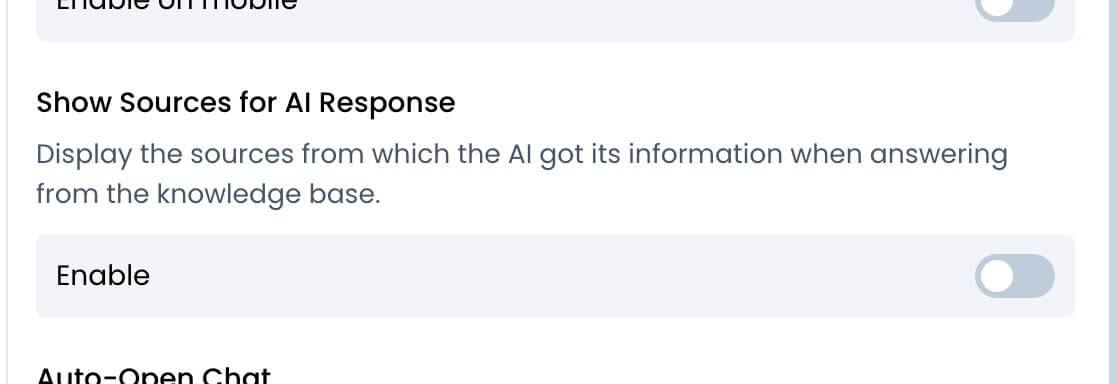 Here's how it appears in the chatbot:
Here's how it appears in the chatbot:
 ---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/web-widget/download-chat-transcripts.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Download transcripts
> A guide to enabling chat transcript downloads for end-users.
If you'd like your chatbot users to have the option to download chat transcripts, you can turn on this feature in the chatbot's appearance settings.
## How to allow end-users to download chat transcripts
1. Open your chatbot's dashboard.
2. Go to the widget designer. To learn how to access it, see [this guide](/web-widget/customize).
3. Click `Configure` from the sidebar.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/web-widget/download-chat-transcripts.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Download transcripts
> A guide to enabling chat transcript downloads for end-users.
If you'd like your chatbot users to have the option to download chat transcripts, you can turn on this feature in the chatbot's appearance settings.
## How to allow end-users to download chat transcripts
1. Open your chatbot's dashboard.
2. Go to the widget designer. To learn how to access it, see [this guide](/web-widget/customize).
3. Click `Configure` from the sidebar.
 4. Enable `Allow users to download chat transcripts`.
4. Enable `Allow users to download chat transcripts`.
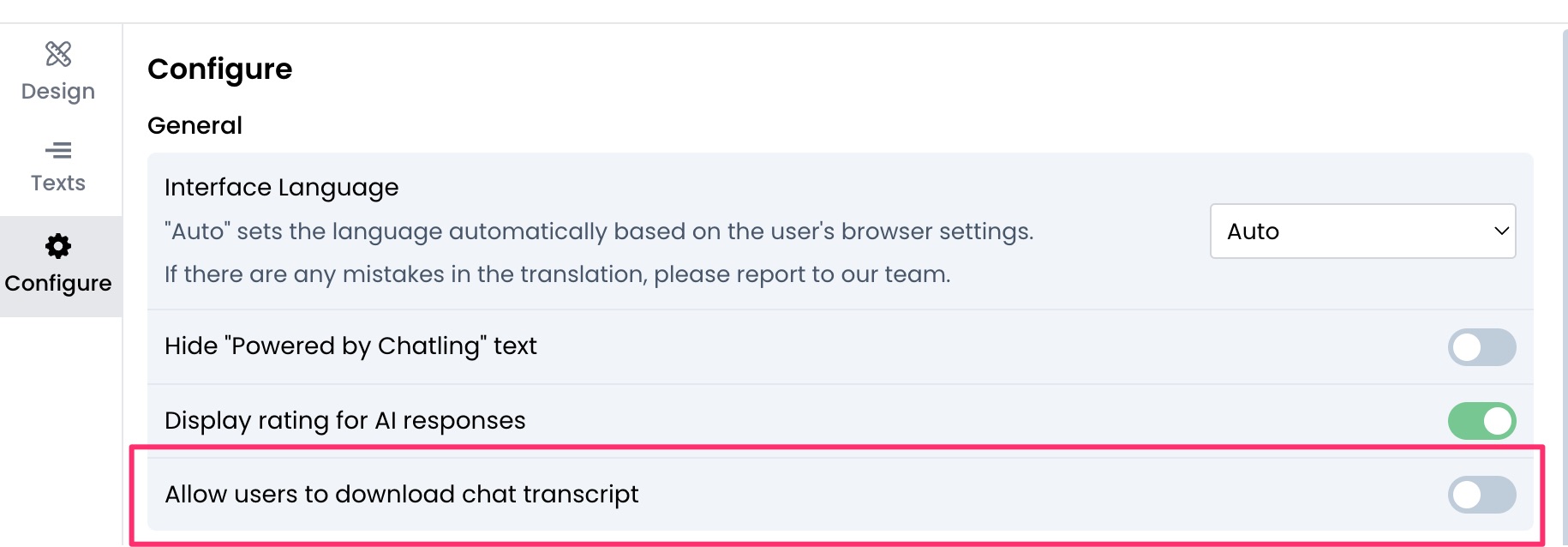 5. Click `Save`.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/api-reference/v2/chatbots/duplicate-chatbot.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Duplicate chatbot
## Request parameters
### Path
The chatbot ID.
## Response
The status of the request. Will be `success` if the request was successful, otherwise `error`.
The unique identifier of the duplicated chatbot.
```json theme={null}
{
"status": "success",
"data": {
"chatbot_id": "5285975738"
}
}
```
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/general-settings/duplicate.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# How to duplicate a chatbot or agent
> Learn how to duplicate a chatbot/agent to create a copy of it.
You can duplicate chatbots or agents and create copies of them to use as templates or to make changes without affecting the original bot. This can be useful if you want to experiment with different configurations or create a backup of your bot.
By duplicating a chatbot or agent, all its settings, appearance, and builder configurations will be copied to the new chatbot. You can then make changes to the duplicated chatbot without affecting the original one.
## Duplicating a chatbot
1. Go to your project's dashboard where you can view all your chatbots and agents.
5. Click `Save`.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/api-reference/v2/chatbots/duplicate-chatbot.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Duplicate chatbot
## Request parameters
### Path
The chatbot ID.
## Response
The status of the request. Will be `success` if the request was successful, otherwise `error`.
The unique identifier of the duplicated chatbot.
```json theme={null}
{
"status": "success",
"data": {
"chatbot_id": "5285975738"
}
}
```
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/general-settings/duplicate.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# How to duplicate a chatbot or agent
> Learn how to duplicate a chatbot/agent to create a copy of it.
You can duplicate chatbots or agents and create copies of them to use as templates or to make changes without affecting the original bot. This can be useful if you want to experiment with different configurations or create a backup of your bot.
By duplicating a chatbot or agent, all its settings, appearance, and builder configurations will be copied to the new chatbot. You can then make changes to the duplicated chatbot without affecting the original one.
## Duplicating a chatbot
1. Go to your project's dashboard where you can view all your chatbots and agents.
 2. Click on the ellipsis `...` icon next to the chatbot or agent you want to duplicate.
2. Click on the ellipsis `...` icon next to the chatbot or agent you want to duplicate.
 3. Select the `Duplicate` option from the dropdown menu.
3. Select the `Duplicate` option from the dropdown menu.
 ---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/api-reference/v2/usage/email-credits.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Email Credits
> Get the email credits usage for the project.
## Response
The status of the request. Will be `success` if the request was successful, otherwise `error`.
The number of email credits used.
The maximum number of email credits allowed for the project.
```json Response theme={null}
{
"status": "success",
"data": {
"used": 125,
"max": 1500
}
}
```
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/blocks/inputs/email.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Email Block
> Learn about the Email input block and how to set it up in the Builder.
The Email block is used to capture a valid email address from the user. You can use this block to collect email addresses of users for various purposes, such as saving them as leads, sending newsletters, or providing account-related information.
## Configuration
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/api-reference/v2/usage/email-credits.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Email Credits
> Get the email credits usage for the project.
## Response
The status of the request. Will be `success` if the request was successful, otherwise `error`.
The number of email credits used.
The maximum number of email credits allowed for the project.
```json Response theme={null}
{
"status": "success",
"data": {
"used": 125,
"max": 1500
}
}
```
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/blocks/inputs/email.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Email Block
> Learn about the Email input block and how to set it up in the Builder.
The Email block is used to capture a valid email address from the user. You can use this block to collect email addresses of users for various purposes, such as saving them as leads, sending newsletters, or providing account-related information.
## Configuration
 The Email block has the following configuration options:
* **Store email in variable**: The variable where the user's email address will be stored.
* **Input required**: Determine whether the user must provide an email address to proceed. If this option is disabled, a Skip button will appear, allowing users to skip the input.
* **Disallowed domains**: Specify a list of email domains that are not allowed. Users will not be able to enter email addresses associated with these domains.
* **[Quick replies](/chatbot/builder/block-options/quick-replies)**
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/knowledge-base/exclude-webpage-sections.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Exclude webpage sections
> Learn how to exclude certain sections of a webpage when adding a data source.
Websites often contain a lot of information that may not be relevant to the AI. When you add webpages to the knowledge base, you can exclude certain sections of the page from being crawled and indexed by the AI.
This can be useful for removing irrelevant information as well as preventing unnecessary characters from being counted towards your plan's limit.
## How to exclude sections of a webpage
1. Go to the `Knowledge Base`.
2. Click the `New Data Source` or `Add new` button.
The Email block has the following configuration options:
* **Store email in variable**: The variable where the user's email address will be stored.
* **Input required**: Determine whether the user must provide an email address to proceed. If this option is disabled, a Skip button will appear, allowing users to skip the input.
* **Disallowed domains**: Specify a list of email domains that are not allowed. Users will not be able to enter email addresses associated with these domains.
* **[Quick replies](/chatbot/builder/block-options/quick-replies)**
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/knowledge-base/exclude-webpage-sections.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Exclude webpage sections
> Learn how to exclude certain sections of a webpage when adding a data source.
Websites often contain a lot of information that may not be relevant to the AI. When you add webpages to the knowledge base, you can exclude certain sections of the page from being crawled and indexed by the AI.
This can be useful for removing irrelevant information as well as preventing unnecessary characters from being counted towards your plan's limit.
## How to exclude sections of a webpage
1. Go to the `Knowledge Base`.
2. Click the `New Data Source` or `Add new` button.
 3. Select `Website`, `Sitemap`, or `URL list` as the data source type.
4. Click the `Advanced Settings` button.
3. Select `Website`, `Sitemap`, or `URL list` as the data source type.
4. Click the `Advanced Settings` button.
 5. You can exclude sections by entering the HTML classes or IDs of the elements you want to exclude. You must press Enter after each class or ID to add it to the list.
You can also select the HTML tags you want to remove, such as `header` or `footer`.
5. You can exclude sections by entering the HTML classes or IDs of the elements you want to exclude. You must press Enter after each class or ID to add it to the list.
You can also select the HTML tags you want to remove, such as `header` or `footer`.
 You can now go ahead with entering the website, sitemap, or list of URLs that you want to add to the knowledge base. The crawler will exclude the sections you specified.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/ai-agent/actions/tutorials/fetch-and-email-order-confirmation.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# 1. Fetch and Email Order Confirmation
In this tutorial, you'll build a simple but real-world flow that (1) fetches order data from an API via the [HTTP Request action](/ai-agent/actions/http-request), and (2) sends an email confirmation to the user with the [Send Email action](/ai-agent/actions/send-email).
By the end, your agent will automatically collect the user's email and order number, call your API to verify and fetch the order, and deliver a personalized confirmation email.
You can now go ahead with entering the website, sitemap, or list of URLs that you want to add to the knowledge base. The crawler will exclude the sections you specified.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/ai-agent/actions/tutorials/fetch-and-email-order-confirmation.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# 1. Fetch and Email Order Confirmation
In this tutorial, you'll build a simple but real-world flow that (1) fetches order data from an API via the [HTTP Request action](/ai-agent/actions/http-request), and (2) sends an email confirmation to the user with the [Send Email action](/ai-agent/actions/send-email).
By the end, your agent will automatically collect the user's email and order number, call your API to verify and fetch the order, and deliver a personalized confirmation email.
 ## Setup Guide
1. Open your agent dashboard and go to Actions.
2. Click the `New` button and choose `HTTP Request`.
3. Set up the action as follows:
**Action name**: get\_order
**When to use**: When user asks to get an email of their order confirmation, first use this action to fetch the order before using email\_order\_confirmation.
**Frequency**: Whenever applicable
**Input parameters**: Add the parameters that are required to fetch the user's order. In this case, we will add the following parameters:
* `email`: The email address of the order. Save it to a variable, such as "email".
* `order_number`: The user's order number. Save it to a variable, such as "order\_number".
## Setup Guide
1. Open your agent dashboard and go to Actions.
2. Click the `New` button and choose `HTTP Request`.
3. Set up the action as follows:
**Action name**: get\_order
**When to use**: When user asks to get an email of their order confirmation, first use this action to fetch the order before using email\_order\_confirmation.
**Frequency**: Whenever applicable
**Input parameters**: Add the parameters that are required to fetch the user's order. In this case, we will add the following parameters:
* `email`: The email address of the order. Save it to a variable, such as "email".
* `order_number`: The user's order number. Save it to a variable, such as "order\_number".
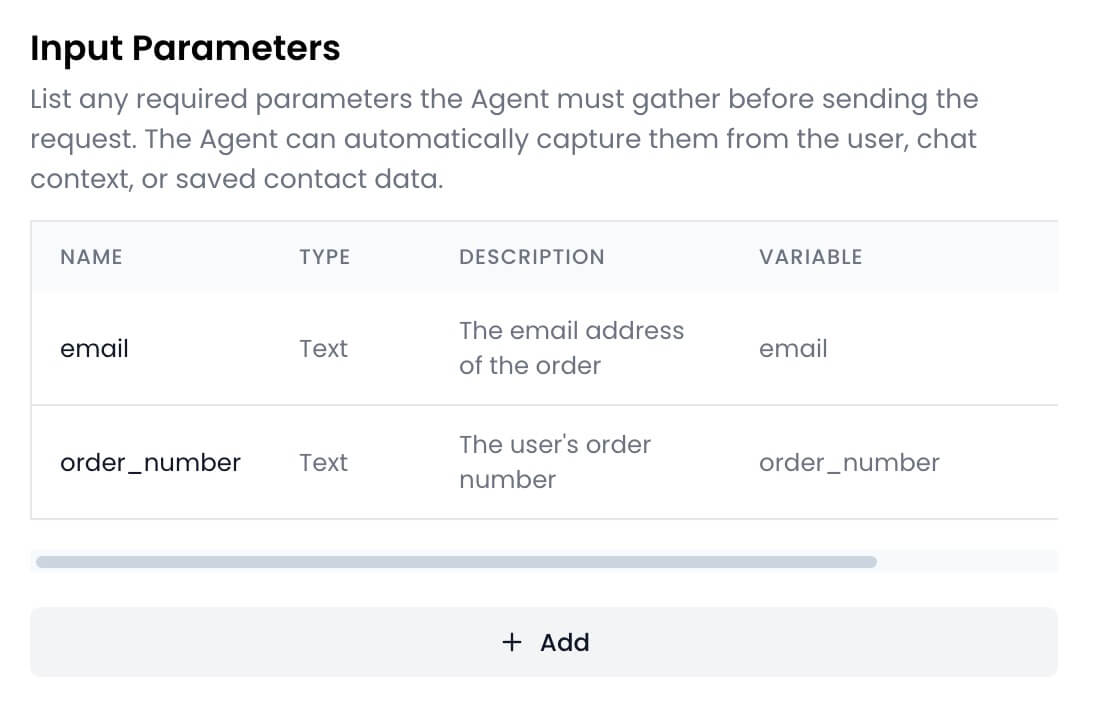 **Request**: Configure the request by defining the API URL, method, payload, and headers that will be used to fetch the user's order.
For this tutorial, we'll use a dummy API that returns an order. However, in a real app, you'd point the HTTP Request to your own or third-party API, include auth (e.g., Bearer token), and the relevant payload such as the user's email and order number.
**Request**: Configure the request by defining the API URL, method, payload, and headers that will be used to fetch the user's order.
For this tutorial, we'll use a dummy API that returns an order. However, in a real app, you'd point the HTTP Request to your own or third-party API, include auth (e.g., Bearer token), and the relevant payload such as the user's email and order number.
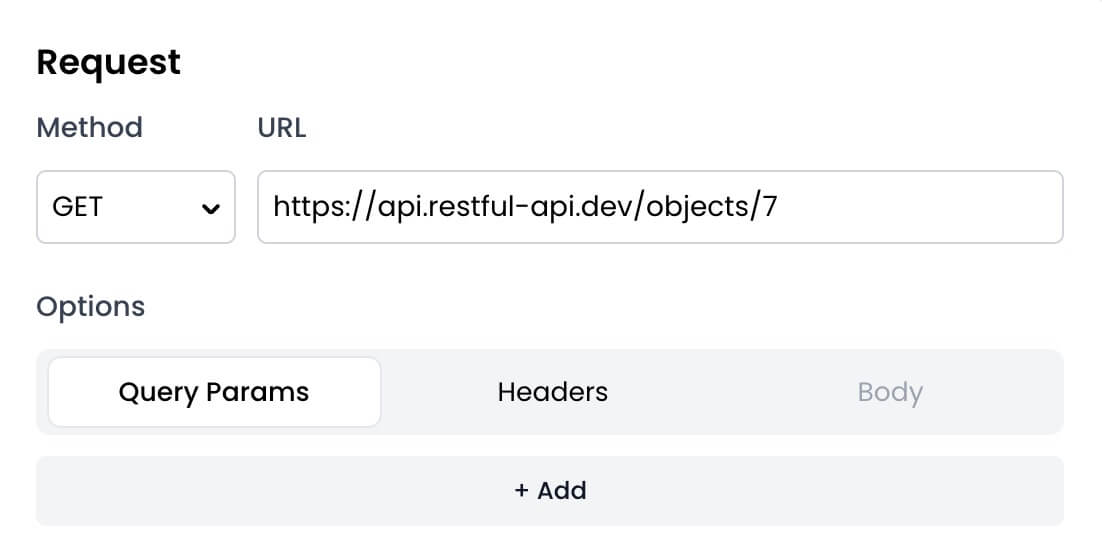 4. Click the `Test Request` button to verify that the request runs successfully and that the agent receives a valid JSON response.
4. Click the `Test Request` button to verify that the request runs successfully and that the agent receives a valid JSON response.
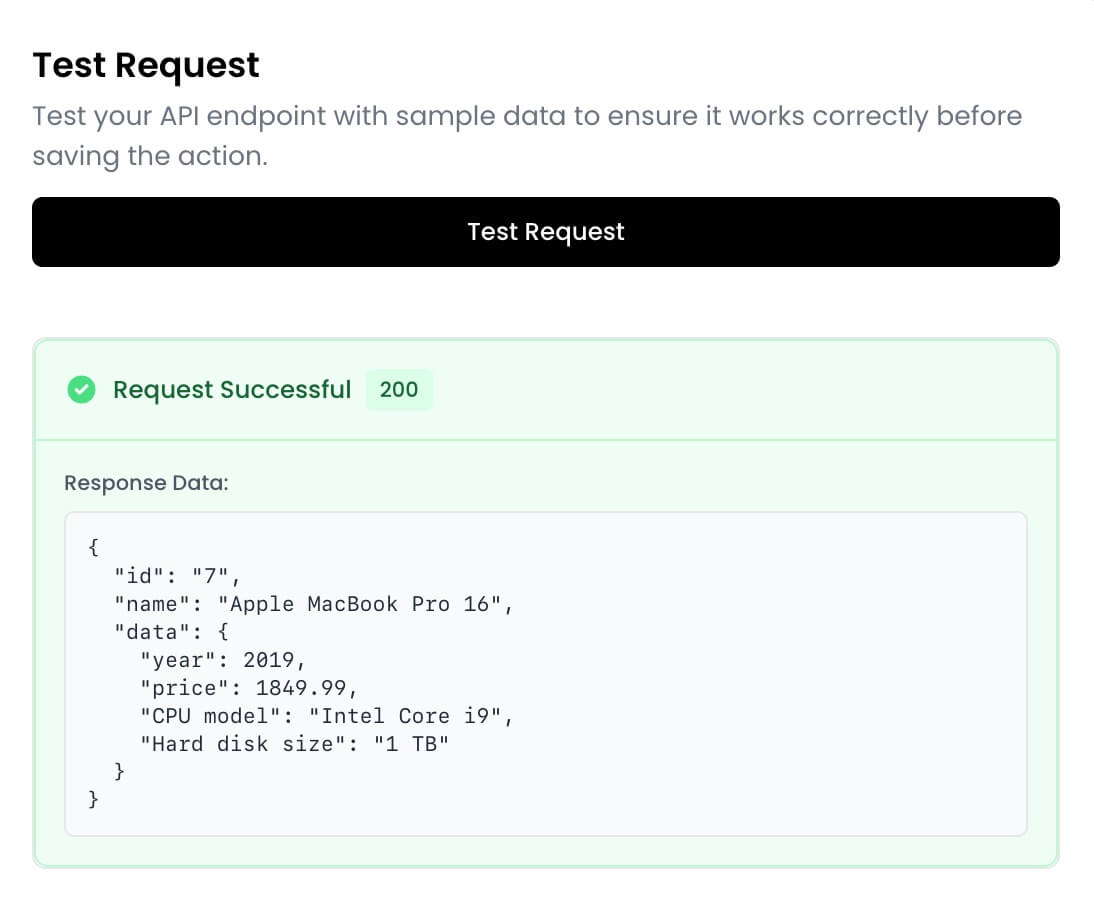 5. Click `Create action` to save the action.
6. Go back to the `Actions` page.
7. Click the `New` button and choose `Send Email`.
8. Set up the action as follows:
**Action name**: email\_order\_confirmation
**When to use**: Use this action to send the order confirmation to the user. First use the get\_order action to get the user's order, then use this action to email the order confirmation to the user.
**Frequency**: Whenever applicable
**Input parameters**: We'll add the following parameters that are required to send the email:
* `email`:
* Description: The email address where the order confirmation should be sent.
* Save to variable: email
* `order_number`:
* Description: The order number of the user's order.
* Save to variable: order\_number
* `order_details`:
* Description: The details of the order that you retrieve from the get\_order action. Format it as HTML with bullet points.
* Save to variable: order\_details
5. Click `Create action` to save the action.
6. Go back to the `Actions` page.
7. Click the `New` button and choose `Send Email`.
8. Set up the action as follows:
**Action name**: email\_order\_confirmation
**When to use**: Use this action to send the order confirmation to the user. First use the get\_order action to get the user's order, then use this action to email the order confirmation to the user.
**Frequency**: Whenever applicable
**Input parameters**: We'll add the following parameters that are required to send the email:
* `email`:
* Description: The email address where the order confirmation should be sent.
* Save to variable: email
* `order_number`:
* Description: The order number of the user's order.
* Save to variable: order\_number
* `order_details`:
* Description: The details of the order that you retrieve from the get\_order action. Format it as HTML with bullet points.
* Save to variable: order\_details
 **Email Setup**: configure the email as follows:
* Sender name: A name of your choice, for example `Apple`
* To: Type in `{{email}}` and press Enter to use the email address of the user.
* Subject: `Order confirmation for #{{order_number}}`
* Message:
```
Hi there!
As requested, here is your confirmation for order #{{order_number}}:
{{order_details}}
```
**Email Setup**: configure the email as follows:
* Sender name: A name of your choice, for example `Apple`
* To: Type in `{{email}}` and press Enter to use the email address of the user.
* Subject: `Order confirmation for #{{order_number}}`
* Message:
```
Hi there!
As requested, here is your confirmation for order #{{order_number}}:
{{order_details}}
```
 9. Click the `Create action` button to save the action.
## Test the actions
Now that you've set up the actions, it's time to test them.
From the `Actions` page, enable both the actions.
Go to the `Playground` page to start a chat with your agent. Ask the agent to email your order confirmation. It should fetch the order details from the API and email the order confirmation to the email address you specify.
Here's an example of how the agent would respond:
9. Click the `Create action` button to save the action.
## Test the actions
Now that you've set up the actions, it's time to test them.
From the `Actions` page, enable both the actions.
Go to the `Playground` page to start a chat with your agent. Ask the agent to email your order confirmation. It should fetch the order details from the API and email the order confirmation to the email address you specify.
Here's an example of how the agent would respond:
 ---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/ai/fix-incorrect-answers.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Fix incorrect AI answers
> Learn how to fix incorrect AI responses using the fine-tuning feature in Chatling.
Although the AI is trained on the data you add to the knowledge base, it may not always get the answer right, such as when it's asked a question that is not in the knowledge base or when it hallucinates.
To fix this, you can use the fine-tuning feature on Chatling's conversations page. This feature is designed to help improve the chatbot's performance by refining incorrect responses.
When you're viewing a conversation, you'll see a "Fine-tune this answer" button below every AI response. This feature allows you to fix incorrect AI responses so that it will learn to answer correctly in the future.
## How to use the fine-tuning feature
1. From the chatbot dashboard, click on the "Conversations" menu.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/ai/fix-incorrect-answers.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Fix incorrect AI answers
> Learn how to fix incorrect AI responses using the fine-tuning feature in Chatling.
Although the AI is trained on the data you add to the knowledge base, it may not always get the answer right, such as when it's asked a question that is not in the knowledge base or when it hallucinates.
To fix this, you can use the fine-tuning feature on Chatling's conversations page. This feature is designed to help improve the chatbot's performance by refining incorrect responses.
When you're viewing a conversation, you'll see a "Fine-tune this answer" button below every AI response. This feature allows you to fix incorrect AI responses so that it will learn to answer correctly in the future.
## How to use the fine-tuning feature
1. From the chatbot dashboard, click on the "Conversations" menu.
 2. Find and open a conversation where the AI has responded incorrectly.
3. Click the `Fine-tune this answer` button below the AI response you want to fix.
2. Find and open a conversation where the AI has responded incorrectly.
3. Click the `Fine-tune this answer` button below the AI response you want to fix.
 4. A dialog will appear where you can edit the AI's answer or replace it with a correct one.
4. A dialog will appear where you can edit the AI's answer or replace it with a correct one.
 5. Once done, click the `Finetune` button. The new answer will be added to the FAQ sources in the knowledge base and will be queued for processing.
Now, when the AI is asked a similar question, it will respond with the answer you provided.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/blocks/inputs/form.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Form Block
> Learn about the Form input block and how to set it up in the Builder.
The Form block is used to collect multiple pieces of information from users in a structured way. You can use this block to create forms for lead generation, user feedback, surveys, and more.
You can add multiple fields to the form and configure each field to collect different types of information, such as text, email, phone number, and more.
5. Once done, click the `Finetune` button. The new answer will be added to the FAQ sources in the knowledge base and will be queued for processing.
Now, when the AI is asked a similar question, it will respond with the answer you provided.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/blocks/inputs/form.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Form Block
> Learn about the Form input block and how to set it up in the Builder.
The Form block is used to collect multiple pieces of information from users in a structured way. You can use this block to create forms for lead generation, user feedback, surveys, and more.
You can add multiple fields to the form and configure each field to collect different types of information, such as text, email, phone number, and more.
 ## Configuration
The Form block has the following configuration options:
* **Fields**: Add and configure the fields you want to include in the form.
* **Label**: The label of the field to indicate what information is being collected.
* **Type**: Type of the field, such as Text, Email, Number, etc. This prevents users from entering invalid data.
* **Store user input in variable**: The variable where the user's response to the field will be stored.
## Configuration
The Form block has the following configuration options:
* **Fields**: Add and configure the fields you want to include in the form.
* **Label**: The label of the field to indicate what information is being collected.
* **Type**: Type of the field, such as Text, Email, Number, etc. This prevents users from entering invalid data.
* **Store user input in variable**: The variable where the user's response to the field will be stored.
 ---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/blocks/action/get-contact.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Get Contact Block
> Learn about the Get Contact block and how to set it up in the Builder.
The `Get Contact` block can be used to retrieve a contact's information.
The block consists of the following components:
* **Search**: Specify the field and value to use to look up the contact. You can enter a variable to search dynamically.
* **Contact details**: Define the properties to retrieve and the variables to store the values in.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/getting-started.md
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/ai-agent/getting-started.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Getting started with AI Agents
> Learn how to create your first AI agent in Chatling
What we'll be covering:
1. [Create an AI Agent](#1-create-an-ai-agent)
2. [Configure the AI settings](#2-configure-the-ai-settings)
3. [Populate the knowledge base](#3-populate-the-knowledge-base)
4. [Create AI actions](#4-create-ai-actions)
5. [Test your Agent](#5-test-your-agent)
6. [Deploy](#6-deploy-your-agent)
## 1. Create an AI Agent
1. Go to your account and open the "My agents" page. Click the `+ Create` or `New` button.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/blocks/action/get-contact.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Get Contact Block
> Learn about the Get Contact block and how to set it up in the Builder.
The `Get Contact` block can be used to retrieve a contact's information.
The block consists of the following components:
* **Search**: Specify the field and value to use to look up the contact. You can enter a variable to search dynamically.
* **Contact details**: Define the properties to retrieve and the variables to store the values in.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/getting-started.md
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/ai-agent/getting-started.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Getting started with AI Agents
> Learn how to create your first AI agent in Chatling
What we'll be covering:
1. [Create an AI Agent](#1-create-an-ai-agent)
2. [Configure the AI settings](#2-configure-the-ai-settings)
3. [Populate the knowledge base](#3-populate-the-knowledge-base)
4. [Create AI actions](#4-create-ai-actions)
5. [Test your Agent](#5-test-your-agent)
6. [Deploy](#6-deploy-your-agent)
## 1. Create an AI Agent
1. Go to your account and open the "My agents" page. Click the `+ Create` or `New` button.
 2. Select `AI Agent` as the type.
2. Select `AI Agent` as the type.
 3. Enter a name for your Agent and click `Create agent`.
3. Enter a name for your Agent and click `Create agent`.
 ## 2. Configure the AI settings
Once your Agent is created, it's time to configure it's AI settings.
1. From your agent's dashboard, click `Settings` in the sidebar.
## 2. Configure the AI settings
Once your Agent is created, it's time to configure it's AI settings.
1. From your agent's dashboard, click `Settings` in the sidebar.
 2. Select the `AI` menu.
2. Select the `AI` menu.
 3. Here you can configure the AI settings, such as:
* **AI Model**: The AI model that the Agent will use to generate responses.
* **Temperature**: Controls randomness of the agent's responses. A lower temperature will make the outputs more focused and deterministic, whereas a higher temperature will make the responses diverse and creative.
* **Instructions**: Define the agent's role, goals, guardrails, and style (often called the "system prompt"). There are templates available to help you get started. Click the `Browse templates` button to see the available templates.
3. Here you can configure the AI settings, such as:
* **AI Model**: The AI model that the Agent will use to generate responses.
* **Temperature**: Controls randomness of the agent's responses. A lower temperature will make the outputs more focused and deterministic, whereas a higher temperature will make the responses diverse and creative.
* **Instructions**: Define the agent's role, goals, guardrails, and style (often called the "system prompt"). There are templates available to help you get started. Click the `Browse templates` button to see the available templates.
 ## 3. Populate the knowledge base
The Knowledge Base is where you upload information the Agent uses to generate responses to user queries. You can upload information about your business, products, services, policies, and more.
You can add several types of data to the knowledge base, such as websites, documents, texts, and FAQs. You can also connect your Zendesk or Zoho account to import articles from your help center.
When a user asks a question, the Agent queries the knowledge base for relevant information and generates a response based on the data it finds.
## 3. Populate the knowledge base
The Knowledge Base is where you upload information the Agent uses to generate responses to user queries. You can upload information about your business, products, services, policies, and more.
You can add several types of data to the knowledge base, such as websites, documents, texts, and FAQs. You can also connect your Zendesk or Zoho account to import articles from your help center.
When a user asks a question, the Agent queries the knowledge base for relevant information and generates a response based on the data it finds.
 To add data to the knowledge base, click the `+ Add data source` button, then select the type of data you want to add.
To add data to the knowledge base, click the `+ Add data source` button, then select the type of data you want to add.
 ## 4. Create AI actions
Actions unlock the true power of AI Agents. Instead of only generating replies, the Agent can actively carry out tasks during a conversation.
This might involve saving details of potential leads, displaying booking widgets, interacting with external systems to fetch or store data, creating support tickets, and more.
1. Click the `Actions` menu from the sidebar.
2. Click `Create action`.
3. Select the type of action you want to create.
4. Configure the action according to your needs.
5. Click the `Create` button to save the action.
To learn more about actions, check out the [Actions](/ai-agent/actions/introduction) documentation.
## 5. Test your Agent
You can test your AI Agent in the Playground. It is your sandbox to experiment with your Agent in real time.
To open the Playground, click `Playground` from the sidebar menu.
You can tweak core settings—like AI model, enabled actions, temperature, and instructions—then chat with the Agent to see exactly how those changes affect behavior.
## 4. Create AI actions
Actions unlock the true power of AI Agents. Instead of only generating replies, the Agent can actively carry out tasks during a conversation.
This might involve saving details of potential leads, displaying booking widgets, interacting with external systems to fetch or store data, creating support tickets, and more.
1. Click the `Actions` menu from the sidebar.
2. Click `Create action`.
3. Select the type of action you want to create.
4. Configure the action according to your needs.
5. Click the `Create` button to save the action.
To learn more about actions, check out the [Actions](/ai-agent/actions/introduction) documentation.
## 5. Test your Agent
You can test your AI Agent in the Playground. It is your sandbox to experiment with your Agent in real time.
To open the Playground, click `Playground` from the sidebar menu.
You can tweak core settings—like AI model, enabled actions, temperature, and instructions—then chat with the Agent to see exactly how those changes affect behavior.
 You can also run side-by-side comparisons of up to 5 instances of your Agent, each with different settings, to quickly identify the configuration that performs best.
You can also run side-by-side comparisons of up to 5 instances of your Agent, each with different settings, to quickly identify the configuration that performs best.
 ## 6. Deploy your Agent
Once you've built your AI Agent, it's time to deploy it to your website, WhatsApp, or other channels.
Click `Deploy` from the sidebar menu. Select the channel you want to deploy your Agent to and follow the on-screen instructions.
## 6. Deploy your Agent
Once you've built your AI Agent, it's time to deploy it to your website, WhatsApp, or other channels.
Click `Deploy` from the sidebar menu. Select the channel you want to deploy your Agent to and follow the on-screen instructions.
 ---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/web-widget/installation/google-tag-manager.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Google Tag Manager
> Learn how to add Chatling to your website using Google Tag Manager
1. Go to your dashboard.
2. Click `Deploy` button in the sidebar menu.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/web-widget/installation/google-tag-manager.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Google Tag Manager
> Learn how to add Chatling to your website using Google Tag Manager
1. Go to your dashboard.
2. Click `Deploy` button in the sidebar menu.
 3. Click the `Manage` button under the `Website Widget` option.
3. Click the `Manage` button under the `Website Widget` option.
 4. Design the appearance of the widget by clicking the `Open widget designer` button.
4. Design the appearance of the widget by clicking the `Open widget designer` button.
 5. Select the display mode for your chatbot, such as "Floating Chat", "Inline", or "Fullscreen".
5. Select the display mode for your chatbot, such as "Floating Chat", "Inline", or "Fullscreen".
 6. Copy the widget code.
6. Copy the widget code.
 7. Go to Google Tag Manager and open your website's container.
8. Click on `Add a new tag`.
7. Go to Google Tag Manager and open your website's container.
8. Click on `Add a new tag`.
 9. Enter a name for the tag, such as `Chatling`.
9. Enter a name for the tag, such as `Chatling`.
 10. Click on `Tag Configuration`.
10. Click on `Tag Configuration`.
 11. Select `Custom HTML`.
11. Select `Custom HTML`.
 12. Paste the widget code into the `HTML` field.
12. Paste the widget code into the `HTML` field.
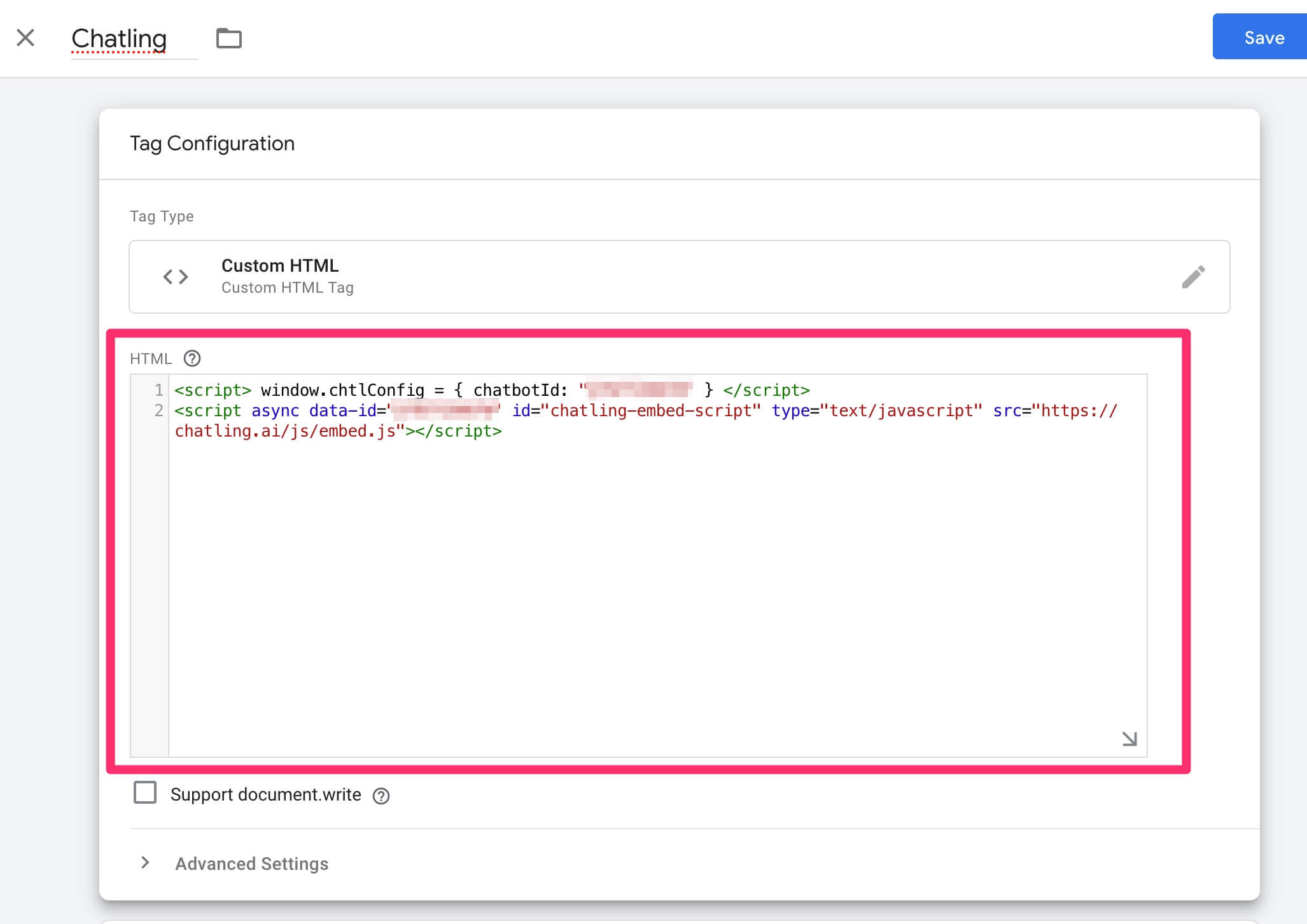 13. Click on `Triggering`.
13. Click on `Triggering`.
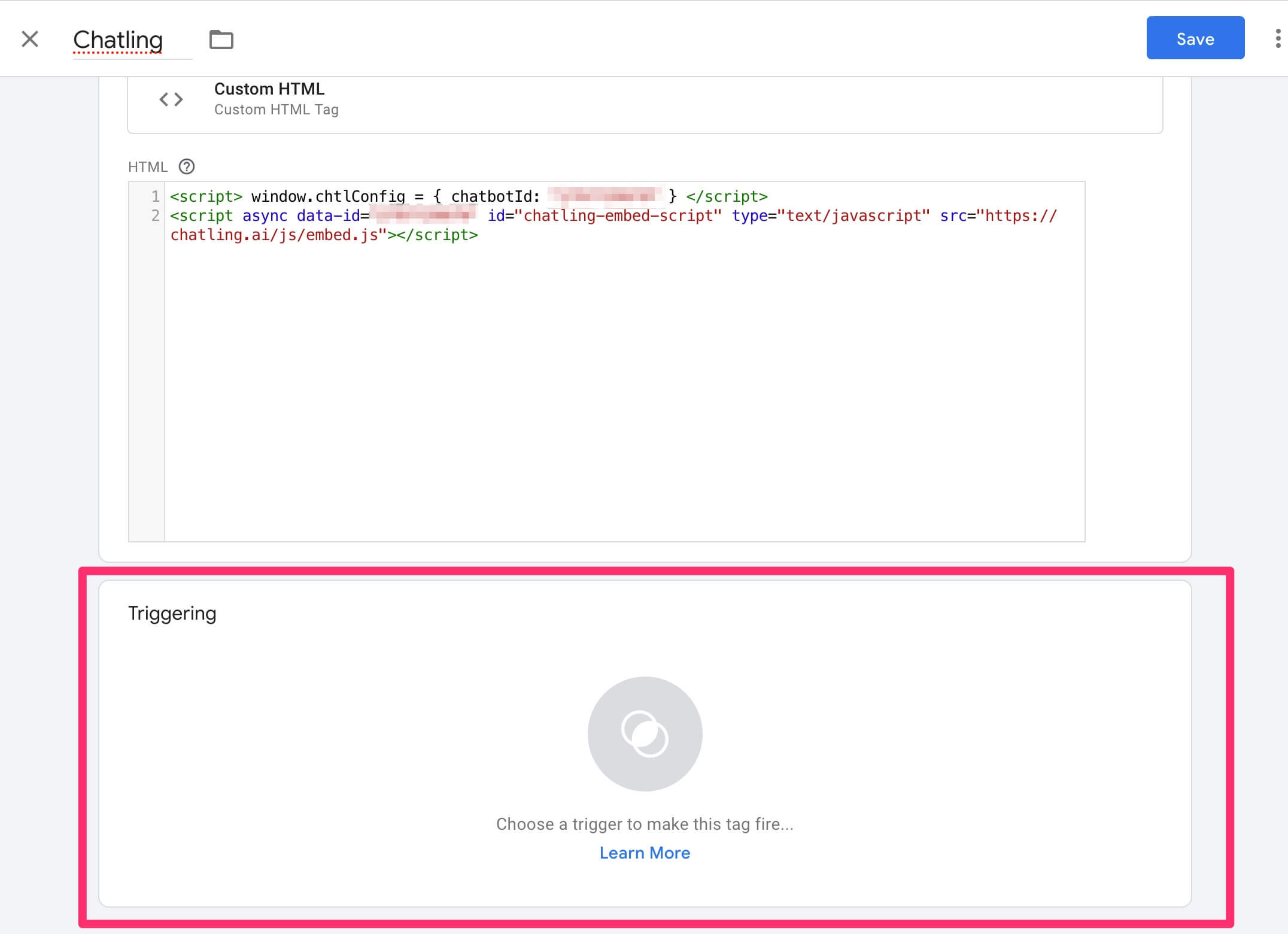 14. Select `All Pages`.
14. Select `All Pages`.
 15. Click `Save`.
15. Click `Save`.
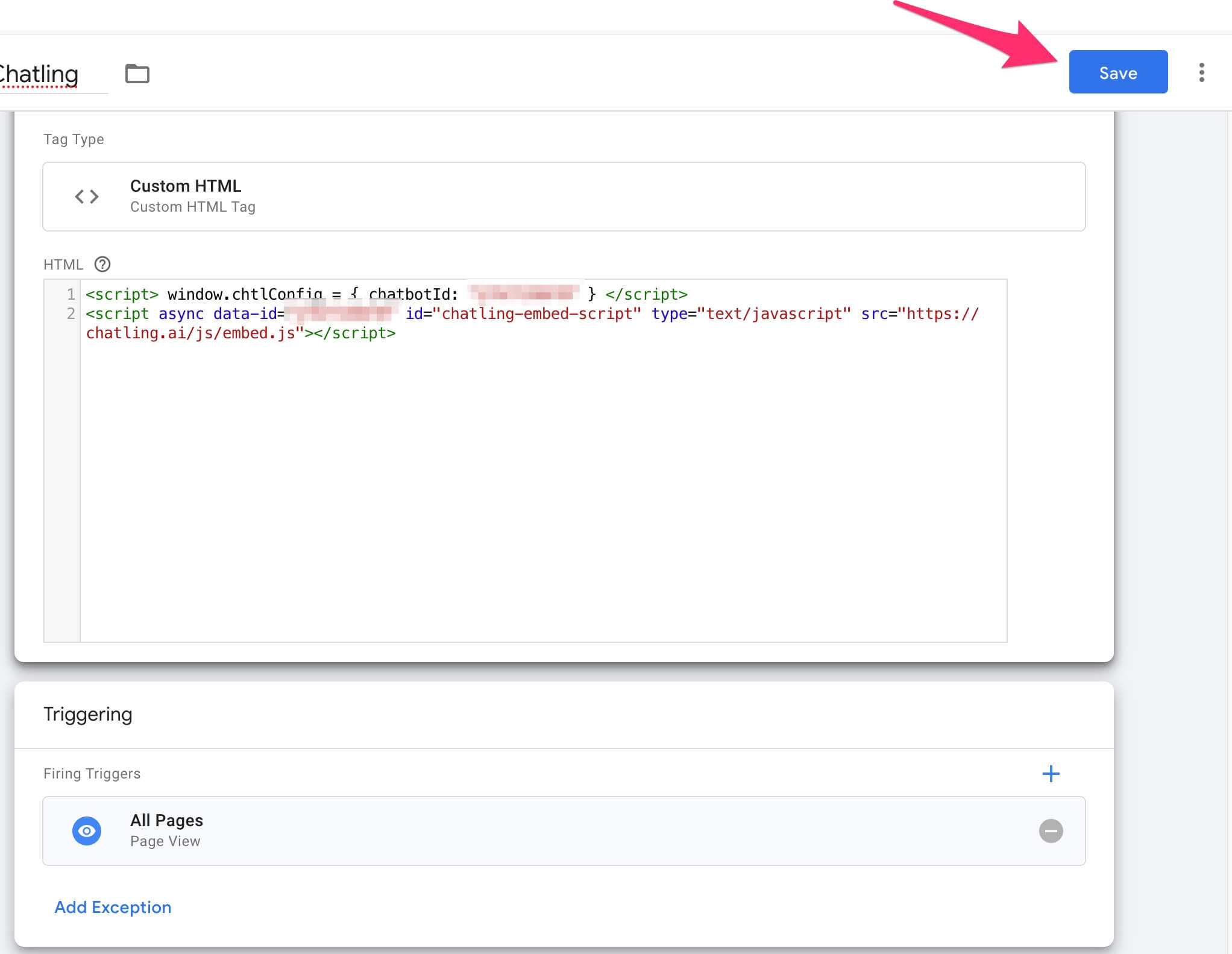 ---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/faq/hide-chatbot-on-specific-pages.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# How to hide the chatbot on specific pages
> Learn how to set the visibility of your chatbot on specific pages.
Sometimes you may want to hide your chatbot on specific pages of your website. This could be for various reasons, such as maintaining a distraction-free environment on certain pages, or to comply with specific page requirements. Chatling provides a simple way to control the visibility of your chatbot by allowing you to specify URLs where the chatbot widget should not appear.
## How to hide the chatbot on specific pages
1. From the chatbot dashboard, go to `Settings`.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/faq/hide-chatbot-on-specific-pages.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# How to hide the chatbot on specific pages
> Learn how to set the visibility of your chatbot on specific pages.
Sometimes you may want to hide your chatbot on specific pages of your website. This could be for various reasons, such as maintaining a distraction-free environment on certain pages, or to comply with specific page requirements. Chatling provides a simple way to control the visibility of your chatbot by allowing you to specify URLs where the chatbot widget should not appear.
## How to hide the chatbot on specific pages
1. From the chatbot dashboard, go to `Settings`.
 2. Click the `Visibility` tab.
3. In the `Hide chatbot on specific pages` section, type the URL of the page where you want to hide the chatbot and press the Enter key.
4. Repeat the previous step for each page where you want to hide the chatbot.
5. Click `Save` to apply the changes.
You can also enter wildcard URLs to hide the chatbot on multiple pages. For example, if you want to hide the chatbot on the blog, you can enter `https://example.com/blog/*` to hide it from all pages in the blog.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/variables/how-to-create-variables.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# How to create variables
> Learn how to create variables in the Builder
Variables can be created from the [sidebar](/chatbot/builder/sidebar) in the Builder. Here's how:
1. Click on the `Variables` menu in the sidebar.
2. Select `+ New`.
2. Click the `Visibility` tab.
3. In the `Hide chatbot on specific pages` section, type the URL of the page where you want to hide the chatbot and press the Enter key.
4. Repeat the previous step for each page where you want to hide the chatbot.
5. Click `Save` to apply the changes.
You can also enter wildcard URLs to hide the chatbot on multiple pages. For example, if you want to hide the chatbot on the blog, you can enter `https://example.com/blog/*` to hide it from all pages in the blog.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/variables/how-to-create-variables.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# How to create variables
> Learn how to create variables in the Builder
Variables can be created from the [sidebar](/chatbot/builder/sidebar) in the Builder. Here's how:
1. Click on the `Variables` menu in the sidebar.
2. Select `+ New`.
 3. Enter a name for the variable and click `Create`. The name must be alphanumeric and can include underscores, such as `first_name`, `firstName`, or `First Name`.
3. Enter a name for the variable and click `Create`. The name must be alphanumeric and can include underscores, such as `first_name`, `firstName`, or `First Name`.
 Note that variable names are case-sensitive. For example, `first name` and `First Name` are considered different variables.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/variables/how-to-use-variables.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# How to use variables
> A guide on how to use Variables in your chatbot
Variables can be used for capturing information, displaying dynamic content, and processing data in your chatbot.
## How to store data in variables
You can store data in variables using the `Store answer in variable` or a similar option that's available for certain blocks in the builder. This option appears in the [block editor](/chatbot/builder/block-editor).
Let's take the [Text input block](/chatbot/builder/blocks/inputs/text) as an example. This block allows users to enter text. To store the user's response in a variable, click the dropdown below the `Store answer in variable` option and select a variable.
Note that variable names are case-sensitive. For example, `first name` and `First Name` are considered different variables.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/variables/how-to-use-variables.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# How to use variables
> A guide on how to use Variables in your chatbot
Variables can be used for capturing information, displaying dynamic content, and processing data in your chatbot.
## How to store data in variables
You can store data in variables using the `Store answer in variable` or a similar option that's available for certain blocks in the builder. This option appears in the [block editor](/chatbot/builder/block-editor).
Let's take the [Text input block](/chatbot/builder/blocks/inputs/text) as an example. This block allows users to enter text. To store the user's response in a variable, click the dropdown below the `Store answer in variable` option and select a variable.
 ## How to display variables in messages
You can display variables in messages using the `{variableName}` syntax. The variable name should be enclosed in curly braces.
As an example, let's you have a variable called `first_name` and you want to greet the user by their name. Here's how to do it:
1. Add a [Text output block](/chatbot/builder/blocks/send/text) to your chatbot.
2. Click the block to open the editor.
3. Type `Hello, {first_name}!` in the message field.
## How to display variables in messages
You can display variables in messages using the `{variableName}` syntax. The variable name should be enclosed in curly braces.
As an example, let's you have a variable called `first_name` and you want to greet the user by their name. Here's how to do it:
1. Add a [Text output block](/chatbot/builder/blocks/send/text) to your chatbot.
2. Click the block to open the editor.
3. Type `Hello, {first_name}!` in the message field.
 4. When the chatbot displays this block, it will replace `{first_name}` with the value stored by the variable.
4. When the chatbot displays this block, it will replace `{first_name}` with the value stored by the variable.
 Note that the values stored are on a per-conversation basis. This means that the value of a variable is unique to each conversation and is not shared across different conversations.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/blocks/action/http-request.md
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/ai-agent/actions/http-request.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# HTTP Request
The HTTP Request action allows the AI Agent to connect to external APIs and services during the chat and perform an action.
The Agent can collect the needed inputs from the user, pull values from chat history, or use saved contact data—then send the request and use the result to respond or take the next step.
## Configuration
### `Action Name`
A short, specific identifier that tells the Agent what this action does (e.g. check\_order\_status, create\_support\_ticket).
### `When to Use`
A detailed description of what the action does and when it must be used.
When applicable, you can specify one or more of the following:
* **Positive cues/phrases**: Example utterances and keywords that signal this action (include a few variations).
* **Preconditions**: What must be true before running.
* **Do not use when**: Explicit exclusions to avoid false triggers.
### `Frequency`
Specify how often the Agent can invoke this action to avoid overusing it, e.g `Once per chat` or `Whenever applicable`.
### `Input parameters`
Define the parameters the Agent must gather before sending the request. The Agent can capture these from user input, existing chat context, or saved contact data.
For each parameter, you can specify the following:
* **Name**: The name of the parameter. Must start with a letter and contain only letters, numbers, and underscores.
* **Description** (optional): A description of the parameter to indicate what it is and if applicable, the formatting rules and min/max length.
* **Save to variable** (optional): The variable where the data can be saved. Applicable when you want to use the data in the HTTP request's parameters, such as URL, body, headers, etc.
### `Request`
Configure how the HTTP call is made.
* **Method**: GET, POST, PUT, PATCH, DELETE
* **URL**: Enter the request URL, such as an API endpoint.
* **Query Params** (optional): Key-value pairs appended to the URL.
* **Body** (optional): The request payload which can be passed as form data, form URL encoded, or raw JSON.
* **Headers** (optional): Data to be sent as the headers of the request, such as Content-Type and Authorization.
### `Test Request`
Run a live test with sample input values to confirm that it's working.
The request must succeed before the action can be created. A request is considered successful if it returns a 2xx status code and a valid JSON response.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/contacts/identify-users.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Identify users across multiple chats
When you save a contact, it's associated with the user and persists across multiple chat sessions. This information can be used to personalize the conversation, skip repetitive questions, and tailor the flow accordingly.
## How it works
The [Get Contact](/chatbot/builder/blocks/action/get-contact) block can be used to fetch the contact information associated with the current user.
The example below shows a flow that identifies the user and takes different actions based on whether their contact details exist.
Note that the values stored are on a per-conversation basis. This means that the value of a variable is unique to each conversation and is not shared across different conversations.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/blocks/action/http-request.md
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/ai-agent/actions/http-request.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# HTTP Request
The HTTP Request action allows the AI Agent to connect to external APIs and services during the chat and perform an action.
The Agent can collect the needed inputs from the user, pull values from chat history, or use saved contact data—then send the request and use the result to respond or take the next step.
## Configuration
### `Action Name`
A short, specific identifier that tells the Agent what this action does (e.g. check\_order\_status, create\_support\_ticket).
### `When to Use`
A detailed description of what the action does and when it must be used.
When applicable, you can specify one or more of the following:
* **Positive cues/phrases**: Example utterances and keywords that signal this action (include a few variations).
* **Preconditions**: What must be true before running.
* **Do not use when**: Explicit exclusions to avoid false triggers.
### `Frequency`
Specify how often the Agent can invoke this action to avoid overusing it, e.g `Once per chat` or `Whenever applicable`.
### `Input parameters`
Define the parameters the Agent must gather before sending the request. The Agent can capture these from user input, existing chat context, or saved contact data.
For each parameter, you can specify the following:
* **Name**: The name of the parameter. Must start with a letter and contain only letters, numbers, and underscores.
* **Description** (optional): A description of the parameter to indicate what it is and if applicable, the formatting rules and min/max length.
* **Save to variable** (optional): The variable where the data can be saved. Applicable when you want to use the data in the HTTP request's parameters, such as URL, body, headers, etc.
### `Request`
Configure how the HTTP call is made.
* **Method**: GET, POST, PUT, PATCH, DELETE
* **URL**: Enter the request URL, such as an API endpoint.
* **Query Params** (optional): Key-value pairs appended to the URL.
* **Body** (optional): The request payload which can be passed as form data, form URL encoded, or raw JSON.
* **Headers** (optional): Data to be sent as the headers of the request, such as Content-Type and Authorization.
### `Test Request`
Run a live test with sample input values to confirm that it's working.
The request must succeed before the action can be created. A request is considered successful if it returns a 2xx status code and a valid JSON response.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/contacts/identify-users.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Identify users across multiple chats
When you save a contact, it's associated with the user and persists across multiple chat sessions. This information can be used to personalize the conversation, skip repetitive questions, and tailor the flow accordingly.
## How it works
The [Get Contact](/chatbot/builder/blocks/action/get-contact) block can be used to fetch the contact information associated with the current user.
The example below shows a flow that identifies the user and takes different actions based on whether their contact details exist.
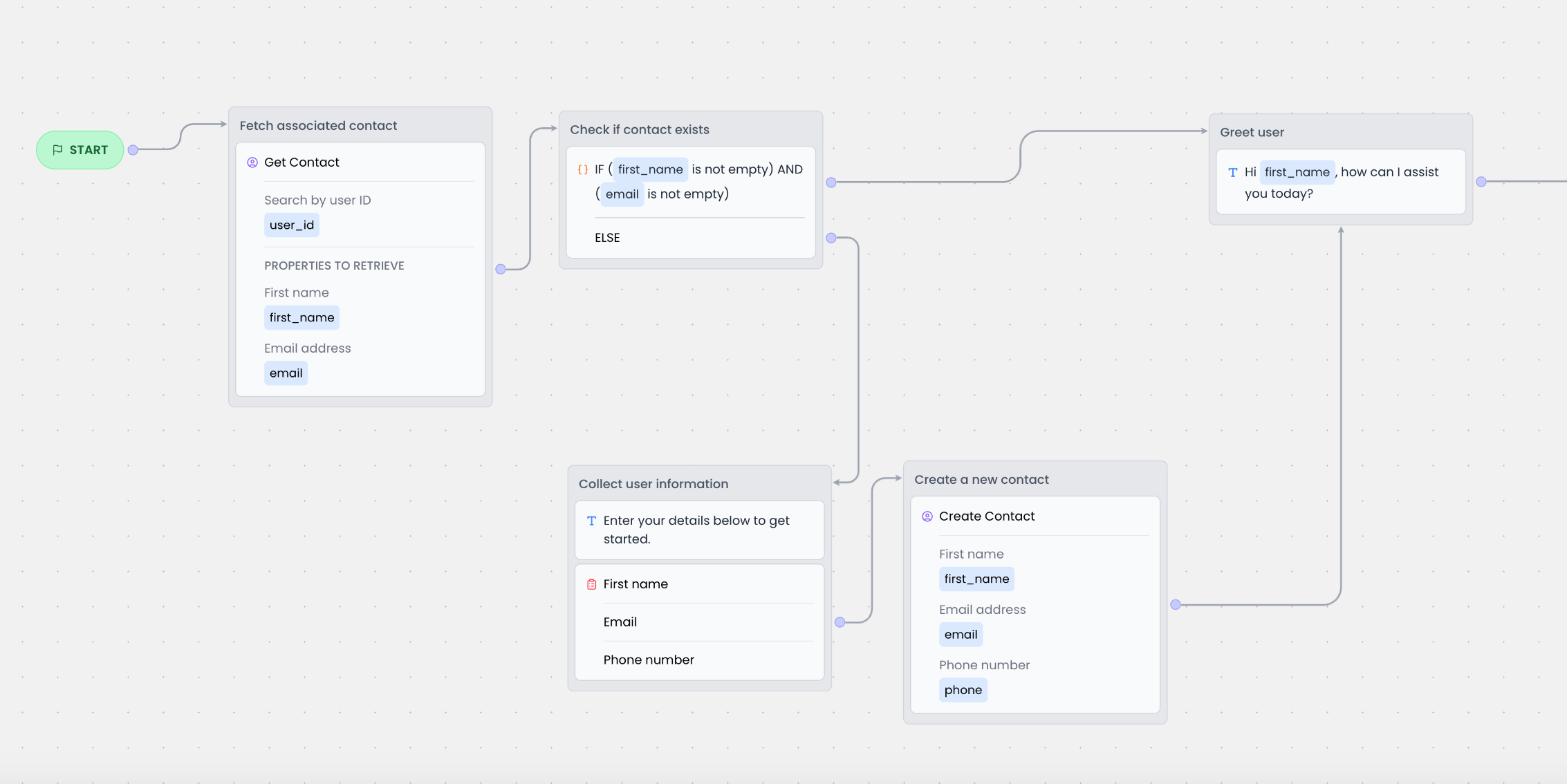 Here's how the above flow works:
1. When the chat starts, the `Get Contact` block is executed to check if a contact exists for the current user.
We're using the `user_id` variable to search for the associated contact. This is a system variable that contains the user's unique ID. If this variable doesn't exist in your builder, you can [import it from the Variables menu](/chatbot/builder/variables/import-system-variables).
2. If a contact is found, the information is stored in variables. For example, we're storing the contact's first name and email in the `first_name` and `email` variables.
3. Next, the [Variable condition block](/chatbot/builder/blocks/condition/variable) is used to check if the `email` and `first_name` variables are not empty.
* If they're not empty, it means the user is a returning user. In this case, we skip the form and greet the user by name.
* If they're empty, it means the user is new. In this case, we show the form to collect the user's name and email.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/blocks/send/image.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Image Block
> Learn about the Image block and how to set it up in the builder
You can use the Image block to display an image to the user. It can be used for various purposes, such as showing product images, providing visual instructions, or adding visual elements to your chatbot conversation.
## Adding an image
You can upload an image or insert its URL. The support image formats are `JPG/JPEG`, `PNG`, `WEBP`, and `GIF`.
Here's how the above flow works:
1. When the chat starts, the `Get Contact` block is executed to check if a contact exists for the current user.
We're using the `user_id` variable to search for the associated contact. This is a system variable that contains the user's unique ID. If this variable doesn't exist in your builder, you can [import it from the Variables menu](/chatbot/builder/variables/import-system-variables).
2. If a contact is found, the information is stored in variables. For example, we're storing the contact's first name and email in the `first_name` and `email` variables.
3. Next, the [Variable condition block](/chatbot/builder/blocks/condition/variable) is used to check if the `email` and `first_name` variables are not empty.
* If they're not empty, it means the user is a returning user. In this case, we skip the form and greet the user by name.
* If they're empty, it means the user is new. In this case, we show the form to collect the user's name and email.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/blocks/send/image.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Image Block
> Learn about the Image block and how to set it up in the builder
You can use the Image block to display an image to the user. It can be used for various purposes, such as showing product images, providing visual instructions, or adding visual elements to your chatbot conversation.
## Adding an image
You can upload an image or insert its URL. The support image formats are `JPG/JPEG`, `PNG`, `WEBP`, and `GIF`.
 ---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/variables/import-system-variables.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Import system variables
> Learn how to import system variables that aren't available by default in your chatbot.
Not all system variables are available by default when you create a chatbot. If you require additional system variables that aren't available, you can import them from the `Variables` menu in the builder's [sidebar](/chatbot/builder/sidebar).
## How to import additional system variables
1. Go to the `Builder` in your chatbot.
2. Click the `Variables` menu in the sidebar.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/variables/import-system-variables.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Import system variables
> Learn how to import system variables that aren't available by default in your chatbot.
Not all system variables are available by default when you create a chatbot. If you require additional system variables that aren't available, you can import them from the `Variables` menu in the builder's [sidebar](/chatbot/builder/sidebar).
## How to import additional system variables
1. Go to the `Builder` in your chatbot.
2. Click the `Variables` menu in the sidebar.
 3. Click `Import system variables`.
3. Click `Import system variables`.
 4. A list is displayed with all the additional system variables that you can import. Select the ones you want to import.
4. A list is displayed with all the additional system variables that you can import. Select the ones you want to import.
 5. Click the `Import` button.
5. Click the `Import` button.
 6. The selected system variables are now available to use in your chatbot.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/ai/instructions.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Instructions
> A guide on what AI Instructions are and how to use them.
Instructions are a way to provide guidance to the AI on how to respond.
You can use instructions to tailor the AI's responses to your specific needs, such as providing more detailed responses, using a specific tone, have a specific personality, or avoiding certain topics.
Here are a few examples:
* Your name is "Joanne" and you are our customer support assistant. When referring to yourself, do not mention anything about being an AI assistant or AI model. Instead, refer to yourself as "Joanne".
* Keep your answers short and to the point, and do not provide unnecessary information.
* Use a friendly and casual tone when responding to users.
* You must act as a professional customer support agent. NEVER break character.
* When responding in English, use American English spelling and grammar.
* Promote special offers or promotions when appropriate. For example, if a customer asks about a product, you can mention that we have a store-wide promotion of 50% off.
* Limit your answers to a maximum of 5 sentences.
* You are a lead generation assistant for a Digital Marketing agency and you are communicating with a prospective customer.
* Do not discuss politics, religion, or any other sensitive topics.
## How to add instructions
The method for adding instructions depends on the [Response Source](/chatbot/builder/blocks/ai/ai-response#what-is-the-response-source) that you've set for the [AI Response](/chatbot/builder/blocks/ai/ai-response) block.
### Response Source: Knowledge Base
If you are using the Knowledge Base as the response source, you can add instructions using the [AI Configuration menu](/chatbot/builder/sidebar#ai-configuration) in the Builder's sidebar.
1. Click on the AI Configuration menu in the sidebar.
6. The selected system variables are now available to use in your chatbot.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/ai/instructions.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Instructions
> A guide on what AI Instructions are and how to use them.
Instructions are a way to provide guidance to the AI on how to respond.
You can use instructions to tailor the AI's responses to your specific needs, such as providing more detailed responses, using a specific tone, have a specific personality, or avoiding certain topics.
Here are a few examples:
* Your name is "Joanne" and you are our customer support assistant. When referring to yourself, do not mention anything about being an AI assistant or AI model. Instead, refer to yourself as "Joanne".
* Keep your answers short and to the point, and do not provide unnecessary information.
* Use a friendly and casual tone when responding to users.
* You must act as a professional customer support agent. NEVER break character.
* When responding in English, use American English spelling and grammar.
* Promote special offers or promotions when appropriate. For example, if a customer asks about a product, you can mention that we have a store-wide promotion of 50% off.
* Limit your answers to a maximum of 5 sentences.
* You are a lead generation assistant for a Digital Marketing agency and you are communicating with a prospective customer.
* Do not discuss politics, religion, or any other sensitive topics.
## How to add instructions
The method for adding instructions depends on the [Response Source](/chatbot/builder/blocks/ai/ai-response#what-is-the-response-source) that you've set for the [AI Response](/chatbot/builder/blocks/ai/ai-response) block.
### Response Source: Knowledge Base
If you are using the Knowledge Base as the response source, you can add instructions using the [AI Configuration menu](/chatbot/builder/sidebar#ai-configuration) in the Builder's sidebar.
1. Click on the AI Configuration menu in the sidebar.
 2. Go to `Instructions`.
2. Go to `Instructions`.
 3. Click the `Add instruction` button and enter your instruction.
3. Click the `Add instruction` button and enter your instruction.
 4. To add more instructions, click the `New` button to create a new instruction.
### Response Source: AI Model
If you are using the AI Model as the response source, you can add instructions directly from the [AI Response block](/chatbot/builder/blocks/ai/ai-response).
1. Click the AI Response block on the canvas to open the block editor.
2. Under the `Instructions` section, you can add all your instructions. You can add multiple instructions in the same field, separated by a new line.
4. To add more instructions, click the `New` button to create a new instruction.
### Response Source: AI Model
If you are using the AI Model as the response source, you can add instructions directly from the [AI Response block](/chatbot/builder/blocks/ai/ai-response).
1. Click the AI Response block on the canvas to open the block editor.
2. Under the `Instructions` section, you can add all your instructions. You can add multiple instructions in the same field, separated by a new line.
 ---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/api-reference/v2/intro.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# API Introduction
> The Chatling API allows you to manage your chatbots programmatically.
Integrate Chatling into your application or interact with your chatbots programmatically using our API.
This documentation guides you through creating your API key, authenticating requests, and sending requests to the API.
## Generate your API key
To send requests to the API, you must include your API key. Here's how to create it:
1. Go to your Chatling account and open the Project Settings.
2. Click the API Keys tab.
3. Press the `New API key` button.
4. Enter a name for the key and press `Generate key`.
5. Copy the newly created key. For security purposes, the API key will be displayed once only. Note it down and store it in a secure place.
If you forget your API key, you must delete it and generate a new one.
## Authentication
Your API key acts as the Bearer token and must be supplied in the `Authorization` header of every request.
```
Authorization: Bearer
```
## Retrieving the chatbot ID
Some endpoints require that you pass a chatbot ID as the path parameter. Here's a couple of ways to retrieve it:
* **Recommended method**: Using the `List chatbots` endpoint, you can fetch all the chatbots along with their IDs.
* Open the chatbot's settings in your account and you will find its ID listed there.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/introduction.md
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/introduction.md
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/intents/introduction.md
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/introduction.md
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/ai-agent/introduction.md
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/ai-agent/actions/introduction.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# AI Actions
Actions unlock the true power of AI Agents. Instead of only generating replies, the agent can actively carry out tasks during a conversation. This might involve saving details of potential leads, interacting with external systems to fetch or store data, creating support tickets, and more.
By using actions, you give your agent the power to handle practical steps on its own. This transforms the chatbot experience from a simple Q\&A into an interactive assistant that can streamline processes, save time, and improve outcomes for both your team and your users.
## Available Actions
* **[Lead Form](/ai-agent/actions/lead-form)**: displays a form to collect the user's details and save them as a contact.
* **[Buttons](/ai-agent/actions/buttons)**: displays a set of buttons in the chat, such as URL buttons to open a webpage or text buttons to send preset replies that keep the flow moving.
* **[HTTP Request](/ai-agent/actions/http-request)**: sends a request to an external API to fetch or store data, or perform an action. This allows you to connect your agent to external tools and services.
* **[Cal.com Booking Widget](/ai-agent/actions/cal-booking)**: Lets users book appointments directly within the chat.
* **[Send Email](/ai-agent/actions/send-email)**: sends a custom email to any recipient.
## How to create an action
1. Go to your AI agent's dashboard.
2. Click on the `Actions` menu from the sidebar.
3. Click the `New` button.
4. Select the action you want to create.
5. Configure the action according to your needs.
6. Click the `Create action` button.
## Tutorials
1. [Fetch and Email Order Confirmation](/ai-agent/actions/tutorials/fetch-and-email-order-confirmation)
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/team-members/invite.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Invite Team Members
> Learn about the different roles and permissions that can be assigned to team members in a project.
You can invite team members to your project if you are an Owner or Admin. Here's how:
1. From the Project menu, go to **Members**.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/api-reference/v2/intro.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# API Introduction
> The Chatling API allows you to manage your chatbots programmatically.
Integrate Chatling into your application or interact with your chatbots programmatically using our API.
This documentation guides you through creating your API key, authenticating requests, and sending requests to the API.
## Generate your API key
To send requests to the API, you must include your API key. Here's how to create it:
1. Go to your Chatling account and open the Project Settings.
2. Click the API Keys tab.
3. Press the `New API key` button.
4. Enter a name for the key and press `Generate key`.
5. Copy the newly created key. For security purposes, the API key will be displayed once only. Note it down and store it in a secure place.
If you forget your API key, you must delete it and generate a new one.
## Authentication
Your API key acts as the Bearer token and must be supplied in the `Authorization` header of every request.
```
Authorization: Bearer
```
## Retrieving the chatbot ID
Some endpoints require that you pass a chatbot ID as the path parameter. Here's a couple of ways to retrieve it:
* **Recommended method**: Using the `List chatbots` endpoint, you can fetch all the chatbots along with their IDs.
* Open the chatbot's settings in your account and you will find its ID listed there.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/introduction.md
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/introduction.md
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/intents/introduction.md
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/introduction.md
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/ai-agent/introduction.md
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/ai-agent/actions/introduction.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# AI Actions
Actions unlock the true power of AI Agents. Instead of only generating replies, the agent can actively carry out tasks during a conversation. This might involve saving details of potential leads, interacting with external systems to fetch or store data, creating support tickets, and more.
By using actions, you give your agent the power to handle practical steps on its own. This transforms the chatbot experience from a simple Q\&A into an interactive assistant that can streamline processes, save time, and improve outcomes for both your team and your users.
## Available Actions
* **[Lead Form](/ai-agent/actions/lead-form)**: displays a form to collect the user's details and save them as a contact.
* **[Buttons](/ai-agent/actions/buttons)**: displays a set of buttons in the chat, such as URL buttons to open a webpage or text buttons to send preset replies that keep the flow moving.
* **[HTTP Request](/ai-agent/actions/http-request)**: sends a request to an external API to fetch or store data, or perform an action. This allows you to connect your agent to external tools and services.
* **[Cal.com Booking Widget](/ai-agent/actions/cal-booking)**: Lets users book appointments directly within the chat.
* **[Send Email](/ai-agent/actions/send-email)**: sends a custom email to any recipient.
## How to create an action
1. Go to your AI agent's dashboard.
2. Click on the `Actions` menu from the sidebar.
3. Click the `New` button.
4. Select the action you want to create.
5. Configure the action according to your needs.
6. Click the `Create action` button.
## Tutorials
1. [Fetch and Email Order Confirmation](/ai-agent/actions/tutorials/fetch-and-email-order-confirmation)
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/team-members/invite.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Invite Team Members
> Learn about the different roles and permissions that can be assigned to team members in a project.
You can invite team members to your project if you are an Owner or Admin. Here's how:
1. From the Project menu, go to **Members**.
 2. Click the **Invite** button.
2. Click the **Invite** button.
 3. Enter the email address of the member you want to invite and select one or more roles to assign to them.
3. Enter the email address of the member you want to invite and select one or more roles to assign to them.
 4. Click **Send invite**.
The user will receive an email invitation to join the project. Once they accept the invitation, they will be added to the project with the assigned roles.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/api-reference/v2/usage/knowledge-base.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Knowledge Base
> Get the knowledge base usage for the project.
## Response
The status of the request. Will be `success` if the request was successful, otherwise `error`.
Total number of characters used in the knowledge base.
The maximum number of characters allowed for the project.
```json Response theme={null}
{
"status": "success",
"data": {
"used": 1500000,
"max": 20000000
}
}
```
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/web-widget/language.md
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/blocks/condition/language.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Language
> Learn how to use the Language condition block in Chatling
The Language condition block is used to define flows based on the user's browser language. This can be useful for creating multilingual bots that respond in the user's preferred language.
Let's say you want to create a bot that supports English, Spanish, and French languages. You can use the Language condition block to define different responses or actions based on the user's preferred language setting in their browser.
Below is an example of such a flow. The Else path is a fallback for users whose language is not supported by the bot. In this case, it falls back to the English language.
4. Click **Send invite**.
The user will receive an email invitation to join the project. Once they accept the invitation, they will be added to the project with the assigned roles.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/api-reference/v2/usage/knowledge-base.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Knowledge Base
> Get the knowledge base usage for the project.
## Response
The status of the request. Will be `success` if the request was successful, otherwise `error`.
Total number of characters used in the knowledge base.
The maximum number of characters allowed for the project.
```json Response theme={null}
{
"status": "success",
"data": {
"used": 1500000,
"max": 20000000
}
}
```
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/web-widget/language.md
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/blocks/condition/language.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Language
> Learn how to use the Language condition block in Chatling
The Language condition block is used to define flows based on the user's browser language. This can be useful for creating multilingual bots that respond in the user's preferred language.
Let's say you want to create a bot that supports English, Spanish, and French languages. You can use the Language condition block to define different responses or actions based on the user's preferred language setting in their browser.
Below is an example of such a flow. The Else path is a fallback for users whose language is not supported by the bot. In this case, it falls back to the English language.
 ---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/ai-agent/actions/lead-form.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Lead Form
Collect qualified leads right inside the conversation. The Lead Form action lets your AI Agent present a form in chat, collect user's information, and save them as a contact.
Any contacts saved by the AI agent will be displayed in the `Contacts` page in your dashboard.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/ai-agent/actions/lead-form.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Lead Form
Collect qualified leads right inside the conversation. The Lead Form action lets your AI Agent present a form in chat, collect user's information, and save them as a contact.
Any contacts saved by the AI agent will be displayed in the `Contacts` page in your dashboard.
 ## Configuration
Below are the configuration options for the Lead Form action:
### `Mandatory`
Determines whether the form submission is mandatory. When enabled, the user will be required to submit the form before they can continue.
If the option is disabled, an "X" button will be displayed in the form to allow the user to dismiss the form.
## Configuration
Below are the configuration options for the Lead Form action:
### `Mandatory`
Determines whether the form submission is mandatory. When enabled, the user will be required to submit the form before they can continue.
If the option is disabled, an "X" button will be displayed in the form to allow the user to dismiss the form.
 ### `Fields`
Add and configure the fields you want to include in the form. You can add multiple fields and specify whether they must be required.
### `Fields`
Add and configure the fields you want to include in the form. You can add multiple fields and specify whether they must be required.
 To reorder, grab the drag handle on the left of a field and move it up or down.
To reorder, grab the drag handle on the left of a field and move it up or down.
 ### `When to Use`
A detailed description of when the AI agent should use this action.
### `When to Use`
A detailed description of when the AI agent should use this action.
 ### `Customize Text`
You can customize the text to be displayed for the submit button and success message.
The success message is the message that is displayed after the form is submitted. It is optional and can be disabled.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/api-reference/v2/ai-kb/list-ai-languages.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# List AI languages
> Get a list of all the supported AI languages.
## Request parameters
### Path
The chatbot ID.
### Query
The page number for pagination.
## Response
The status of the request. Will be `success` if the request was successful, otherwise `error`.
The current page number.
The last page number.
The number of items per page.
The unique identifier of the language.
The name of the language.
```json Response theme={null}
{
"status": "success",
"data": {
"pages": {
"current_page": 1,
"last_page": 6,
"per_page": 15
},
"languages": [
{
"id": 1,
"name": "Auto"
},
{
"id": 2,
"name": "English"
},
{
"id": 3,
"name": "Albanian"
},
{
"id": 4,
"name": "Arabic"
},
{
"id": 5,
"name": "Armenian"
},
{
"id": 7,
"name": "Azerbaijani"
},
{
"id": 9,
"name": "Basque"
},
{
"id": 10,
"name": "Belarusian"
},
{
"id": 11,
"name": "Bengali"
},
{
"id": 12,
"name": "Bhojpuri"
},
{
"id": 13,
"name": "Bosnian"
},
{
"id": 15,
"name": "Bulgarian"
},
{
"id": 17,
"name": "Catalan"
},
{
"id": 19,
"name": "Chinese (Simplified)"
},
{
"id": 20,
"name": "Croatian"
}
]
}
}
```
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/api-reference/v2/ai-kb/list-ai-models.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# List AI models
> Get a list of all the supported AI models.
## Request parameters
### Path
The chatbot ID.
### Query
The page number for pagination.
## Response
The status of the request. Will be `success` if the request was successful, otherwise `error`.
The current page number.
The last page number.
The number of items per page.
The unique identifier of the AI model.
The name of the model.
The number of AI credits consumed for each response generated by the model.
The minimum and maximum temperature values for the model.
```json Response theme={null}
{
"status": "success",
"data": {
"pages": {
"current_page": 1,
"last_page": 1,
"per_page": 15
},
"models": [
{
"id": 1,
"name": "GPT-3.5 Turbo",
"credits": 1,
"temperature": {
"min": 0,
"max": 1
}
},
{
"id": 2,
"name": "GPT-4",
"credits": 10,
"temperature": {
"min": 0,
"max": 1
}
},
{
"id": 3,
"name": "Claude 3 Opus",
"credits": 18,
"temperature": {
"min": 0,
"max": 1
}
},
{
"id": 4,
"name": "Claude 3 Sonnet",
"credits": 4,
"temperature": {
"min": 0,
"max": 1
}
},
{
"id": 5,
"name": "Claude 3 Haiku",
"credits": 1,
"temperature": {
"min": 0,
"max": 1
}
},
{
"id": 6,
"name": "GPT-4o",
"credits": 5,
"temperature": {
"min": 0,
"max": 1
}
},
{
"id": 7,
"name": "Claude 3.5 Sonnet",
"credits": 4,
"temperature": {
"min": 0,
"max": 1
}
},
]
}
}
```
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/api-reference/v2/chatbots/list-chatbot-templates.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# List chatbot templates
> Get a list of all the available chatbot templates. Can be used to create a new chatbot.
## Request parameters
### Query
The page number for pagination.
## Response
The status of the request. Will be `success` if the request was successful, otherwise `error`.
The current page number.
The last page number.
The number of items per page.
The unique identifier of the template.
The name of the template.
The description of the template.
```json theme={null}
{
"status": "success",
"data": {
"pages": {
"current_page": 1,
"last_page": 1,
"per_page": 25
},
"templates": [
{
"id": 1,
"name": "AI Chatbot",
"description": "Uses AI to automatically respond to customers by leveraging your data, such as your website content, documents, and more."
},
{
"id": 2,
"name": "Basic Lead Generation",
"description": "Engage with prospective leads and capture their contact information."
}
]
}
}
```
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/api-reference/v2/chatbots/list-chatbots.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# List chatbots
> Get a list of all the chatbots in the project.
## Request parameters
### Query
The page number for pagination.
## Response
The status of the request. Will be `success` if the request was successful, otherwise `error`.
The current page number.
The last page number.
The number of items per page.
The unique identifier of the chatbot.
The name of the chatbot.
The version of the chatbot.
The visibility of the chatbot. Can be `public` or `private`.
The date the chatbot was created.
```json Response theme={null}
{
"status": "success",
"data": {
"pages": {
"current_page": 1,
"last_page": 1,
"per_page": 25
},
"chatbots": [
{
"id": "8917794239",
"name": "My first chatbot",
"version": "2.0",
"visibility": "public",
"created_at": "2024-06-05T12:13:35:00+00:00"
}
]
}
}
```
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/api-reference/v2/contacts/list-contacts.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# List contacts
> Get a list of all the contacts and leads saved by the chatbot.
## Request parameters
### Path
The chatbot ID.
### Query
The page number for pagination.
The sort order. Possible values:
* `date_desc`: Sort by date in descending order.
* `date_asc`: Sort by date in ascending order.
## Response
The status of the request. Will be `success` if the request was successful, otherwise `error`.
The current page number.
The last page number.
The number of items per page.
The unique identifier of the contact.
The name of the contact.
The email address of the contact.
The job title of the contact.
The phone number of the contact.
The website URL of the contact.
The company name of the contact.
The date and time when the contact was created.
```json Response theme={null}
{
"status": "success",
"data": {
"pages": {
"current_page": 1,
"last_page": 1,
"per_page": 25
},
"contacts": [
{
"id": "qtr89df0-112d-d197-b541-3f8674663246",
"name": "Mark Zuckerberg",
"email": "mark@meta.com",
"job_title": "CEO",
"phone": "555-555-5555",
"website": "https://meta.com",
"company": "Meta Inc.",
"created_at": "2024-06-08T13:38:33+00:00"
}
]
}
}
```
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/api-reference/v2/conversations/list-conversation-messages.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# List conversation messages
> Get a list of all the messages for a conversation
## Request parameters
### Path
The chatbot ID.
The conversation ID.
### Query
The page number for pagination.
The sort order. Possible values:
* `date_desc`: Sort by date in descending order.
* `date_asc`: Sort by date in ascending order.
## Response
The status of the request. Will be `success` if the request was successful, otherwise `error`.
The current page number.
The last page number.
The number of items per page.
The text content of the message.
The role of the sender of the message (bot, user, or system).
Whether the message is AI generated and uses the knowledge base.
The data of the message. Varies depending on the message type.
The date and time when the message was created.
```json Response theme={null}
{
"status": "success",
"data": {
"pages": {
"current_page": 1,
"last_page": 1,
"per_page": 15
},
"messages": [
{
"text": "System variables are predefined variables that contain system information or can be used to perform specific actions. These variables are automatically created by the Builder.",
"role": "bot",
"is_ai_kb_response": true,
"data": {
"helpful_value": null,
"sources": [
{
"type": "webpage",
"title": "Types of variables - Chatling Documentation",
"url": "https://docs.chatling.ai/builder/variables/variable-types"
},
{
"type": "webpage",
"title": "Sidebar - Chatling Documentation",
"url": "https://docs.chatling.ai/builder/sidebar"
},
{
"type": "webpage",
"title": "What are variables? - Chatling Documentation",
"url": "https://docs.chatling.ai/builder/variables/what-are-variables"
}
]
},
"created_at": "2024-06-17T16:09:52+00:00"
},
{
"text": "What are system variables",
"role": "user",
"created_at": "2024-06-17T16:09:45+00:00"
},
{
"text": "**Hello! How can I assist you today?**\n\nIf you have any questions related to our chatbot or services, please feel free to ask. I'm here to help!",
"role": "bot",
"is_ai_kb_response": true,
"data": {
"helpful_value": null,
"sources": []
},
"created_at": "2024-06-14T15:45:39+00:00"
},
{
"text": "Hello!",
"role": "user",
"created_at": "2024-06-14T15:45:34+00:00"
}
]
}
}
```
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/api-reference/v2/conversations/list-conversations.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# List conversations
> Get a list of all the chatbot's conversations with users.
## Request parameters
### Path
The chatbot ID.
### Query
The page number for pagination.
The sort order. Possible values:
* `date_desc`: Sort by date in descending order.
* `date_asc`: Sort by date in ascending order.
## Response
The status of the request. Will be `success` if the request was successful, otherwise `error`.
The current page number.
The last page number.
The number of items per page.
The unique identifier of the conversation.
The unique identifier of the contact associated with the conversation.
Whether the conversation is archived (by the admin).
Whether the conversation is marked as important.
The date and time when the conversation was created.
List of the most recent 20 messages in the conversation.
The unique identifier of the message.
The text content of the message.
The role of the sender of the message (bot, user, or system).
Whether the message is generated by the AI using the knowledge base.
The data of the message. Varies depending on the message type.
(AI response) Whether the AI's response was marked as helpful by the user. Possible values are `1` for helpful, `0` for not helpful, and `null` for not rated.
(AI response) The sources used by the AI to generate the response.
The date and time when the message was created.
```json Response theme={null}
{
"status": "success",
"data": {
"pages": {
"current_page": 1,
"last_page": 11,
"per_page": 5
},
"conversations": [
{
"id": "8977617953",
"contact_id": "qtr89df0-112d-d197-b541-3f8674663246",
"archived": 0,
"important": 1,
"created_at": "2024-06-14T15:45:34+00:00",
"messages": [
{
"text": "System variables are predefined variables that contain system information or can be used to perform specific actions. These variables are automatically created by the Builder.",
"role": "bot",
"is_ai_kb_response": true,
"data": {
"helpful_value": null,
"sources": [
{
"type": "webpage",
"title": "Types of variables - Chatling Documentation",
"url": "https://docs.chatling.ai/builder/variables/variable-types"
},
{
"type": "webpage",
"title": "Sidebar - Chatling Documentation",
"url": "https://docs.chatling.ai/builder/sidebar"
},
{
"type": "webpage",
"title": "What are variables? - Chatling Documentation",
"url": "https://docs.chatling.ai/builder/variables/what-are-variables"
}
]
},
"created_at": "2024-06-17T16:09:52+00:00"
},
{
"text": "What are system variables",
"role": "user",
"created_at": "2024-06-17T16:09:45+00:00"
},
{
"text": "**Hello! How can I assist you today?**\n\nIf you have any questions related to our chatbot or services, please feel free to ask. I'm here to help!",
"role": "bot",
"is_ai_kb_response": true,
"data": {
"helpful_value": null,
"sources": []
},
"created_at": "2024-06-14T15:45:39+00:00"
},
{
"text": "Hello!",
"role": "user",
"created_at": "2024-06-14T15:45:34+00:00"
}
]
}
]
}
}
```
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/api-reference/v2/knowledge-base/list-data-sources.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# List data sources
> Get a list of the data sources added to the knowledge base.
## Request parameters
### Path
The chatbot ID.
### Query
The page number for pagination.
The sort order. Possible values:
* `date_desc`: Sort by date in descending order.
* `date_asc`: Sort by date in ascending order.
Filter by the type of the data source. Possible values are `link`, `text`, `faq`, `document`, and `zoho`.
Leave blank to get all types of data sources.
## Response
The status of the request. Will be `success` if the request was successful, otherwise `error`.
The current page number.
The last page number.
The number of items per page.
The unique identifier of the data source.
The type of the data source.
The processing status of the data source. Possible values are `pending`, `processing`, `processed`, `error`.
The number of characters used by the data source.
Whether the data source is queued for resync.
Additional data based on the type of the data source.
The date and time when the data source was created.
```json Response theme={null}
{
{
"status": "success",
"data": {
"pages": {
"current_page": 1,
"last_page": 3,
"per_page": 25
},
"sources": [
{
"id": "321e979b-a174-89fc-25de-f0b31dbd659f",
"type": "link",
"status": "processed",
"characters": 6232,
"resync_queued": false,
"data": {
"url": "https://chatling.ai",
"page_title": "No-Code AI Chatbot for Your Website | Chatling"
},
"created_at": "2024-06-15T12:23:41"
},
]
}
}
```
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/api-reference/v2/members/list-members.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# List members
> Get a list of all the members in the project.
## Request parameters
### Query
The page number for pagination.
## Response
The status of the request. Will be `success` if the request was successful, otherwise `error`.
The current page number.
The last page number.
The number of items per page.
The email address of the member.
The status of the member (`Active` or `Pending`).
The roles of the member in the project.
```json Response theme={null}
{
"status": "success",
"data": {
"pages": {
"current_page": 1,
"last_page": 1,
"per_page": 15
},
"members": [
{
"email": "elon@tesla.com",
"status": "Active",
"roles": [
"Owner"
]
},
{
"email": "mark@meta.com",
"status": "Active",
"roles": [
"Admin"
]
},
{
"email": "sundar@google.com",
"status": "Pending",
"roles": [
"Editor",
"Billing"
]
}
]
}
}
```
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/api-reference/v2/project/list-settings.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# List settings
> Retrieve the settings of the project.
## Response
The status of the request. Will be `success` if the request was successful, otherwise `error`.
The unique identifier of the project.
The name of the project.
```json Response theme={null}
{
"status": "success",
"data": {
"project_id": "8917794239",
"name": "My first project"
}
}
```
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/intents/manage.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Manage intents
> A guide on how to create and manage your chatbot's intents
## Accessing the Intent page
The Intents page is located inside your chatbot's builder. To access it:
1. Open the Builder.
2. Click on the `Intents` button in the top left.
### `Customize Text`
You can customize the text to be displayed for the submit button and success message.
The success message is the message that is displayed after the form is submitted. It is optional and can be disabled.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/api-reference/v2/ai-kb/list-ai-languages.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# List AI languages
> Get a list of all the supported AI languages.
## Request parameters
### Path
The chatbot ID.
### Query
The page number for pagination.
## Response
The status of the request. Will be `success` if the request was successful, otherwise `error`.
The current page number.
The last page number.
The number of items per page.
The unique identifier of the language.
The name of the language.
```json Response theme={null}
{
"status": "success",
"data": {
"pages": {
"current_page": 1,
"last_page": 6,
"per_page": 15
},
"languages": [
{
"id": 1,
"name": "Auto"
},
{
"id": 2,
"name": "English"
},
{
"id": 3,
"name": "Albanian"
},
{
"id": 4,
"name": "Arabic"
},
{
"id": 5,
"name": "Armenian"
},
{
"id": 7,
"name": "Azerbaijani"
},
{
"id": 9,
"name": "Basque"
},
{
"id": 10,
"name": "Belarusian"
},
{
"id": 11,
"name": "Bengali"
},
{
"id": 12,
"name": "Bhojpuri"
},
{
"id": 13,
"name": "Bosnian"
},
{
"id": 15,
"name": "Bulgarian"
},
{
"id": 17,
"name": "Catalan"
},
{
"id": 19,
"name": "Chinese (Simplified)"
},
{
"id": 20,
"name": "Croatian"
}
]
}
}
```
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/api-reference/v2/ai-kb/list-ai-models.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# List AI models
> Get a list of all the supported AI models.
## Request parameters
### Path
The chatbot ID.
### Query
The page number for pagination.
## Response
The status of the request. Will be `success` if the request was successful, otherwise `error`.
The current page number.
The last page number.
The number of items per page.
The unique identifier of the AI model.
The name of the model.
The number of AI credits consumed for each response generated by the model.
The minimum and maximum temperature values for the model.
```json Response theme={null}
{
"status": "success",
"data": {
"pages": {
"current_page": 1,
"last_page": 1,
"per_page": 15
},
"models": [
{
"id": 1,
"name": "GPT-3.5 Turbo",
"credits": 1,
"temperature": {
"min": 0,
"max": 1
}
},
{
"id": 2,
"name": "GPT-4",
"credits": 10,
"temperature": {
"min": 0,
"max": 1
}
},
{
"id": 3,
"name": "Claude 3 Opus",
"credits": 18,
"temperature": {
"min": 0,
"max": 1
}
},
{
"id": 4,
"name": "Claude 3 Sonnet",
"credits": 4,
"temperature": {
"min": 0,
"max": 1
}
},
{
"id": 5,
"name": "Claude 3 Haiku",
"credits": 1,
"temperature": {
"min": 0,
"max": 1
}
},
{
"id": 6,
"name": "GPT-4o",
"credits": 5,
"temperature": {
"min": 0,
"max": 1
}
},
{
"id": 7,
"name": "Claude 3.5 Sonnet",
"credits": 4,
"temperature": {
"min": 0,
"max": 1
}
},
]
}
}
```
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/api-reference/v2/chatbots/list-chatbot-templates.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# List chatbot templates
> Get a list of all the available chatbot templates. Can be used to create a new chatbot.
## Request parameters
### Query
The page number for pagination.
## Response
The status of the request. Will be `success` if the request was successful, otherwise `error`.
The current page number.
The last page number.
The number of items per page.
The unique identifier of the template.
The name of the template.
The description of the template.
```json theme={null}
{
"status": "success",
"data": {
"pages": {
"current_page": 1,
"last_page": 1,
"per_page": 25
},
"templates": [
{
"id": 1,
"name": "AI Chatbot",
"description": "Uses AI to automatically respond to customers by leveraging your data, such as your website content, documents, and more."
},
{
"id": 2,
"name": "Basic Lead Generation",
"description": "Engage with prospective leads and capture their contact information."
}
]
}
}
```
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/api-reference/v2/chatbots/list-chatbots.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# List chatbots
> Get a list of all the chatbots in the project.
## Request parameters
### Query
The page number for pagination.
## Response
The status of the request. Will be `success` if the request was successful, otherwise `error`.
The current page number.
The last page number.
The number of items per page.
The unique identifier of the chatbot.
The name of the chatbot.
The version of the chatbot.
The visibility of the chatbot. Can be `public` or `private`.
The date the chatbot was created.
```json Response theme={null}
{
"status": "success",
"data": {
"pages": {
"current_page": 1,
"last_page": 1,
"per_page": 25
},
"chatbots": [
{
"id": "8917794239",
"name": "My first chatbot",
"version": "2.0",
"visibility": "public",
"created_at": "2024-06-05T12:13:35:00+00:00"
}
]
}
}
```
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/api-reference/v2/contacts/list-contacts.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# List contacts
> Get a list of all the contacts and leads saved by the chatbot.
## Request parameters
### Path
The chatbot ID.
### Query
The page number for pagination.
The sort order. Possible values:
* `date_desc`: Sort by date in descending order.
* `date_asc`: Sort by date in ascending order.
## Response
The status of the request. Will be `success` if the request was successful, otherwise `error`.
The current page number.
The last page number.
The number of items per page.
The unique identifier of the contact.
The name of the contact.
The email address of the contact.
The job title of the contact.
The phone number of the contact.
The website URL of the contact.
The company name of the contact.
The date and time when the contact was created.
```json Response theme={null}
{
"status": "success",
"data": {
"pages": {
"current_page": 1,
"last_page": 1,
"per_page": 25
},
"contacts": [
{
"id": "qtr89df0-112d-d197-b541-3f8674663246",
"name": "Mark Zuckerberg",
"email": "mark@meta.com",
"job_title": "CEO",
"phone": "555-555-5555",
"website": "https://meta.com",
"company": "Meta Inc.",
"created_at": "2024-06-08T13:38:33+00:00"
}
]
}
}
```
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/api-reference/v2/conversations/list-conversation-messages.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# List conversation messages
> Get a list of all the messages for a conversation
## Request parameters
### Path
The chatbot ID.
The conversation ID.
### Query
The page number for pagination.
The sort order. Possible values:
* `date_desc`: Sort by date in descending order.
* `date_asc`: Sort by date in ascending order.
## Response
The status of the request. Will be `success` if the request was successful, otherwise `error`.
The current page number.
The last page number.
The number of items per page.
The text content of the message.
The role of the sender of the message (bot, user, or system).
Whether the message is AI generated and uses the knowledge base.
The data of the message. Varies depending on the message type.
The date and time when the message was created.
```json Response theme={null}
{
"status": "success",
"data": {
"pages": {
"current_page": 1,
"last_page": 1,
"per_page": 15
},
"messages": [
{
"text": "System variables are predefined variables that contain system information or can be used to perform specific actions. These variables are automatically created by the Builder.",
"role": "bot",
"is_ai_kb_response": true,
"data": {
"helpful_value": null,
"sources": [
{
"type": "webpage",
"title": "Types of variables - Chatling Documentation",
"url": "https://docs.chatling.ai/builder/variables/variable-types"
},
{
"type": "webpage",
"title": "Sidebar - Chatling Documentation",
"url": "https://docs.chatling.ai/builder/sidebar"
},
{
"type": "webpage",
"title": "What are variables? - Chatling Documentation",
"url": "https://docs.chatling.ai/builder/variables/what-are-variables"
}
]
},
"created_at": "2024-06-17T16:09:52+00:00"
},
{
"text": "What are system variables",
"role": "user",
"created_at": "2024-06-17T16:09:45+00:00"
},
{
"text": "**Hello! How can I assist you today?**\n\nIf you have any questions related to our chatbot or services, please feel free to ask. I'm here to help!",
"role": "bot",
"is_ai_kb_response": true,
"data": {
"helpful_value": null,
"sources": []
},
"created_at": "2024-06-14T15:45:39+00:00"
},
{
"text": "Hello!",
"role": "user",
"created_at": "2024-06-14T15:45:34+00:00"
}
]
}
}
```
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/api-reference/v2/conversations/list-conversations.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# List conversations
> Get a list of all the chatbot's conversations with users.
## Request parameters
### Path
The chatbot ID.
### Query
The page number for pagination.
The sort order. Possible values:
* `date_desc`: Sort by date in descending order.
* `date_asc`: Sort by date in ascending order.
## Response
The status of the request. Will be `success` if the request was successful, otherwise `error`.
The current page number.
The last page number.
The number of items per page.
The unique identifier of the conversation.
The unique identifier of the contact associated with the conversation.
Whether the conversation is archived (by the admin).
Whether the conversation is marked as important.
The date and time when the conversation was created.
List of the most recent 20 messages in the conversation.
The unique identifier of the message.
The text content of the message.
The role of the sender of the message (bot, user, or system).
Whether the message is generated by the AI using the knowledge base.
The data of the message. Varies depending on the message type.
(AI response) Whether the AI's response was marked as helpful by the user. Possible values are `1` for helpful, `0` for not helpful, and `null` for not rated.
(AI response) The sources used by the AI to generate the response.
The date and time when the message was created.
```json Response theme={null}
{
"status": "success",
"data": {
"pages": {
"current_page": 1,
"last_page": 11,
"per_page": 5
},
"conversations": [
{
"id": "8977617953",
"contact_id": "qtr89df0-112d-d197-b541-3f8674663246",
"archived": 0,
"important": 1,
"created_at": "2024-06-14T15:45:34+00:00",
"messages": [
{
"text": "System variables are predefined variables that contain system information or can be used to perform specific actions. These variables are automatically created by the Builder.",
"role": "bot",
"is_ai_kb_response": true,
"data": {
"helpful_value": null,
"sources": [
{
"type": "webpage",
"title": "Types of variables - Chatling Documentation",
"url": "https://docs.chatling.ai/builder/variables/variable-types"
},
{
"type": "webpage",
"title": "Sidebar - Chatling Documentation",
"url": "https://docs.chatling.ai/builder/sidebar"
},
{
"type": "webpage",
"title": "What are variables? - Chatling Documentation",
"url": "https://docs.chatling.ai/builder/variables/what-are-variables"
}
]
},
"created_at": "2024-06-17T16:09:52+00:00"
},
{
"text": "What are system variables",
"role": "user",
"created_at": "2024-06-17T16:09:45+00:00"
},
{
"text": "**Hello! How can I assist you today?**\n\nIf you have any questions related to our chatbot or services, please feel free to ask. I'm here to help!",
"role": "bot",
"is_ai_kb_response": true,
"data": {
"helpful_value": null,
"sources": []
},
"created_at": "2024-06-14T15:45:39+00:00"
},
{
"text": "Hello!",
"role": "user",
"created_at": "2024-06-14T15:45:34+00:00"
}
]
}
]
}
}
```
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/api-reference/v2/knowledge-base/list-data-sources.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# List data sources
> Get a list of the data sources added to the knowledge base.
## Request parameters
### Path
The chatbot ID.
### Query
The page number for pagination.
The sort order. Possible values:
* `date_desc`: Sort by date in descending order.
* `date_asc`: Sort by date in ascending order.
Filter by the type of the data source. Possible values are `link`, `text`, `faq`, `document`, and `zoho`.
Leave blank to get all types of data sources.
## Response
The status of the request. Will be `success` if the request was successful, otherwise `error`.
The current page number.
The last page number.
The number of items per page.
The unique identifier of the data source.
The type of the data source.
The processing status of the data source. Possible values are `pending`, `processing`, `processed`, `error`.
The number of characters used by the data source.
Whether the data source is queued for resync.
Additional data based on the type of the data source.
The date and time when the data source was created.
```json Response theme={null}
{
{
"status": "success",
"data": {
"pages": {
"current_page": 1,
"last_page": 3,
"per_page": 25
},
"sources": [
{
"id": "321e979b-a174-89fc-25de-f0b31dbd659f",
"type": "link",
"status": "processed",
"characters": 6232,
"resync_queued": false,
"data": {
"url": "https://chatling.ai",
"page_title": "No-Code AI Chatbot for Your Website | Chatling"
},
"created_at": "2024-06-15T12:23:41"
},
]
}
}
```
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/api-reference/v2/members/list-members.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# List members
> Get a list of all the members in the project.
## Request parameters
### Query
The page number for pagination.
## Response
The status of the request. Will be `success` if the request was successful, otherwise `error`.
The current page number.
The last page number.
The number of items per page.
The email address of the member.
The status of the member (`Active` or `Pending`).
The roles of the member in the project.
```json Response theme={null}
{
"status": "success",
"data": {
"pages": {
"current_page": 1,
"last_page": 1,
"per_page": 15
},
"members": [
{
"email": "elon@tesla.com",
"status": "Active",
"roles": [
"Owner"
]
},
{
"email": "mark@meta.com",
"status": "Active",
"roles": [
"Admin"
]
},
{
"email": "sundar@google.com",
"status": "Pending",
"roles": [
"Editor",
"Billing"
]
}
]
}
}
```
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/api-reference/v2/project/list-settings.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# List settings
> Retrieve the settings of the project.
## Response
The status of the request. Will be `success` if the request was successful, otherwise `error`.
The unique identifier of the project.
The name of the project.
```json Response theme={null}
{
"status": "success",
"data": {
"project_id": "8917794239",
"name": "My first project"
}
}
```
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/intents/manage.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Manage intents
> A guide on how to create and manage your chatbot's intents
## Accessing the Intent page
The Intents page is located inside your chatbot's builder. To access it:
1. Open the Builder.
2. Click on the `Intents` button in the top left.
 ## Creating an intent
1. Open the Intents page.
2. Click the `New` button.
## Creating an intent
1. Open the Intents page.
2. Click the `New` button.
 3. Enter the details for the intent.
* **Name**: A clear, descriptive identifier (e.g., "Order Tracking", "Submit ticket").
* **Description**: Explains the user's goal or purpose this intent represents.
* **Sample phrases**: Examples of user messages that should trigger this intent. This helps the chatbot understand and match the intent.
3. Enter the details for the intent.
* **Name**: A clear, descriptive identifier (e.g., "Order Tracking", "Submit ticket").
* **Description**: Explains the user's goal or purpose this intent represents.
* **Sample phrases**: Examples of user messages that should trigger this intent. This helps the chatbot understand and match the intent.
 4. Click the `Create intent` button.
## Editing an intent
1. Open the Intents page to view all the existing intents.
2. Find and click on the intent you want to edit.
3. Make changes to the intent's details, such as name, description, and sample phrases.
4. Click the `Create intent` button.
## Editing an intent
1. Open the Intents page to view all the existing intents.
2. Find and click on the intent you want to edit.
3. Make changes to the intent's details, such as name, description, and sample phrases.
 4. Click the `Save` button to save your changes.
## Deleting intents
1. Open the Intents page to view all the existing intents.
2. Click the checkbox next to one or more intents you want to delete.
4. Click the `Save` button to save your changes.
## Deleting intents
1. Open the Intents page to view all the existing intents.
2. Click the checkbox next to one or more intents you want to delete.
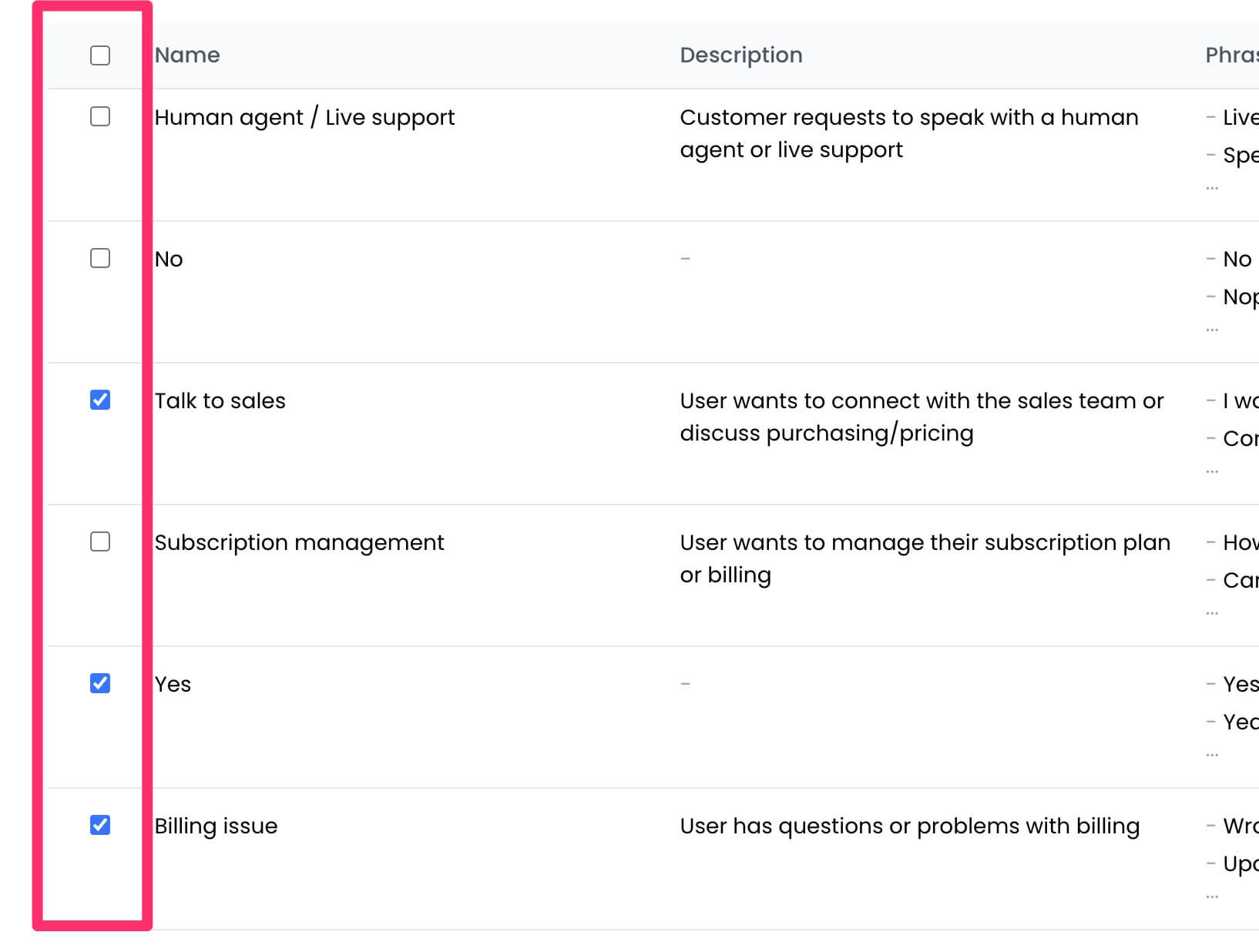 3. Click the `Delete` button in the top left.
3. Click the `Delete` button in the top left.
 ---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/missing-topics.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Got other questions?
If there are any topics you'd like to see covered in the documentation, please let us know! We're always looking to improve our documentation and make it as helpful as possible for our users.
Please reach out to us at [support@chatling.ai](mailto:support@chatling.ai) with your suggestions and any questions you have.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/blocks/inputs/number.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Number Block
> Learn about the Number input block and how to set it up in the Builder.
The Number block is used to collect numerical input from users. You can use this block to ask users for numbers, such as quantities, prices, or percentages.
## Configuration
The Number block has the following configuration options:
* **Store answer in variable**: The variable where the user's input will be stored.
* **Input required**: Whether the user's input is mandatory. If disabled, a Skip button will appear, allowing users to skip the input.
* **Date type**: The type of number the block will accept. You can choose from the following options:
* \*\*Number (Integer/Decimal): Accepts any number, including whole numbers and decimals.
* **Integer**: Accepts only whole numbers.
* **Min**: The minimum value the user can input.
* **Max**: The maximum value the user can input.
* **[Quick replies](/chatbot/builder/block-options/quick-replies)**
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/missing-topics.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Got other questions?
If there are any topics you'd like to see covered in the documentation, please let us know! We're always looking to improve our documentation and make it as helpful as possible for our users.
Please reach out to us at [support@chatling.ai](mailto:support@chatling.ai) with your suggestions and any questions you have.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/blocks/inputs/number.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Number Block
> Learn about the Number input block and how to set it up in the Builder.
The Number block is used to collect numerical input from users. You can use this block to ask users for numbers, such as quantities, prices, or percentages.
## Configuration
The Number block has the following configuration options:
* **Store answer in variable**: The variable where the user's input will be stored.
* **Input required**: Whether the user's input is mandatory. If disabled, a Skip button will appear, allowing users to skip the input.
* **Date type**: The type of number the block will accept. You can choose from the following options:
* \*\*Number (Integer/Decimal): Accepts any number, including whole numbers and decimals.
* **Integer**: Accepts only whole numbers.
* **Min**: The minimum value the user can input.
* **Max**: The maximum value the user can input.
* **[Quick replies](/chatbot/builder/block-options/quick-replies)**
 ---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/web-widget/operating-hours.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Operating hours
> Schedule the chatbot to be visible at certain times.
You can set the operating hours for your chatbot to define when it should be available to users. This is useful if you want to limit the chatbot's availability to certain times of the day or week, e.g during business hours or off-hours.
When outside of the operating hours, your chatbot will be automatically hidden, ensuring it's only live when you want it to be.
## Set operating hours
1. From your chatbot's dashboard, go to the **Settings** page.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/web-widget/operating-hours.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Operating hours
> Schedule the chatbot to be visible at certain times.
You can set the operating hours for your chatbot to define when it should be available to users. This is useful if you want to limit the chatbot's availability to certain times of the day or week, e.g during business hours or off-hours.
When outside of the operating hours, your chatbot will be automatically hidden, ensuring it's only live when you want it to be.
## Set operating hours
1. From your chatbot's dashboard, go to the **Settings** page.
 2. Click the `Visibility` tab.
2. Click the `Visibility` tab.
 3. Under the `Operating hours` section, click the `Set operating hours` button.
3. Under the `Operating hours` section, click the `Set operating hours` button.
 4. Select the days and times when the chatbot should be visible. **Note that the timezone is UTC.**
To keep the chatbot visible throughout the day, leave the start and end times empty.
4. Select the days and times when the chatbot should be visible. **Note that the timezone is UTC.**
To keep the chatbot visible throughout the day, leave the start and end times empty.
 5. Click the `Add` button to add the schedule.
6. Click the `Save` button to save the changes.
Once you define the operating hours, the chatbot will be visible during the specified times and hidden outside of these hours.
## Edit existing operating hours
To edit the operating hours, you have to delete one or more schedules that you want to edit and then add the new schedules.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/whatsapp/overview.md
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/web-widget/installation/overview.md
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/team-members/overview.md
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/knowledge-base/overview.md
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/contacts/overview.md
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/blocks/trigger/overview.md
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/blocks/overview.md
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/blocks/hubspot/overview.md
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/blocks/condition/overview.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Overview
> Learn about the condition blocks and how to use them
Condition blocks are used to create conditional logic in your bot. You can use it to check if a certain condition is met and then perform different actions based on the result.
Similar to an "if-else" statement in programming, condition blocks evaluate a condition and executes different paths based on whether the condition is true or false.
5. Click the `Add` button to add the schedule.
6. Click the `Save` button to save the changes.
Once you define the operating hours, the chatbot will be visible during the specified times and hidden outside of these hours.
## Edit existing operating hours
To edit the operating hours, you have to delete one or more schedules that you want to edit and then add the new schedules.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/whatsapp/overview.md
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/web-widget/installation/overview.md
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/team-members/overview.md
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/knowledge-base/overview.md
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/contacts/overview.md
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/blocks/trigger/overview.md
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/blocks/overview.md
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/blocks/hubspot/overview.md
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/blocks/condition/overview.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Overview
> Learn about the condition blocks and how to use them
Condition blocks are used to create conditional logic in your bot. You can use it to check if a certain condition is met and then perform different actions based on the result.
Similar to an "if-else" statement in programming, condition blocks evaluate a condition and executes different paths based on whether the condition is true or false.
 ## Types of condition blocks
There are two types of condition blocks available in Chatling:
* [**Variable**](./variable): Compares a variable with a value or another variable.
* **Language**: Checks if the user's language matches a specific language. Useful for creating multilingual bots.
## How do condition blocks work?
Condition blocks consist of two main parts:
* **Conditions**: The conditions that the block will evaluate. You can use variables, languages, comparison operators, and logical operators to create complex conditions.
* **Paths**: The paths that the block will follow based on the result of the conditions. Every condition you add will have a corresponding path that the block will follow if the condition is true.
## Types of condition blocks
There are two types of condition blocks available in Chatling:
* [**Variable**](./variable): Compares a variable with a value or another variable.
* **Language**: Checks if the user's language matches a specific language. Useful for creating multilingual bots.
## How do condition blocks work?
Condition blocks consist of two main parts:
* **Conditions**: The conditions that the block will evaluate. You can use variables, languages, comparison operators, and logical operators to create complex conditions.
* **Paths**: The paths that the block will follow based on the result of the conditions. Every condition you add will have a corresponding path that the block will follow if the condition is true.
 Here's an example of how a condition block works:
1. The block evaluates conditions in the order they are added.
2. If a condition is true, the block follows the path associated with that condition.
3. If none of the conditions are true, the block follows the "Else" path.
## The Else condition
The `Else` condition is executed if none of the other conditions are met. You can use it to define a fallback path that the block will follow if none of the other conditions are true.
## Comparison operators
Conditions support a variety of comparison operators that you can use to compare values. Here are some of the operators you can use:
* **Equals**: Checks if the variable is equal to the value.
* **Not equals**: Checks if the variable is not equal to the value.
* **Contains**: Checks if the variable contains the value.
* **Not contains**: Checks if the variable does not contain the value.
* **Greater than or equals**: Checks if the variable is greater than or equal to the value.
* **Less than**: Checks if the variable is less than the value.
* **Less than or equals**: Checks if the variable is less than or equal to the value.
* **Starts with**: Checks if the variable starts with the value.
* **Ends with**: Checks if the variable ends with the value.
* **Is empty**: Checks if the variable is empty.
* **Is not empty**: Checks if the variable is not empty.
## Group and child conditions
Conditions are grouped together to create complex logic using logical operators like "AND" and "OR". Every group contains one or more conditions that are evaluated together.
Here's an example of how a condition block works:
1. The block evaluates conditions in the order they are added.
2. If a condition is true, the block follows the path associated with that condition.
3. If none of the conditions are true, the block follows the "Else" path.
## The Else condition
The `Else` condition is executed if none of the other conditions are met. You can use it to define a fallback path that the block will follow if none of the other conditions are true.
## Comparison operators
Conditions support a variety of comparison operators that you can use to compare values. Here are some of the operators you can use:
* **Equals**: Checks if the variable is equal to the value.
* **Not equals**: Checks if the variable is not equal to the value.
* **Contains**: Checks if the variable contains the value.
* **Not contains**: Checks if the variable does not contain the value.
* **Greater than or equals**: Checks if the variable is greater than or equal to the value.
* **Less than**: Checks if the variable is less than the value.
* **Less than or equals**: Checks if the variable is less than or equal to the value.
* **Starts with**: Checks if the variable starts with the value.
* **Ends with**: Checks if the variable ends with the value.
* **Is empty**: Checks if the variable is empty.
* **Is not empty**: Checks if the variable is not empty.
## Group and child conditions
Conditions are grouped together to create complex logic using logical operators like "AND" and "OR". Every group contains one or more conditions that are evaluated together.
 Conditions within a group are evaluated together to determine if the group is true or false. You can use logical operators such as "AND" and "OR" to combine conditions within a group.
For example, you can create a group with two conditions and set it to "AND" to require both conditions to be true for the group to be true. On the other hand, you can set it to "OR" to require only one of the conditions to be true for the group to be true.
By default, condition blocks have one group with one condition. To add additional groups, click the `Add group condition` button.
## Logical operators
Logical operators are used to combine conditions within a group. You can choose from the following logical operators:
* **AND**: Requires all conditions in the group to be true for the group to be true.
* **OR**: Requires at least one condition in the group to be true for the group to be true.
- Group 1:
* Condition 1: Variable A equals 5
* Condition 2: Variable B equals 10
* Logical operator: AND
- Group 2:
* Condition 1: Variable C contains "hello"
* Condition 2: Variable D contains "world"
* Logical operator: OR
In this example, Group 1 will be true only if Variable A equals 5 and Variable B equals 10. Group 2 will be true if either Variable C contains "hello" or Variable D contains "world".
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/web-widget/pass-custom-data.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# How to pass custom data to your chatbot
> Learn how to send any data, such as customer information, to the chatbot widget.
With the widget's code snippet, you can pass any data to the chatbot. This is useful if you want to send customer information, such as name and email, or any other data to the chatbot and use them in your flow.
## Before you begin
* You must know how to use [variables](/chatbot/builder/variables) in the builder.
* You have to [create variables](/chatbot/builder/variables/how-to-create-variables) in the builder for the data you want to pass to the chatbot. If the variables already exist, you can skip this step.
## Pass custom data during launch
When you [install the chatbot](/web-widget/installation/overview) on your website, you get a code snippet similar to this:
```html theme={null}
```
You can pass custom data during launch by adding the `variables` property to the `chtlConfig` object, and listing the variable names and their values.
```javascript theme={null}
window.chtlConfig = {
chatbotId: "",
variables: {
"variable_name_1": "",
"variable_name_2": "",
"variable_name_3": ""
}
}
```
### Example
Let's say you want to pass the user's name, email and age to the chatbot. First, you need to [create variables](/chatbot/builder/variables/how-to-create-variables) for them in the builder.
Conditions within a group are evaluated together to determine if the group is true or false. You can use logical operators such as "AND" and "OR" to combine conditions within a group.
For example, you can create a group with two conditions and set it to "AND" to require both conditions to be true for the group to be true. On the other hand, you can set it to "OR" to require only one of the conditions to be true for the group to be true.
By default, condition blocks have one group with one condition. To add additional groups, click the `Add group condition` button.
## Logical operators
Logical operators are used to combine conditions within a group. You can choose from the following logical operators:
* **AND**: Requires all conditions in the group to be true for the group to be true.
* **OR**: Requires at least one condition in the group to be true for the group to be true.
- Group 1:
* Condition 1: Variable A equals 5
* Condition 2: Variable B equals 10
* Logical operator: AND
- Group 2:
* Condition 1: Variable C contains "hello"
* Condition 2: Variable D contains "world"
* Logical operator: OR
In this example, Group 1 will be true only if Variable A equals 5 and Variable B equals 10. Group 2 will be true if either Variable C contains "hello" or Variable D contains "world".
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/web-widget/pass-custom-data.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# How to pass custom data to your chatbot
> Learn how to send any data, such as customer information, to the chatbot widget.
With the widget's code snippet, you can pass any data to the chatbot. This is useful if you want to send customer information, such as name and email, or any other data to the chatbot and use them in your flow.
## Before you begin
* You must know how to use [variables](/chatbot/builder/variables) in the builder.
* You have to [create variables](/chatbot/builder/variables/how-to-create-variables) in the builder for the data you want to pass to the chatbot. If the variables already exist, you can skip this step.
## Pass custom data during launch
When you [install the chatbot](/web-widget/installation/overview) on your website, you get a code snippet similar to this:
```html theme={null}
```
You can pass custom data during launch by adding the `variables` property to the `chtlConfig` object, and listing the variable names and their values.
```javascript theme={null}
window.chtlConfig = {
chatbotId: "",
variables: {
"variable_name_1": "",
"variable_name_2": "",
"variable_name_3": ""
}
}
```
### Example
Let's say you want to pass the user's name, email and age to the chatbot. First, you need to [create variables](/chatbot/builder/variables/how-to-create-variables) for them in the builder.
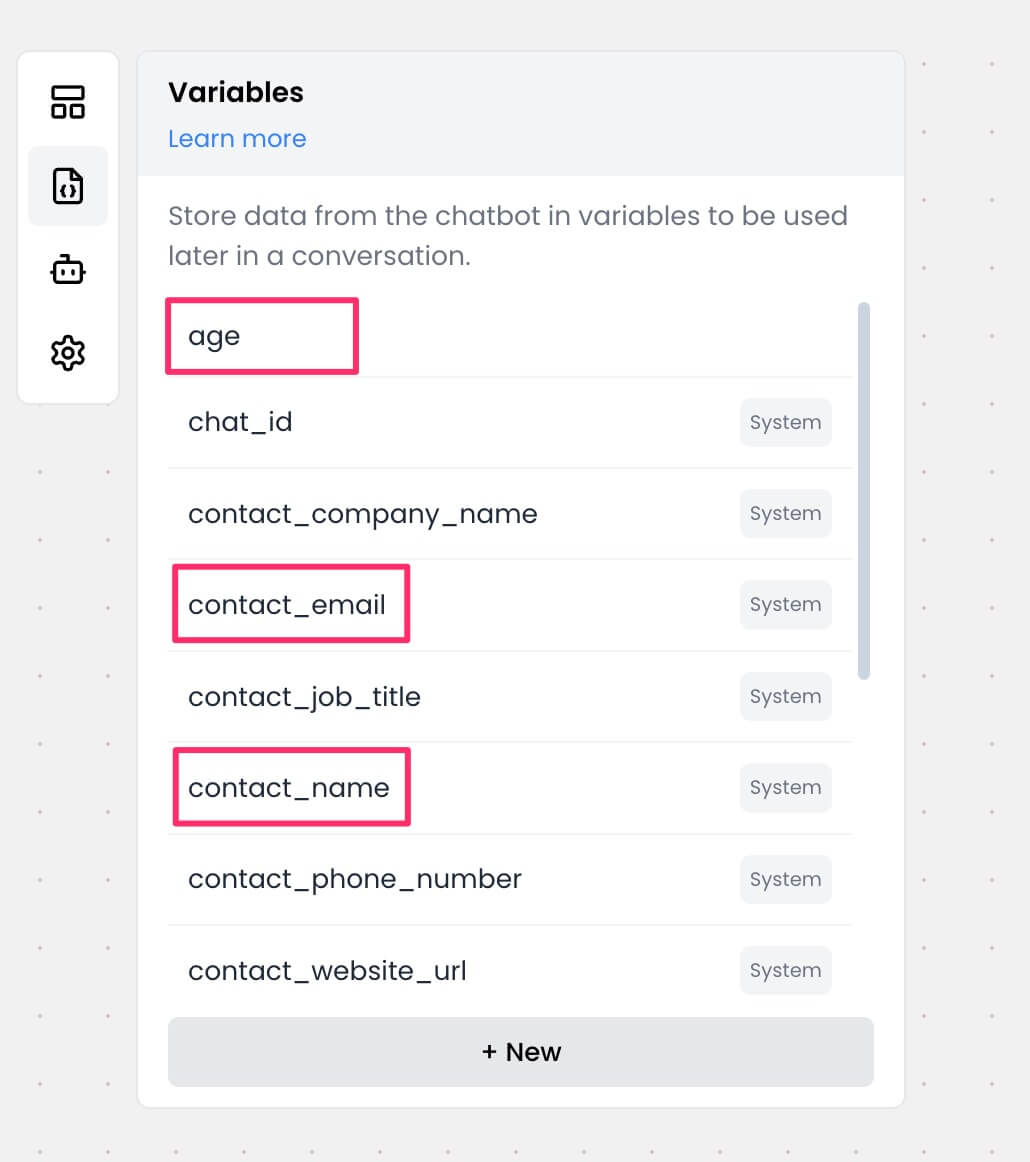 Next, add the variable values to your widget's code snippet. You must make sure that the variable names match exactly as they are in the builder.
```javascript theme={null}
window.chtlConfig = {
chatbotId: "",
variables: {
"contact_name": "John Doe",
"contact_email": "john.doe@example.com",
"age": 25
}
}
```
Now if you use the variables in your chatbot's flow, they will have the values you passed during launch.
Next, add the variable values to your widget's code snippet. You must make sure that the variable names match exactly as they are in the builder.
```javascript theme={null}
window.chtlConfig = {
chatbotId: "",
variables: {
"contact_name": "John Doe",
"contact_email": "john.doe@example.com",
"age": 25
}
}
```
Now if you use the variables in your chatbot's flow, they will have the values you passed during launch.
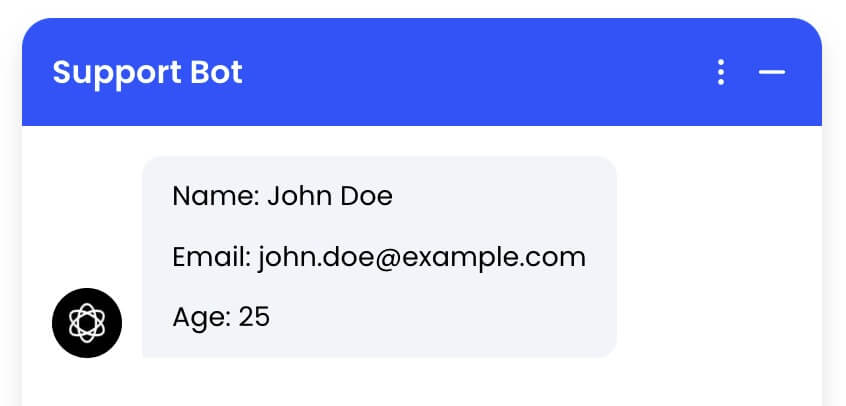 ## Pass custom data after launch
If at any point after launching the chatbot, you want to pass some data to it, you can do so by calling the `window.Chatling.setVariables` function.
```javascript theme={null}
window.Chatling.setVariables({
"contact_name": "Rick Astley",
"contact_email": "rick.astley@example.com",
"age": 30
}, function(success, errorMessage) {
if (!success) {
// handle error
}
});
```
**Note:**
* The `setVariables` function must be called after the chatbot widget has loaded.
- Variables must be present in the builder and the names must match exactly.
- This will overwrite any existing values for the variables.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/blocks/inputs/phone.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Phone Block
> Learn about the Phone input block and how to set it up in the Builder.
The Phone block is used to collect phone numbers from users.
At the moment, the Phone block is not fully developed and doesn't have the ability to validate phone numbers or provide option for users to select their country code. We are working on improving this block and will update this documentation once the changes are live.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/ai-agent/playground.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Playground
The Playground is your sandbox to experiment with your AI agent in real time. You can tweak core settings—like AI model, enabled actions, temperature, and instructions—then chat with the agent to see exactly how those changes affect behavior.
You can also run side-by-side comparisons of up to 5 instances of your agent, each with different settings, to quickly identify the configuration that performs best.
## Pass custom data after launch
If at any point after launching the chatbot, you want to pass some data to it, you can do so by calling the `window.Chatling.setVariables` function.
```javascript theme={null}
window.Chatling.setVariables({
"contact_name": "Rick Astley",
"contact_email": "rick.astley@example.com",
"age": 30
}, function(success, errorMessage) {
if (!success) {
// handle error
}
});
```
**Note:**
* The `setVariables` function must be called after the chatbot widget has loaded.
- Variables must be present in the builder and the names must match exactly.
- This will overwrite any existing values for the variables.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/blocks/inputs/phone.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Phone Block
> Learn about the Phone input block and how to set it up in the Builder.
The Phone block is used to collect phone numbers from users.
At the moment, the Phone block is not fully developed and doesn't have the ability to validate phone numbers or provide option for users to select their country code. We are working on improving this block and will update this documentation once the changes are live.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/ai-agent/playground.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Playground
The Playground is your sandbox to experiment with your AI agent in real time. You can tweak core settings—like AI model, enabled actions, temperature, and instructions—then chat with the agent to see exactly how those changes affect behavior.
You can also run side-by-side comparisons of up to 5 instances of your agent, each with different settings, to quickly identify the configuration that performs best.
 ## How to compare multiple variations of your agent?
To test with different variations of your agent, click the `Compare` button in the top right corner of the playground. A new instance of your agent will be created with default settings.
## How to compare multiple variations of your agent?
To test with different variations of your agent, click the `Compare` button in the top right corner of the playground. A new instance of your agent will be created with default settings.
 You can then tweak the settings of the new instance and chat with it to see how it performs.
You can then tweak the settings of the new instance and chat with it to see how it performs.
 All inputs to agents are synced between the instances, so you can see how the agent behaves with different settings. If you want to disable this, you can toggle the `Sync` button above one of the agents.
All inputs to agents are synced between the instances, so you can see how the agent behaves with different settings. If you want to disable this, you can toggle the `Sync` button above one of the agents.
 To remove an agent, click the `X` button above it.
To remove an agent, click the `X` button above it.
 ---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/web-widget/installation/prestashop.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# PrestaShop
> Learn how to add Chatling to your PrestaShop website
1. Go to your dashboard.
2. Click `Deploy` button in the sidebar menu.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/web-widget/installation/prestashop.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# PrestaShop
> Learn how to add Chatling to your PrestaShop website
1. Go to your dashboard.
2. Click `Deploy` button in the sidebar menu.
 3. Click the `Manage` button under the `Website Widget` option.
3. Click the `Manage` button under the `Website Widget` option.
 4. Design the appearance of the widget by clicking the `Open widget designer` button.
4. Design the appearance of the widget by clicking the `Open widget designer` button.
 5. Select the display mode for your chatbot, such as "Floating Chat", "Inline", or "Fullscreen".
5. Select the display mode for your chatbot, such as "Floating Chat", "Inline", or "Fullscreen".
 6. Copy the widget code.
6. Copy the widget code.
 7. Download our [PrestaShop module](https://static.chatling.ai/files/chatling-prestashop-v1-0.zip).
8. Extract the zip file and open the `chatling` folder.
7. Download our [PrestaShop module](https://static.chatling.ai/files/chatling-prestashop-v1-0.zip).
8. Extract the zip file and open the `chatling` folder.
 9. Inside the folder, open the `chatling.php` file using a text editor of your choice, such as Notepad on Windows or TextEdit on macOS.
9. Inside the folder, open the `chatling.php` file using a text editor of your choice, such as Notepad on Windows or TextEdit on macOS.
 10. Go to the bottom of the file and find the line that says `Paste code snippet here`.
10. Go to the bottom of the file and find the line that says `Paste code snippet here`.
 Replace it with the code snippet you copied in step #2, as shown below.
Replace it with the code snippet you copied in step #2, as shown below.
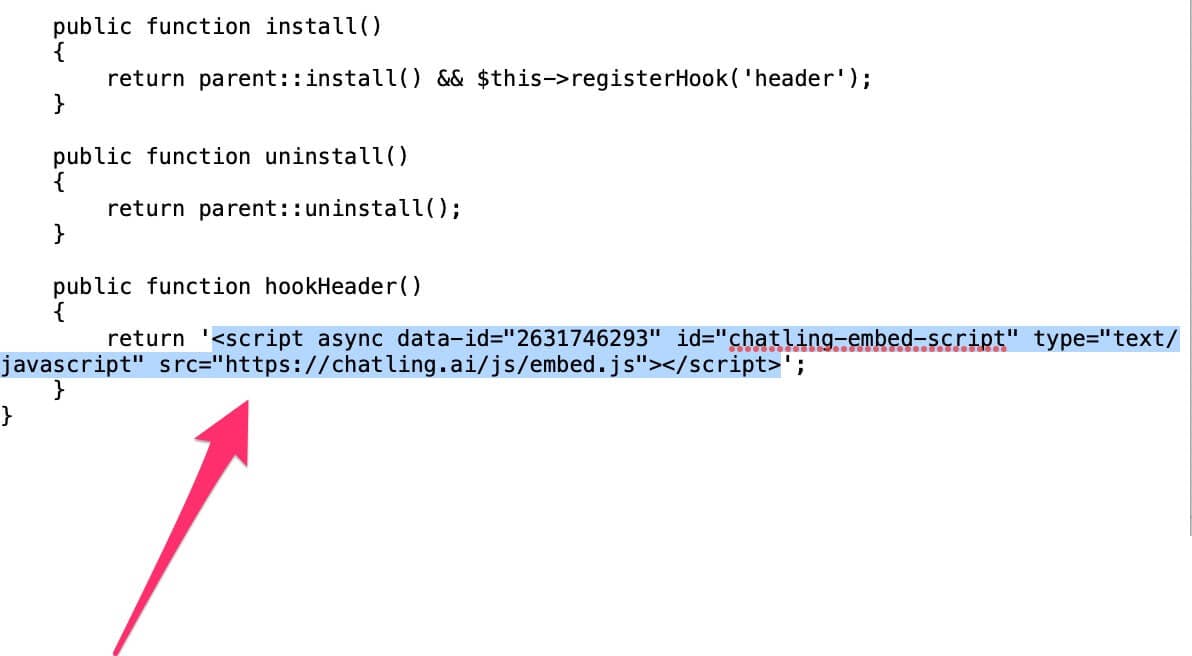 11. Save the file and close it.
12. Zip the `chatling` folder. Do not rename the folder to anything else otherwise the module won't work.
11. Save the file and close it.
12. Zip the `chatling` folder. Do not rename the folder to anything else otherwise the module won't work.
 13. Go to your PrestaShop admin panel. From the sidebar menu, click `Module` > `Module Manager`.
13. Go to your PrestaShop admin panel. From the sidebar menu, click `Module` > `Module Manager`.
 14. Click the `Upload a module` button in the top right. Browse and select the module's zip file.
14. Click the `Upload a module` button in the top right. Browse and select the module's zip file.
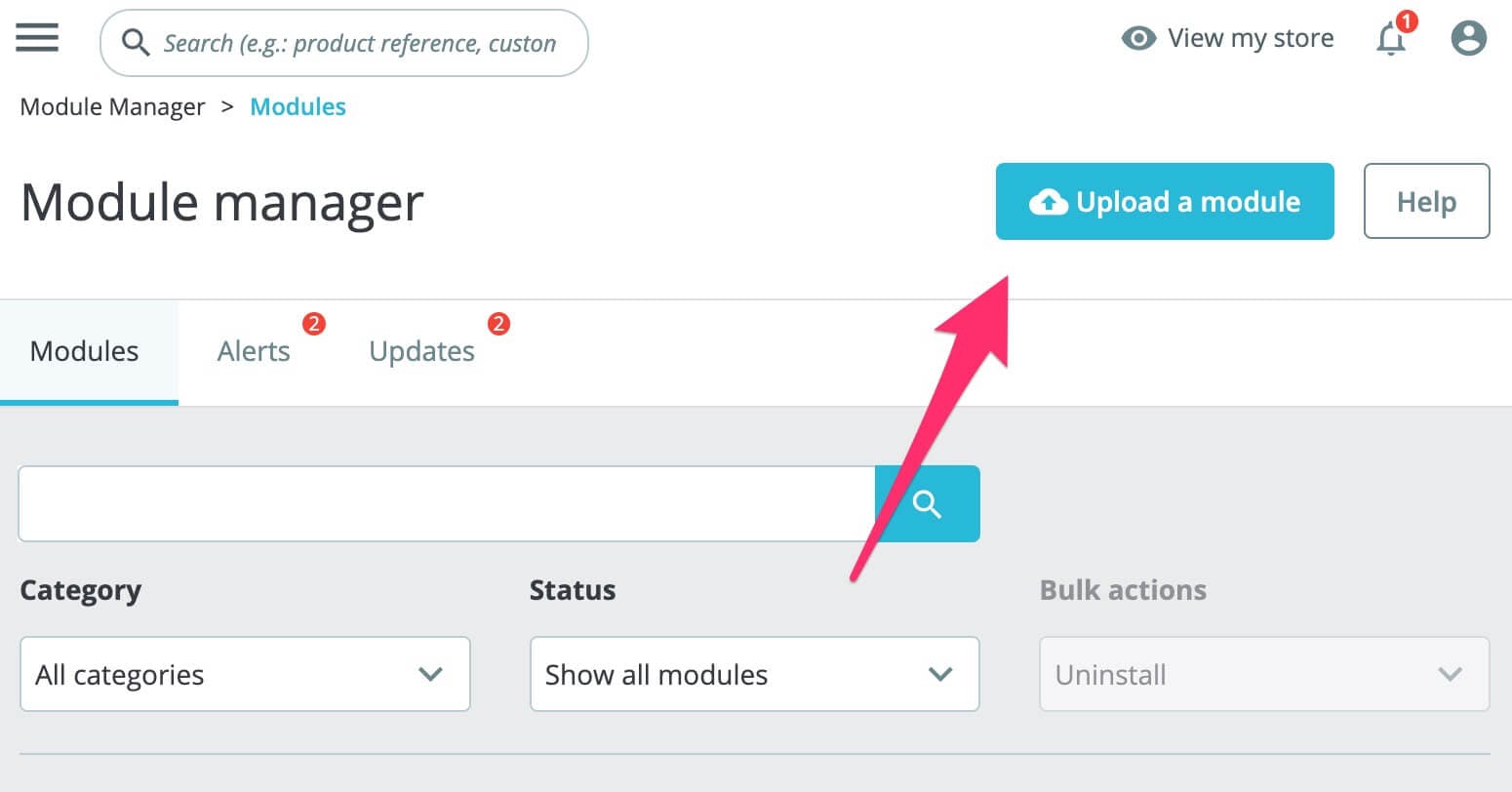 15. Once the module is uploaded, the widget will be live on your website.
15. Once the module is uploaded, the widget will be live on your website.
 ---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/publish-your-chatbot.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Publish your chatbot
> Learn how to publish your chatbot and make it live.
Once you've built your chatbot and tested it thoroughly, you can publish it to make it live.
By publishing, any changes you've made to the chatbot will become available to users where the chatbot is embedded.
To publish your chatbot, click the `Publish` button in the top right corner of the Builder.

---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/block-options/quick-replies.md
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/ai-agent/quick-replies.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Adding Quick Replies to AI Agents
Quick replies are buttons displayed above the input field that allow users to ask common questions without typing.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/publish-your-chatbot.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Publish your chatbot
> Learn how to publish your chatbot and make it live.
Once you've built your chatbot and tested it thoroughly, you can publish it to make it live.
By publishing, any changes you've made to the chatbot will become available to users where the chatbot is embedded.
To publish your chatbot, click the `Publish` button in the top right corner of the Builder.

---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/block-options/quick-replies.md
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/ai-agent/quick-replies.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Adding Quick Replies to AI Agents
Quick replies are buttons displayed above the input field that allow users to ask common questions without typing.
 This guide is for adding quick replies to AI Agents. For AI Chatbots, refer to [this guide](/chatbot/builder/block-options/quick-replies)
## How to add quick replies to your AI Agent
1. Go to the `Deploy` page of your AI agent.
This guide is for adding quick replies to AI Agents. For AI Chatbots, refer to [this guide](/chatbot/builder/block-options/quick-replies)
## How to add quick replies to your AI Agent
1. Go to the `Deploy` page of your AI agent.
 2. Under the `Website Widget` option, click the brush icon to open the widget editor.
2. Under the `Website Widget` option, click the brush icon to open the widget editor.
 3. Click `Texts` from the sidebar and go to the `Quick Replies` section.
3. Click `Texts` from the sidebar and go to the `Quick Replies` section.
 4. Click the `Add` button to add a new quick reply. Each quick reply will have a label and a message. The label will be displayed on the button and the message will be sent when the user clicks on the button.
Label is optional, but recommended to keep the button short and descriptive.
4. Click the `Add` button to add a new quick reply. Each quick reply will have a label and a message. The label will be displayed on the button and the message will be sent when the user clicks on the button.
Label is optional, but recommended to keep the button short and descriptive.
 5. You can also add translations for the quick replies, which will be displayed automatically based on the user's language.
6. The `Auto-hide quick replies` option allows you to automatically hide the quick replies after a certain number of messages are sent by the user. This is useful to prevent the quick replies from being displayed at all times.
5. You can also add translations for the quick replies, which will be displayed automatically based on the user's language.
6. The `Auto-hide quick replies` option allows you to automatically hide the quick replies after a certain number of messages are sent by the user. This is useful to prevent the quick replies from being displayed at all times.
 7. Once you are done, click the `Save` button to save the changes.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/api-reference/v2/conversations/rate-ai-answer.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Rate AI answer
Use this endpoint to rate an AI answer as helpful or not helpful. You can only rate AI answers generated using the Knowledge Base.
## Request parameters
### Path
The chatbot ID.
The conversation ID.
The message ID.
### Body
* `0`: Remove rating
* `1`: Helpful
* `-1`: Not helpful
## Response
The status of the request. Will be `success` if the request was successful, otherwise `error`.
```json Response theme={null}
{
"status": "success",
"data": null
}
```
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/general-settings/rate-limit.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Rate limit
> Learn how to set a rate limit for your chatbot to prevent it from being spammed.
Rate limiting allows you to limit the number of messages a user can send to your chatbot in a given period of time. This helps prevent end-users from spamming your chatbot and depleting your account credits.
## How to set a rate limit
1. Open your chatbot's dashboard.
2. Go to chatbot settings.
7. Once you are done, click the `Save` button to save the changes.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/api-reference/v2/conversations/rate-ai-answer.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Rate AI answer
Use this endpoint to rate an AI answer as helpful or not helpful. You can only rate AI answers generated using the Knowledge Base.
## Request parameters
### Path
The chatbot ID.
The conversation ID.
The message ID.
### Body
* `0`: Remove rating
* `1`: Helpful
* `-1`: Not helpful
## Response
The status of the request. Will be `success` if the request was successful, otherwise `error`.
```json Response theme={null}
{
"status": "success",
"data": null
}
```
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/general-settings/rate-limit.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Rate limit
> Learn how to set a rate limit for your chatbot to prevent it from being spammed.
Rate limiting allows you to limit the number of messages a user can send to your chatbot in a given period of time. This helps prevent end-users from spamming your chatbot and depleting your account credits.
## How to set a rate limit
1. Open your chatbot's dashboard.
2. Go to chatbot settings.
 3. Click the `Security` tab.
4. Under the `Rate limiting` section, add a rate limit, e.g. 10 messages per minute. You can add multiple rate limits for different periods of time, such as per minute, per hour, or per day.
The rate limit is applied to individual users. For example, if you set a rate limit of 10 messages per minute, each user can send up to 10 messages per minute.
5. You can also add a custom error message to be displayed when the rate limit is exceeded. If left blank, a default error message will be displayed.
The default error message is automatically translated into the language of your chatbot widget. If you override it with a custom message, it won't be translated.
6. Click `Save`.
Once you've set the rate limits, your chatbot will prevent end-users from sending more messages than the rate limit in a given period of time. If the rate limit is exceeded, an error message will be displayed.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/api-reference/v2/rate-limiting.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Rate limiting
> Our API has rate limits to prevent abuse and ensure fair usage.
We enforce rate limits to balance the load on our servers and provide a fair environment for all developers to interact with the Chatling API.
Therefore, the number of requests you send to the API will be measured and throttled if you surpass the allowed rate limit.
## Rate limit
The default rate limit is **300 API calls per minute** for each API key. We may adjust these limits in the future.
When you exceed the rate limit, you will receive a 429 status code with the following response:
```json theme={null}
{
"status": "error",
"message": "Too many requests"
}
```
## When does the rate limit reset?
The rate limit lasts 1 minute, and the number of requests you've sent within that window will reset at the next minute.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/knowledge-base/re-sync-data-sources.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Re-sync data sources
> Learn how to re-sync data sources in the Knowledge Base.
If you've made changes to your Link data sources (websites/webpages) or want to update the information in the Knowledge Base, you can re-sync the data sources to fetch the latest data. This process will re-fetch the data from the source and update the information in the Knowledge Base.
## Supported data sources
Re-syncing is available for Links data sources only, which include websites and webpages. Other data sources like Documents, Text, and FAQs do not require re-syncing as they are static and do not change unless you manually update them.
## How to re-sync a data source
To re-sync data sources in the Knowledge Base, follow these steps:
* Go to the `Knowledge Base`.
* Click on the `Link` tab to view all the links you have added.
* Next to every link is a re-sync icon, as shown below. Click on the icon to queue the link for re-syncing.
3. Click the `Security` tab.
4. Under the `Rate limiting` section, add a rate limit, e.g. 10 messages per minute. You can add multiple rate limits for different periods of time, such as per minute, per hour, or per day.
The rate limit is applied to individual users. For example, if you set a rate limit of 10 messages per minute, each user can send up to 10 messages per minute.
5. You can also add a custom error message to be displayed when the rate limit is exceeded. If left blank, a default error message will be displayed.
The default error message is automatically translated into the language of your chatbot widget. If you override it with a custom message, it won't be translated.
6. Click `Save`.
Once you've set the rate limits, your chatbot will prevent end-users from sending more messages than the rate limit in a given period of time. If the rate limit is exceeded, an error message will be displayed.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/api-reference/v2/rate-limiting.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Rate limiting
> Our API has rate limits to prevent abuse and ensure fair usage.
We enforce rate limits to balance the load on our servers and provide a fair environment for all developers to interact with the Chatling API.
Therefore, the number of requests you send to the API will be measured and throttled if you surpass the allowed rate limit.
## Rate limit
The default rate limit is **300 API calls per minute** for each API key. We may adjust these limits in the future.
When you exceed the rate limit, you will receive a 429 status code with the following response:
```json theme={null}
{
"status": "error",
"message": "Too many requests"
}
```
## When does the rate limit reset?
The rate limit lasts 1 minute, and the number of requests you've sent within that window will reset at the next minute.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/knowledge-base/re-sync-data-sources.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Re-sync data sources
> Learn how to re-sync data sources in the Knowledge Base.
If you've made changes to your Link data sources (websites/webpages) or want to update the information in the Knowledge Base, you can re-sync the data sources to fetch the latest data. This process will re-fetch the data from the source and update the information in the Knowledge Base.
## Supported data sources
Re-syncing is available for Links data sources only, which include websites and webpages. Other data sources like Documents, Text, and FAQs do not require re-syncing as they are static and do not change unless you manually update them.
## How to re-sync a data source
To re-sync data sources in the Knowledge Base, follow these steps:
* Go to the `Knowledge Base`.
* Click on the `Link` tab to view all the links you have added.
* Next to every link is a re-sync icon, as shown below. Click on the icon to queue the link for re-syncing.
 ## Re-sync data sources in bulk
To re-sync multiple data sources at once, click on the checkbox next to the links you want to re-sync. Then, click on the `Bulk action` dropdown and select `Re-sync links`.
## Re-sync data sources in bulk
To re-sync multiple data sources at once, click on the checkbox next to the links you want to re-sync. Then, click on the `Bulk action` dropdown and select `Re-sync links`.
 ---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/whatsapp/reconnect-account.md
# Reconnect WhatsApp account
> Learn how to reconnect your WhatsApp account to your chatbot in Chatling.
If you want to restart the connection between your WhatsApp account and your chatbot, you can disconnect and reconnect your account.
1. From your chatbot's dashboard, click the `Settings` button under the Chatbot menu.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/whatsapp/reconnect-account.md
# Reconnect WhatsApp account
> Learn how to reconnect your WhatsApp account to your chatbot in Chatling.
If you want to restart the connection between your WhatsApp account and your chatbot, you can disconnect and reconnect your account.
1. From your chatbot's dashboard, click the `Settings` button under the Chatbot menu.
 2. Go to the `WhatsApp` tab.
2. Go to the `WhatsApp` tab.
 3. Click the `Disconnect` button.
3. Click the `Disconnect` button.
 4. An onboarding will be displayed to reconnect your account. Follow the on-screen instructions to reconnect your account. You can also check [this guide](/chatbot/whatsapp/setup) for the steps to connect your account.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/web-widget/remove-powered-by-chatling-branding.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Remove "Powered by Chatling" branding
> Learn how to remove the Chatling branding from your chatbot widget.
## Which plans can remove the branding?
The branding can be removed if you're on the **Ultimate** plan or by purchasing the [Remove "Powered by Chatling" branding add-on](https://chatling.com/pricing).
## How to remove the branding
1. Open the widget designer. To learn how to access it, see [this guide](/web-widget/customize#how-to-customize-the-widget).
2. Go to `Configure`.
4. An onboarding will be displayed to reconnect your account. Follow the on-screen instructions to reconnect your account. You can also check [this guide](/chatbot/whatsapp/setup) for the steps to connect your account.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/web-widget/remove-powered-by-chatling-branding.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Remove "Powered by Chatling" branding
> Learn how to remove the Chatling branding from your chatbot widget.
## Which plans can remove the branding?
The branding can be removed if you're on the **Ultimate** plan or by purchasing the [Remove "Powered by Chatling" branding add-on](https://chatling.com/pricing).
## How to remove the branding
1. Open the widget designer. To learn how to access it, see [this guide](/web-widget/customize#how-to-customize-the-widget).
2. Go to `Configure`.
 3. Enable the `Hide "Powered by Chatling"` option.
4. Click the `Save` button to apply the changes.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/team-members/remove.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Remove Team Members
> Learn how to remove team members from your project.
To remove team members from your project:
1. From the Project menu, go to **Members**.
3. Enable the `Hide "Powered by Chatling"` option.
4. Click the `Save` button to apply the changes.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/team-members/remove.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Remove Team Members
> Learn how to remove team members from your project.
To remove team members from your project:
1. From the Project menu, go to **Members**.
 2. Find the member you want to remove and click the ellipsis icon next to them.
2. Find the member you want to remove and click the ellipsis icon next to them.
 3. Click **Remove member**.
The member will be removed from the project immediately and will no longer have access to it.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/faq/reset-chat-on-page-load.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# How to reset the chat on page load?
By default, chat history is retained when users navigate away from the chatbot and return to it, refresh the page, or go to a different page. This means that when users return to the chatbot, they can see their existing chat and continue from where they left off.
If you want to disable this so that the chat is reset on page load, you can do so by following these steps:
1. From your chatbot dashboard, go to `Builder`.
3. Click **Remove member**.
The member will be removed from the project immediately and will no longer have access to it.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/faq/reset-chat-on-page-load.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# How to reset the chat on page load?
By default, chat history is retained when users navigate away from the chatbot and return to it, refresh the page, or go to a different page. This means that when users return to the chatbot, they can see their existing chat and continue from where they left off.
If you want to disable this so that the chat is reset on page load, you can do so by following these steps:
1. From your chatbot dashboard, go to `Builder`.
 2. Click the settings icon in the sidebar.
2. Click the settings icon in the sidebar.
 3. Enable the the `Reset chat on page load` option.
3. Enable the the `Reset chat on page load` option.
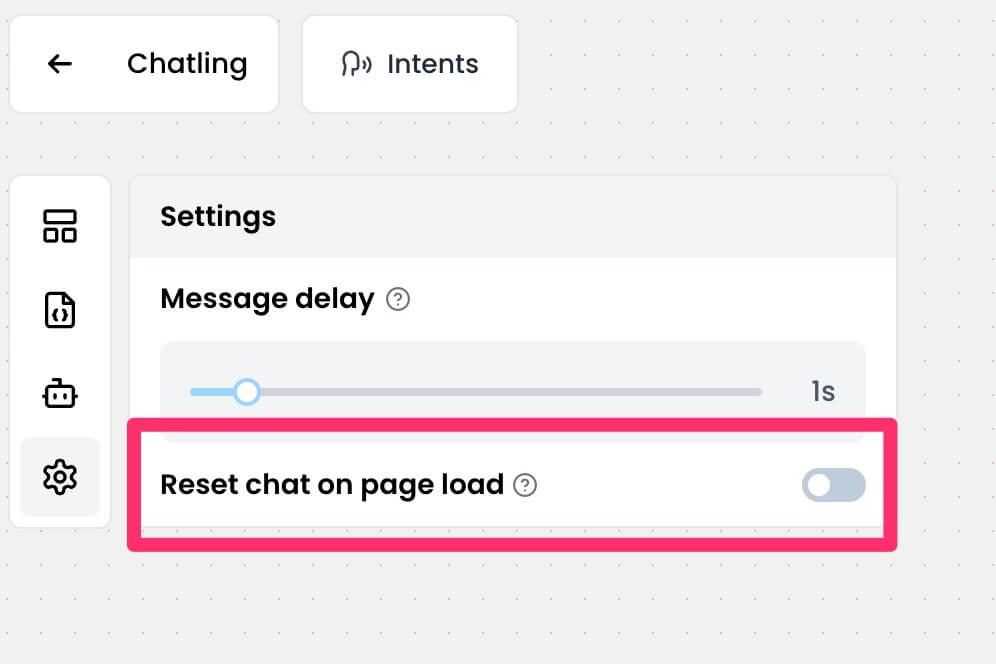 ---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/api-reference/v2/knowledge-base/resync-source.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Resync data source
> Resync a data source.
**The following limitations apply:**
* The supported sources are links and Zoho articles.
* You can have up to 50 data sources queued for resync. If you exceed this limit, you will receive an error and must wait until some of the queued resyncs are complete.
* You can only resync data sources that are in the `processed` state.
## Request parameters
### Path
The chatbot ID.
The data source ID.
## Response
The status of the request. Will be `success` if the request was successful, otherwise `error`.
```json Response theme={null}
{
"status": "success"
}
```
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/api-reference/v2/chatbots/retrieve-chatbot.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Retrieve chatbot
> Retrieve a chatbot by its ID.
## Request parameters
### Path
The chatbot ID.
## Response
The status of the request. Will be `success` if the request was successful, otherwise `error`.
The unique identifier of the chatbot.
The name of the chatbot.
The version of the chatbot.
The visibility of the chatbot.
The date and time when the chatbot was created.
```json theme={null}
{
"status": "success",
"data": {
"id": "9761342719",
"name": "My chatbot",
"version": "2.0",
"visibility": "public",
"created_at": "2024-06-17T12:00:00+00:00"
}
}
```
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/blocks/hubspot/retrieve-contact.md
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/api-reference/v2/contacts/retrieve-contact.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Retrieve contact
> Retrieve a contact by its ID.
## Request parameters
### Path
The contact ID.
The chatbot ID.
## Response
The status of the request. Will be `success` if the request was successful, otherwise `error`.
The unique identifier of the contact.
The name of the contact.
The email address of the contact.
The job title of the contact.
The phone number of the contact.
The website URL of the contact.
The company name of the contact.
The date and time when the contact was created.
```json theme={null}
{
"status": "success",
"data": {
"id": "qtr89df0-112d-d197-b541-3f8674663246",
"name": "Mark Zuckerberg",
"email": "mark@meta.com",
"job_title": "CEO",
"phone": "555-555-5555",
"website": "https://meta.com",
"company": "Meta Inc.",
"created_at": "2024-06-08T13:38:33+00:00"
}
}
```
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/api-reference/v2/conversations/retrieve-conversation.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Retrieve conversation
> Retrieve a conversation by its ID.
## Request parameters
### Path
The chatbot ID.
The conversation ID.
## Response
The status of the request. Will be `success` if the request was successful, otherwise `error`.
The unique identifier of the conversation.
The unique identifier of the contact associated with the conversation.
Whether the conversation is archived (by the admin).
Whether the conversation is marked as important.
The date and time when the conversation was created.
List of the most recent 20 messages in the conversation.
The unique identifier of the message.
The text content of the message.
The role of the sender of the message (bot, user, or system).
Whether the message is generated by the AI using the knowledge base.
The data of the message. Varies depending on the message type.
(AI response) Whether the AI's response was marked as helpful by the user. Possible values are `1` for helpful, `0` for not helpful, and `null` for not rated.
(AI response) The sources used by the AI to generate the response.
The date and time when the message was created.
```json theme={null}
{
"status": "success",
"data": {
"id": "8977617953",
"contact_id": "qtr89df0-112d-d197-b541-3f8674663246",
"archived": 0,
"important": 1,
"created_at": "2024-06-14T15:45:34+00:00",
"messages": [
{
"text": "System variables are predefined variables that contain system information or can be used to perform specific actions. These variables are automatically created by the Builder.",
"role": "bot",
"is_ai_kb_response": true,
"data": {
"helpful_value": null,
"sources": [
{
"type": "webpage",
"title": "Types of variables - Chatling Documentation",
"url": "https://docs.chatling.ai/builder/variables/variable-types"
},
{
"type": "webpage",
"title": "Sidebar - Chatling Documentation",
"url": "https://docs.chatling.ai/builder/sidebar"
},
{
"type": "webpage",
"title": "What are variables? - Chatling Documentation",
"url": "https://docs.chatling.ai/builder/variables/what-are-variables"
}
]
},
"created_at": "2024-06-17T16:09:52+00:00"
},
{
"text": "What are system variables",
"role": "user",
"created_at": "2024-06-17T16:09:45+00:00"
},
{
"text": "**Hello! How can I assist you today?**\n\nIf you have any questions related to our chatbot or services, please feel free to ask. I'm here to help!",
"role": "bot",
"is_ai_kb_response": true,
"data": {
"helpful_value": null,
"sources": []
},
"created_at": "2024-06-14T15:45:39+00:00"
},
{
"text": "Hello!",
"role": "user",
"created_at": "2024-06-14T15:45:34+00:00"
}
]
}
}
```
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/team-members/roles.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Roles & Permissions
> Learn how to invite team members to your project and assign them different roles.
Members can be assigned one or more roles, each having different permissions.
Here are the available roles and their permissions:
1. **Admin**: Full access to all settings and features, including inviting members, creating chatbots and API keys, and managing billing.
* Create, update, and delete projects
* Create, view, test, and delete chatbots
* View analytics
* View and update chatbot settings
* View, update, and publish chatbots in the Builder
* View, update, and delete conversations
* View, update, export, and delete leads
* View and update appearance settings
* View and update knowledge base
* View, create, update, and delete members
* Share chatbots
* View, create, and delete API keys
* View and update billing settings
* View usage
* View invoices
* View, download, and delete exports
2. **Editor**: Can access and modify the builder, knowledge base, and widget appearance. Can also create chatbots and view usage.
* Create, view, and test chatbots
* View and update chatbot settings
* View, update, and publish chatbots in the Builder
* View and update appearance settings
* View and update knowledge base
* Share chatbots
* View billing
* View usage
3. **Analyst**: Can access chatbot analytics, conversations, and leads.
* View chatbots
* View analytics
* View, update, and delete conversations
* View, update, export, and delete leads
* View, download, and delete exports
* View billing
* View usage
4. **Billing**: Can update account billing and view usage.
* View and update billing settings
* View usage
* View invoices
5. **Viewer**: Can view the builder and test chatbots, but doesn't have the ability to modify.
* View and test chatbots
* View chatbot flow in the Builder
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/web-widget/satisfaction-survey.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Satisfaction survey
> A guide on how to set up and display satisfaction surveys.
You can collect feedback from users at the end of their chat by displaying a satisfaction survey. This can help you gain insights into user satisfaction, identify areas for improvement, and track the overall effectiveness of your chatbot over time.
## How to set up a satisfaction survey
1. From the chatbot dashboard, go to `Settings`.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/api-reference/v2/knowledge-base/resync-source.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Resync data source
> Resync a data source.
**The following limitations apply:**
* The supported sources are links and Zoho articles.
* You can have up to 50 data sources queued for resync. If you exceed this limit, you will receive an error and must wait until some of the queued resyncs are complete.
* You can only resync data sources that are in the `processed` state.
## Request parameters
### Path
The chatbot ID.
The data source ID.
## Response
The status of the request. Will be `success` if the request was successful, otherwise `error`.
```json Response theme={null}
{
"status": "success"
}
```
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/api-reference/v2/chatbots/retrieve-chatbot.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Retrieve chatbot
> Retrieve a chatbot by its ID.
## Request parameters
### Path
The chatbot ID.
## Response
The status of the request. Will be `success` if the request was successful, otherwise `error`.
The unique identifier of the chatbot.
The name of the chatbot.
The version of the chatbot.
The visibility of the chatbot.
The date and time when the chatbot was created.
```json theme={null}
{
"status": "success",
"data": {
"id": "9761342719",
"name": "My chatbot",
"version": "2.0",
"visibility": "public",
"created_at": "2024-06-17T12:00:00+00:00"
}
}
```
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/blocks/hubspot/retrieve-contact.md
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/api-reference/v2/contacts/retrieve-contact.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Retrieve contact
> Retrieve a contact by its ID.
## Request parameters
### Path
The contact ID.
The chatbot ID.
## Response
The status of the request. Will be `success` if the request was successful, otherwise `error`.
The unique identifier of the contact.
The name of the contact.
The email address of the contact.
The job title of the contact.
The phone number of the contact.
The website URL of the contact.
The company name of the contact.
The date and time when the contact was created.
```json theme={null}
{
"status": "success",
"data": {
"id": "qtr89df0-112d-d197-b541-3f8674663246",
"name": "Mark Zuckerberg",
"email": "mark@meta.com",
"job_title": "CEO",
"phone": "555-555-5555",
"website": "https://meta.com",
"company": "Meta Inc.",
"created_at": "2024-06-08T13:38:33+00:00"
}
}
```
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/api-reference/v2/conversations/retrieve-conversation.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Retrieve conversation
> Retrieve a conversation by its ID.
## Request parameters
### Path
The chatbot ID.
The conversation ID.
## Response
The status of the request. Will be `success` if the request was successful, otherwise `error`.
The unique identifier of the conversation.
The unique identifier of the contact associated with the conversation.
Whether the conversation is archived (by the admin).
Whether the conversation is marked as important.
The date and time when the conversation was created.
List of the most recent 20 messages in the conversation.
The unique identifier of the message.
The text content of the message.
The role of the sender of the message (bot, user, or system).
Whether the message is generated by the AI using the knowledge base.
The data of the message. Varies depending on the message type.
(AI response) Whether the AI's response was marked as helpful by the user. Possible values are `1` for helpful, `0` for not helpful, and `null` for not rated.
(AI response) The sources used by the AI to generate the response.
The date and time when the message was created.
```json theme={null}
{
"status": "success",
"data": {
"id": "8977617953",
"contact_id": "qtr89df0-112d-d197-b541-3f8674663246",
"archived": 0,
"important": 1,
"created_at": "2024-06-14T15:45:34+00:00",
"messages": [
{
"text": "System variables are predefined variables that contain system information or can be used to perform specific actions. These variables are automatically created by the Builder.",
"role": "bot",
"is_ai_kb_response": true,
"data": {
"helpful_value": null,
"sources": [
{
"type": "webpage",
"title": "Types of variables - Chatling Documentation",
"url": "https://docs.chatling.ai/builder/variables/variable-types"
},
{
"type": "webpage",
"title": "Sidebar - Chatling Documentation",
"url": "https://docs.chatling.ai/builder/sidebar"
},
{
"type": "webpage",
"title": "What are variables? - Chatling Documentation",
"url": "https://docs.chatling.ai/builder/variables/what-are-variables"
}
]
},
"created_at": "2024-06-17T16:09:52+00:00"
},
{
"text": "What are system variables",
"role": "user",
"created_at": "2024-06-17T16:09:45+00:00"
},
{
"text": "**Hello! How can I assist you today?**\n\nIf you have any questions related to our chatbot or services, please feel free to ask. I'm here to help!",
"role": "bot",
"is_ai_kb_response": true,
"data": {
"helpful_value": null,
"sources": []
},
"created_at": "2024-06-14T15:45:39+00:00"
},
{
"text": "Hello!",
"role": "user",
"created_at": "2024-06-14T15:45:34+00:00"
}
]
}
}
```
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/team-members/roles.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Roles & Permissions
> Learn how to invite team members to your project and assign them different roles.
Members can be assigned one or more roles, each having different permissions.
Here are the available roles and their permissions:
1. **Admin**: Full access to all settings and features, including inviting members, creating chatbots and API keys, and managing billing.
* Create, update, and delete projects
* Create, view, test, and delete chatbots
* View analytics
* View and update chatbot settings
* View, update, and publish chatbots in the Builder
* View, update, and delete conversations
* View, update, export, and delete leads
* View and update appearance settings
* View and update knowledge base
* View, create, update, and delete members
* Share chatbots
* View, create, and delete API keys
* View and update billing settings
* View usage
* View invoices
* View, download, and delete exports
2. **Editor**: Can access and modify the builder, knowledge base, and widget appearance. Can also create chatbots and view usage.
* Create, view, and test chatbots
* View and update chatbot settings
* View, update, and publish chatbots in the Builder
* View and update appearance settings
* View and update knowledge base
* Share chatbots
* View billing
* View usage
3. **Analyst**: Can access chatbot analytics, conversations, and leads.
* View chatbots
* View analytics
* View, update, and delete conversations
* View, update, export, and delete leads
* View, download, and delete exports
* View billing
* View usage
4. **Billing**: Can update account billing and view usage.
* View and update billing settings
* View usage
* View invoices
5. **Viewer**: Can view the builder and test chatbots, but doesn't have the ability to modify.
* View and test chatbots
* View chatbot flow in the Builder
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/web-widget/satisfaction-survey.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Satisfaction survey
> A guide on how to set up and display satisfaction surveys.
You can collect feedback from users at the end of their chat by displaying a satisfaction survey. This can help you gain insights into user satisfaction, identify areas for improvement, and track the overall effectiveness of your chatbot over time.
## How to set up a satisfaction survey
1. From the chatbot dashboard, go to `Settings`.
 2. Click the `Satisfaction Survey` tab.
2. Click the `Satisfaction Survey` tab.
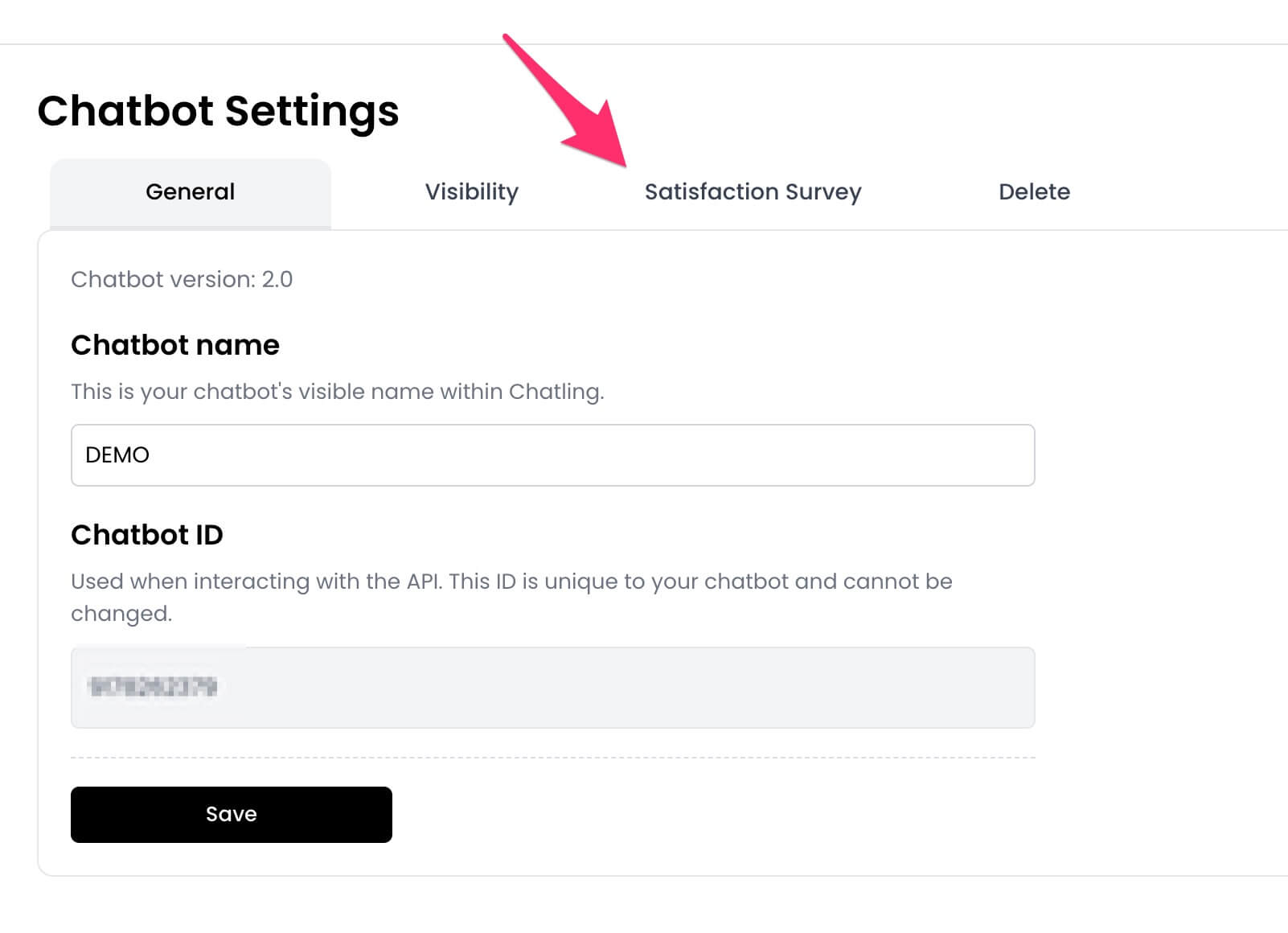 3. Toggle on the `Show survey` option.
3. Toggle on the `Show survey` option.
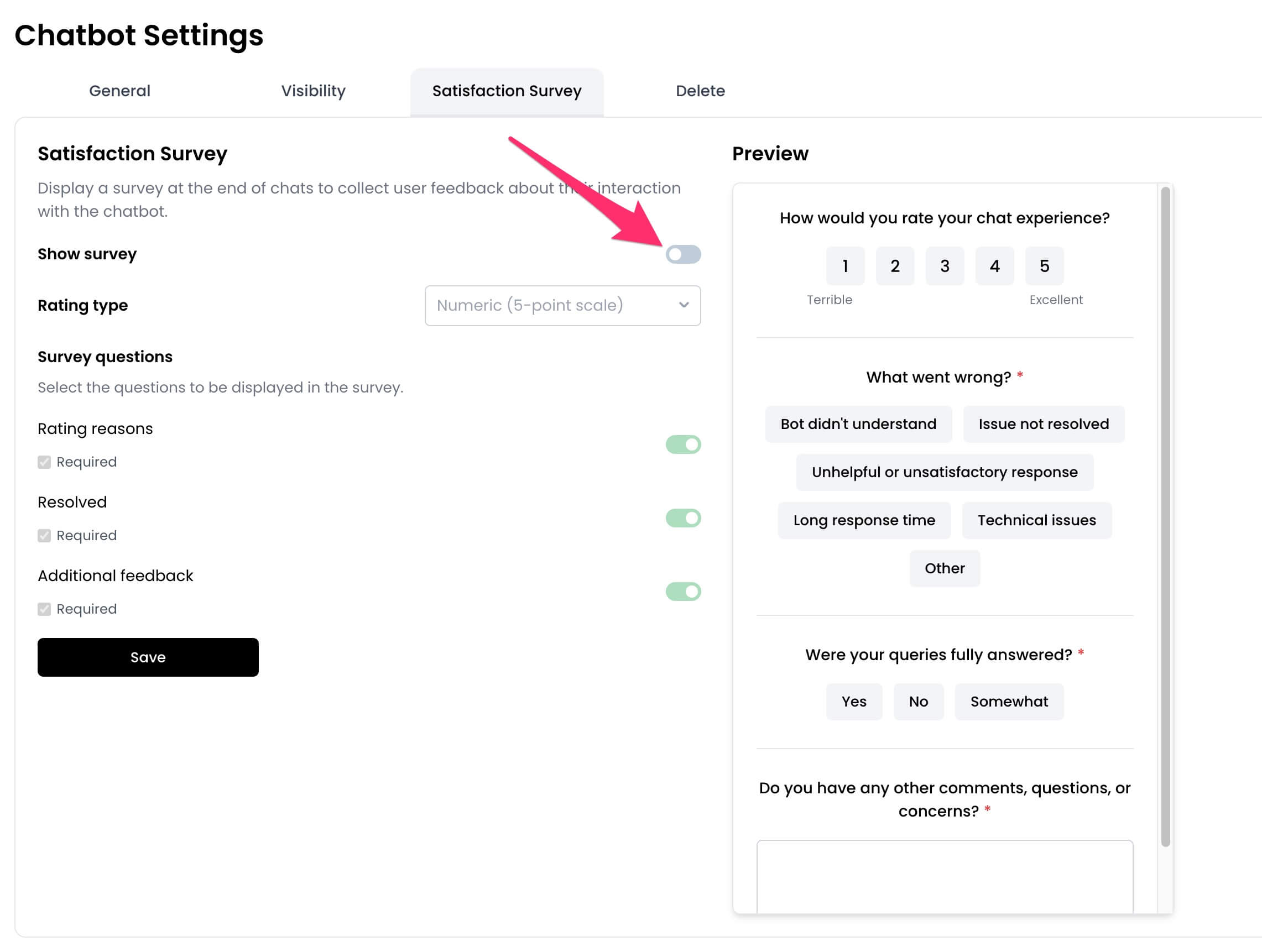 4. Customize the survey by selecting the rating type, questions to display, and more.
4. Customize the survey by selecting the rating type, questions to display, and more.
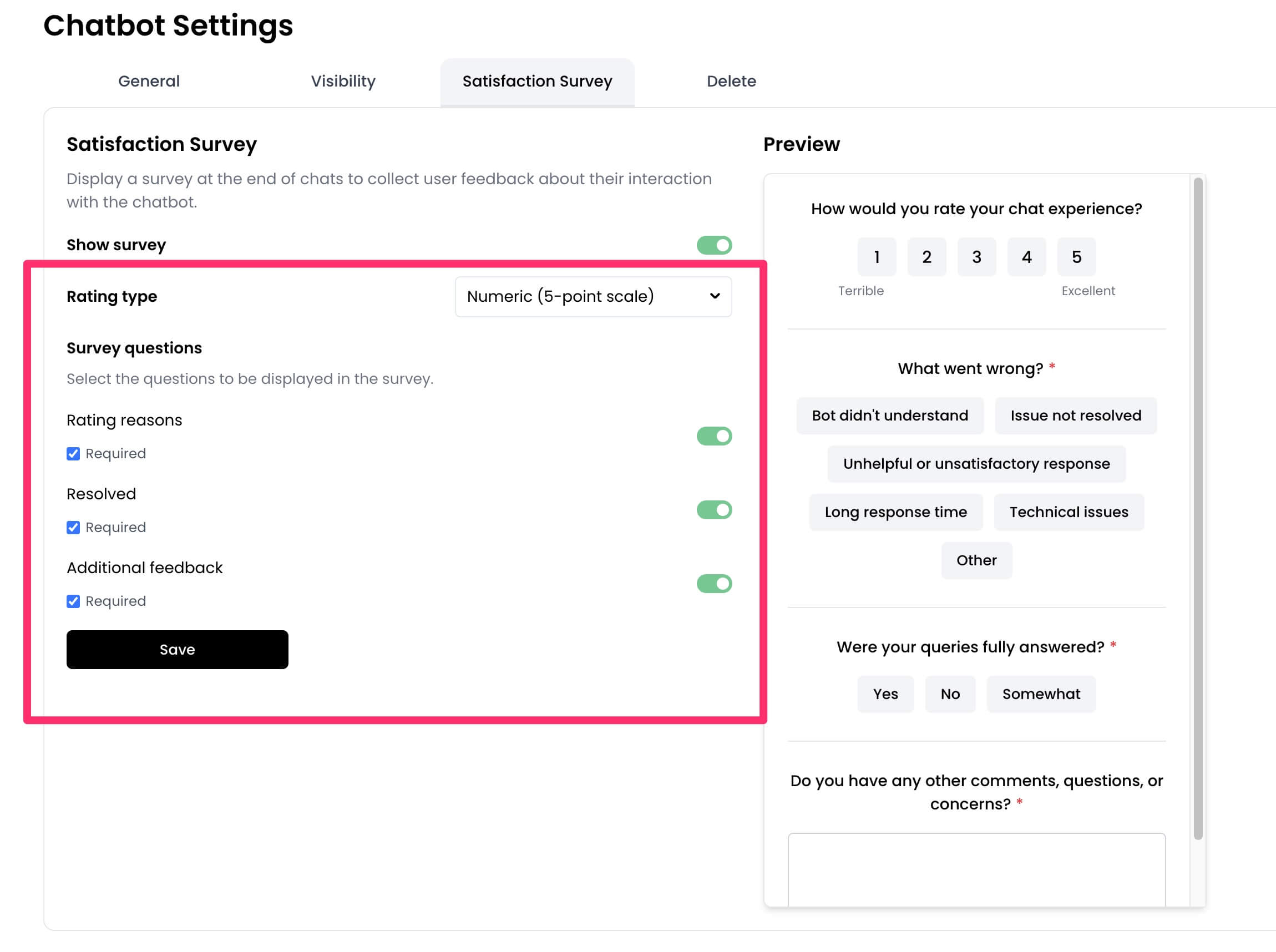 5. Click `Save` to apply the changes.
5. Click `Save` to apply the changes.
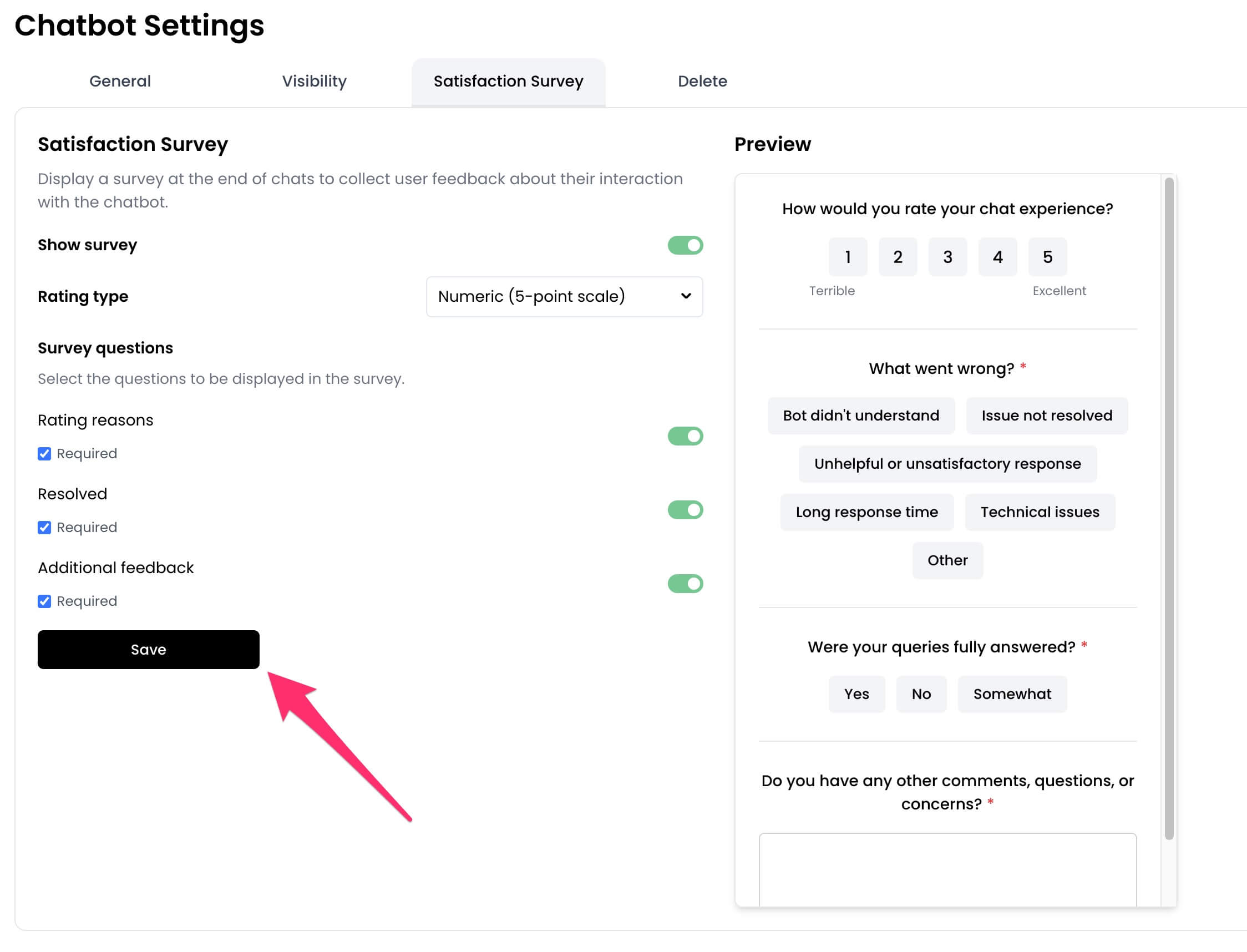 ## View survey responses
You can view survey responses from the `Conversations` page of your chatbot dashboard. If a conversation has a survey response, the result will appear within the conversation thread as well as on the `Details` section in the sidebar.
## View survey responses
You can view survey responses from the `Conversations` page of your chatbot dashboard. If a conversation has a survey response, the result will appear within the conversation thread as well as on the `Details` section in the sidebar.
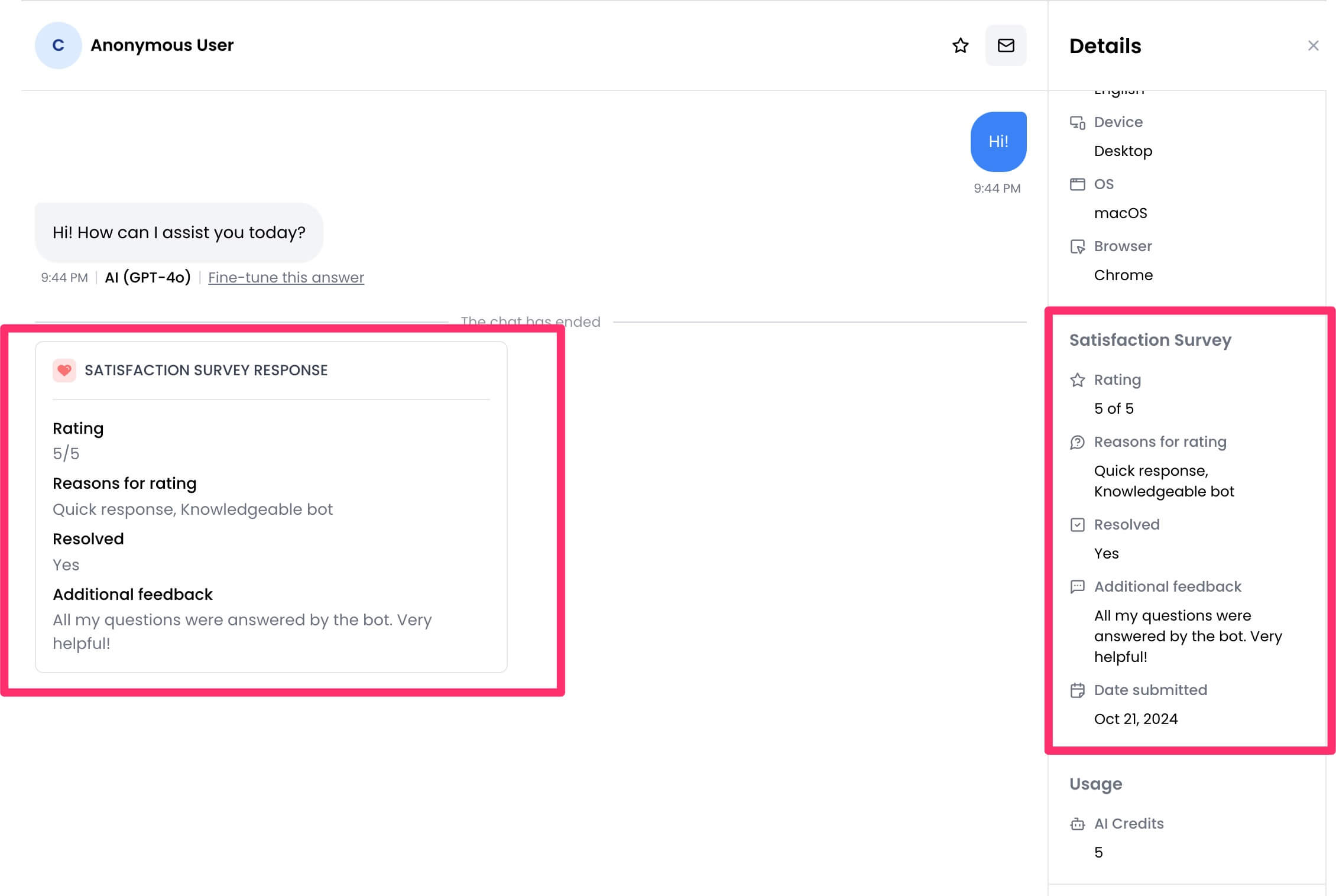 ---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/save-your-work.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Save your work
> Learn how to save your changes in the Builder.
Any changes you make to your chatbot's flow in the [Builder](/chatbot/builder/introduction) is saved automatically. You can also save it manually by clicking the `Save` button in the top right side of the screen.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/save-your-work.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Save your work
> Learn how to save your changes in the Builder.
Any changes you make to your chatbot's flow in the [Builder](/chatbot/builder/introduction) is saved automatically. You can also save it manually by clicking the `Save` button in the top right side of the screen.
 When you save your changes, it will be saved as a draft and will not be published. This allows you to work on the chatbot and test it without affecting the live version.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/blocks/action/send-email.md
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/ai-agent/actions/send-email.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Send Email
The Send Email action allows the AI Agent to send emails to one or more recipients. You can use it to send notifications, follow ups, order confirmations, transactional emails and other types of emails.
When you save your changes, it will be saved as a draft and will not be published. This allows you to work on the chatbot and test it without affecting the live version.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/blocks/action/send-email.md
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/ai-agent/actions/send-email.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Send Email
The Send Email action allows the AI Agent to send emails to one or more recipients. You can use it to send notifications, follow ups, order confirmations, transactional emails and other types of emails.
 ## Configuration
### `Action Name`
A short, specific identifier that tells the Agent what this action does (e.g. best\_sellers\_buttons, support\_button).
### `When to Use`
A detailed description of what the action does and when it must be used.
When applicable, you can specify one or more of the following:
* **Positive cues/phrases**: Example utterances and keywords that signal this action (include a few variations).
* **Preconditions**: What must be true before running.
* **Do not use when**: Explicit exclusions to avoid false triggers.
## Configuration
### `Action Name`
A short, specific identifier that tells the Agent what this action does (e.g. best\_sellers\_buttons, support\_button).
### `When to Use`
A detailed description of what the action does and when it must be used.
When applicable, you can specify one or more of the following:
* **Positive cues/phrases**: Example utterances and keywords that signal this action (include a few variations).
* **Preconditions**: What must be true before running.
* **Do not use when**: Explicit exclusions to avoid false triggers.
 ### `Frequency`
Specify how often the Agent can invoke this action to avoid overusing it, e.g `Once per chat` or `Whenever applicable`.
### `Frequency`
Specify how often the Agent can invoke this action to avoid overusing it, e.g `Once per chat` or `Whenever applicable`.
 ### `Input parameters`
Define the parameters the Agent must gather before sending the request. The Agent can capture these from user input, existing chat context, or saved contact data.
For each parameter, you can specify the following:
* **Name**: The name of the parameter. Must start with a letter and contain only letters, numbers, and underscores.
* **Description** (optional): A description of the parameter to indicate what it is and if applicable, the formatting rules and min/max length.
* **Save to variable** (optional): The variable where the data can be saved. Useful when you want to use the data in the email setup, such as the recipient's email address.
### `Email Setup`
Configure the email setup.
* **Sender Name**: The name of the sender.
* **To**: The email addresses of the recipients (max 5).
* **Reply-to**: The email addresses to reply to (max 5).
* **CC**: The email addresses of the recipients who will receive a copy of the email (max 5).
* **Subject**: The subject of the email.
* **Message**: The content of the email.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/ai/set-ai-model.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Setting the AI model
> Learn how to set the LLM model used by the AI.
There are various [AI models](/ai/supported-ai-models) available in Chatling that you can use to generate responses for your chatbot.
We recommend testing with different models to see which one works best for your chatbot and provides the most accurate responses. Each model uses a different amount of credits per response.
## How to set the AI model?
The method for choosing the AI model depends on the [Response Source](/chatbot/builder/blocks/ai/ai-response#what-is-the-response-source) that you've set for the [AI Response](/chatbot/builder/blocks/ai/ai-response) block.
Below are the instructions based on the response source you've selected.
### 1. Response Source: Knowledge Base
If you are using the Knowledge Base as the response source, you can set the AI model using the [AI Configuration menu](/chatbot/builder/sidebar#ai-configuration) in the Builder's sidebar.
1. Click on the AI Configuration menu in the sidebar.
### `Input parameters`
Define the parameters the Agent must gather before sending the request. The Agent can capture these from user input, existing chat context, or saved contact data.
For each parameter, you can specify the following:
* **Name**: The name of the parameter. Must start with a letter and contain only letters, numbers, and underscores.
* **Description** (optional): A description of the parameter to indicate what it is and if applicable, the formatting rules and min/max length.
* **Save to variable** (optional): The variable where the data can be saved. Useful when you want to use the data in the email setup, such as the recipient's email address.
### `Email Setup`
Configure the email setup.
* **Sender Name**: The name of the sender.
* **To**: The email addresses of the recipients (max 5).
* **Reply-to**: The email addresses to reply to (max 5).
* **CC**: The email addresses of the recipients who will receive a copy of the email (max 5).
* **Subject**: The subject of the email.
* **Message**: The content of the email.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/ai/set-ai-model.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Setting the AI model
> Learn how to set the LLM model used by the AI.
There are various [AI models](/ai/supported-ai-models) available in Chatling that you can use to generate responses for your chatbot.
We recommend testing with different models to see which one works best for your chatbot and provides the most accurate responses. Each model uses a different amount of credits per response.
## How to set the AI model?
The method for choosing the AI model depends on the [Response Source](/chatbot/builder/blocks/ai/ai-response#what-is-the-response-source) that you've set for the [AI Response](/chatbot/builder/blocks/ai/ai-response) block.
Below are the instructions based on the response source you've selected.
### 1. Response Source: Knowledge Base
If you are using the Knowledge Base as the response source, you can set the AI model using the [AI Configuration menu](/chatbot/builder/sidebar#ai-configuration) in the Builder's sidebar.
1. Click on the AI Configuration menu in the sidebar.
 2. Go to `Settings`.
2. Go to `Settings`.
 3. Select the AI model you want to use from the dropdown list.
3. Select the AI model you want to use from the dropdown list.
 Once you've selected the AI model, all AI Response blocks that use the Knowledge Base as the response source will use this model to generate responses.
#### Setting the model on a per-block basis
If you want to set the AI model on a per-block basis, you can do so by opening the AI Response block's editor and settings the `Model` option. This will override the default model set in the AI Configuration settings.
Once you've selected the AI model, all AI Response blocks that use the Knowledge Base as the response source will use this model to generate responses.
#### Setting the model on a per-block basis
If you want to set the AI model on a per-block basis, you can do so by opening the AI Response block's editor and settings the `Model` option. This will override the default model set in the AI Configuration settings.
 ### 2. Response Source: AI Model
If you are using the "AI Model" as the response source, you can set the AI model from the block's editor using the `Model` option.
### 2. Response Source: AI Model
If you are using the "AI Model" as the response source, you can set the AI model from the block's editor using the `Model` option.
 ---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/blocks/action/set-variable.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Set Variable
> Learn about the Set Variable block and how to set it up in the Builder.
The Set Variable block is used to set the value of one or more variables. With it, you can modify variable values dynamically at any point in the flow.
## How to configure
1. Click on the Set Variable block in the canvas to open its settings.
2. Select the variable you want to modify.
3. Select the type of the modification:
* **Value**: Set the variable to a specific value. You can also insert variables to make the value dynamic.
* **Add/Subtract/Multiply/Divide**: Perform a mathematical operation on the variable. You can add, subtract, multiply, or divide the variable by a specific value. The value must be a number.
4. Enter the value.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/blocks/action/set-variable.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Set Variable
> Learn about the Set Variable block and how to set it up in the Builder.
The Set Variable block is used to set the value of one or more variables. With it, you can modify variable values dynamically at any point in the flow.
## How to configure
1. Click on the Set Variable block in the canvas to open its settings.
2. Select the variable you want to modify.
3. Select the type of the modification:
* **Value**: Set the variable to a specific value. You can also insert variables to make the value dynamic.
* **Add/Subtract/Multiply/Divide**: Perform a mathematical operation on the variable. You can add, subtract, multiply, or divide the variable by a specific value. The value must be a number.
4. Enter the value.
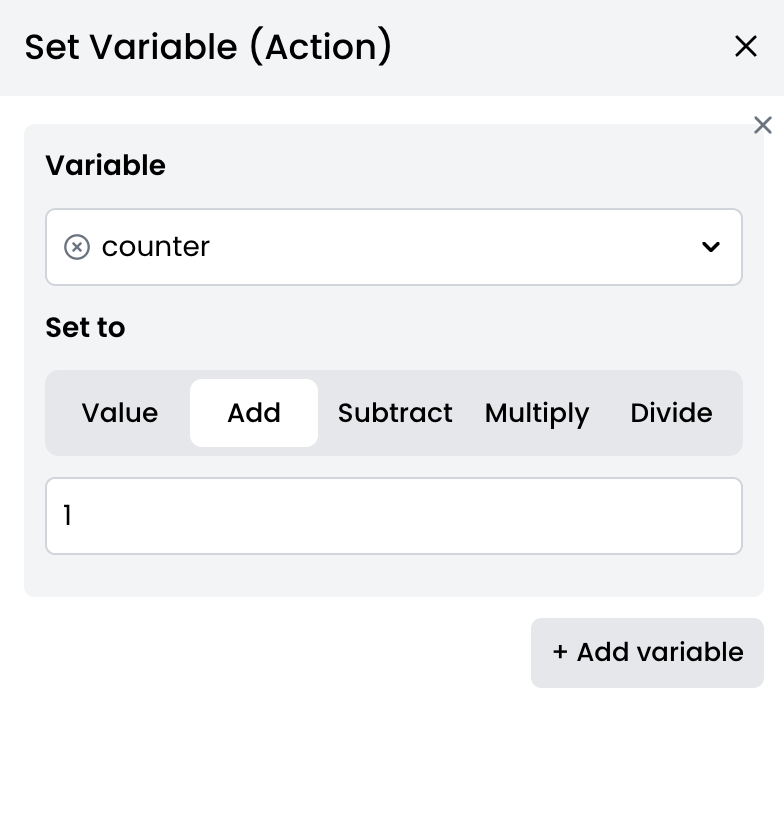 ## Multiple variables
You can set multiple variables at once by clicking on the **Add variable** button. This will add a new row where you can select another variable and set its value.
## Multiple variables
You can set multiple variables at once by clicking on the **Add variable** button. This will add a new row where you can select another variable and set its value.
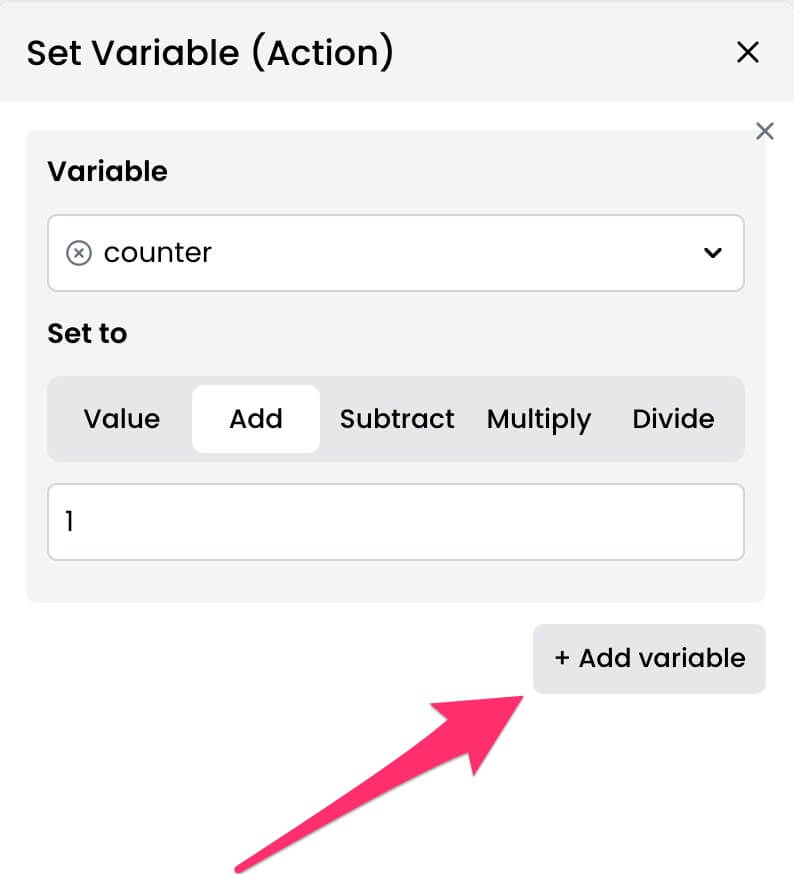 ## Example
Let's say you're building a lead generation chatbot for a real estate brokerage. You want to prompt the AI to ask the customer three questions about their requirements and forward the answers to the team. You can do this by using a counter variable that increments each time the user answers a question.
Below is a sample flow that demonstrates how to use the Set Variable block.
## Example
Let's say you're building a lead generation chatbot for a real estate brokerage. You want to prompt the AI to ask the customer three questions about their requirements and forward the answers to the team. You can do this by using a counter variable that increments each time the user answers a question.
Below is a sample flow that demonstrates how to use the Set Variable block.
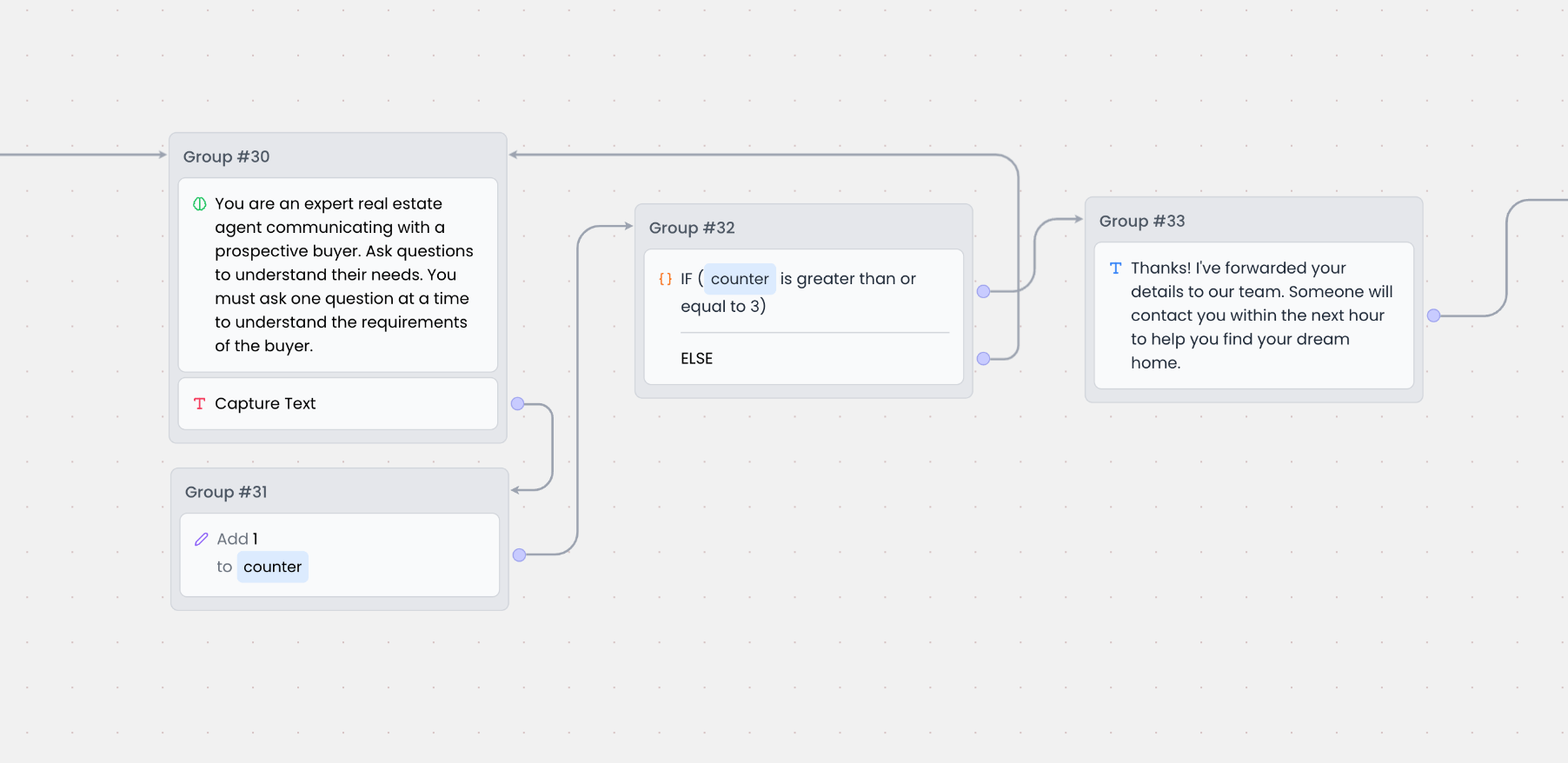 We're using a variable called `counter` to keep track of the number of questions that have been asked. This variable is incremented by 1 each time the user answers a question.
Then, we're using the Condition block to check if the counter is greater or equal to 3. If it is, a message is displayed to inform the user that their inquiry has been forwarded to the team. Else, the AI asks the next question.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/whatsapp/setup.md
# How to connect your WhatsApp Business account
When you create a WhatsApp chatbot, an onboarding is displayed to guide you through the process of connecting your WhatsApp Business account to Chatling. We'll walk you through the steps below.
## Before you start
The phone number you connect must not be in use by a WhatsApp account. If it's in use, you must delete the account from WhatsApp before continuing.
Here's how to delete a WhatsApp account:
1. Open the WhatsApp app.
2. Go to `Settings` > `Account` > `Delete my account`.
3. Type in your phone number for confirmation and tap on `Delete my account`.
Once deleted, the phone number can be used to connect a new WhatsApp Business account.
## How to connect your WhatsApp Business account
1. Click the `Login with Facebook` button.
We're using a variable called `counter` to keep track of the number of questions that have been asked. This variable is incremented by 1 each time the user answers a question.
Then, we're using the Condition block to check if the counter is greater or equal to 3. If it is, a message is displayed to inform the user that their inquiry has been forwarded to the team. Else, the AI asks the next question.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/whatsapp/setup.md
# How to connect your WhatsApp Business account
When you create a WhatsApp chatbot, an onboarding is displayed to guide you through the process of connecting your WhatsApp Business account to Chatling. We'll walk you through the steps below.
## Before you start
The phone number you connect must not be in use by a WhatsApp account. If it's in use, you must delete the account from WhatsApp before continuing.
Here's how to delete a WhatsApp account:
1. Open the WhatsApp app.
2. Go to `Settings` > `Account` > `Delete my account`.
3. Type in your phone number for confirmation and tap on `Delete my account`.
Once deleted, the phone number can be used to connect a new WhatsApp Business account.
## How to connect your WhatsApp Business account
1. Click the `Login with Facebook` button.
 2. A Facebook authentication window will open. Click the `Continue` button.
2. A Facebook authentication window will open. Click the `Continue` button.
 3. Select `Get started` to continue.
3. Select `Get started` to continue.
 4. Select a business profile or create a new one.
4. Select a business profile or create a new one.
 5. Choose or create a new WhatsApp Business account and profile.
5. Choose or create a new WhatsApp Business account and profile.
 6. Enter the required information to create a new business profile.
* *Skip this step if you selected an existing business profile.*
7. Add and verify your phone number.
* *Skip this step if you selected an existing business profile.*
6. Enter the required information to create a new business profile.
* *Skip this step if you selected an existing business profile.*
7. Add and verify your phone number.
* *Skip this step if you selected an existing business profile.*
 8. Click the `Continue` button.
8. Click the `Continue` button.
 9. Facebook begins verifying the information you provided. Once it's completed successfully, you should see a message similar to below. Click the `Finish` button.
9. Facebook begins verifying the information you provided. Once it's completed successfully, you should see a message similar to below. Click the `Finish` button.
 10. Go back to Chatling and a message will be displayed that your authentication is being processed. If successful, you should see a message similar to below.
10. Go back to Chatling and a message will be displayed that your authentication is being processed. If successful, you should see a message similar to below.
 11. Next, you must enter a six digit code for two-factor authentication so that your phone number can be registered with WhatsApp. If the number already has 2FA enabled, enter the same code you had set up.
11. Next, you must enter a six digit code for two-factor authentication so that your phone number can be registered with WhatsApp. If the number already has 2FA enabled, enter the same code you had set up.
 12. Once the phone number is registered successfully, you're all set and your WhatsApp Business account is connected to Chatling. Click the `Open Dashboard` button to continue.
12. Once the phone number is registered successfully, you're all set and your WhatsApp Business account is connected to Chatling. Click the `Open Dashboard` button to continue.
 WhatsApp provides 1,000 free conversations per month. If you reach this limit, you must add a payment method in your Facebook Business Manager to continue sending and receiving messages.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/general-settings/sharing.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Share
> A guide on how to share your chatbot or agent with others.
You can generate a unique link for your chatbot or agent, and share it with others for testing, collaboration, or other purposes. Here's how to do it:
1. From the dashboard, click `Share`.
WhatsApp provides 1,000 free conversations per month. If you reach this limit, you must add a payment method in your Facebook Business Manager to continue sending and receiving messages.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/general-settings/sharing.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Share
> A guide on how to share your chatbot or agent with others.
You can generate a unique link for your chatbot or agent, and share it with others for testing, collaboration, or other purposes. Here's how to do it:
1. From the dashboard, click `Share`.
 2. Click `Generate Link`.
2. Click `Generate Link`.
 3. To password protect the link, enable `Require password` and type in a password.
3. To password protect the link, enable `Require password` and type in a password.
 4. Copy the link and share it with others.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/web-widget/installation/shopify.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Shopify
> Learn how to add Chatling to your Shopify store
## Method 1: Using theme.liquid
1. Go to your dashboard.
2. Click `Deploy` button in the sidebar menu.
4. Copy the link and share it with others.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/web-widget/installation/shopify.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Shopify
> Learn how to add Chatling to your Shopify store
## Method 1: Using theme.liquid
1. Go to your dashboard.
2. Click `Deploy` button in the sidebar menu.
 3. Click the `Manage` button under the `Website Widget` option.
3. Click the `Manage` button under the `Website Widget` option.
 4. Design the appearance of the widget by clicking the `Open widget designer` button.
4. Design the appearance of the widget by clicking the `Open widget designer` button.
 5. Select the display mode for your chatbot, such as "Floating Chat", "Inline", or "Fullscreen".
5. Select the display mode for your chatbot, such as "Floating Chat", "Inline", or "Fullscreen".
 6. Copy the widget code.
6. Copy the widget code.
 7. Go to your Shopify dashboard and click on `Online Store` from the sidebar.
7. Go to your Shopify dashboard and click on `Online Store` from the sidebar.
 8. Edit your theme by clicking the ellipsis icon next to your current theme and choosing `Edit code`.
8. Edit your theme by clicking the ellipsis icon next to your current theme and choosing `Edit code`.
 9. Find and open the `theme.liquid` file From the sidebar where the list of files is displayed.
9. Find and open the `theme.liquid` file From the sidebar where the list of files is displayed.
 10. Paste the widget code in the `` section. You can paste it anywhere between the opening `` tag and the closing `` tag.
10. Paste the widget code in the `` section. You can paste it anywhere between the opening `` tag and the closing `` tag.
 11. Click the Save button.
The chatbot will be live on your website and should appear across all your store's pages.
11. Click the Save button.
The chatbot will be live on your website and should appear across all your store's pages.
 ## Method 2: Using Customization
1. Follow steps 1-6 from Method 1 to copy the widget code.
2. From your Shopify dashboard, click on `Online Store` and go to `Themes`.
## Method 2: Using Customization
1. Follow steps 1-6 from Method 1 to copy the widget code.
2. From your Shopify dashboard, click on `Online Store` and go to `Themes`.
 3. Click on the `Customize` button next to your current theme.
3. Click on the `Customize` button next to your current theme.
 4. Under the `Header` section, choose `Add section`. Search for `Custom liquid` and add it.
4. Under the `Header` section, choose `Add section`. Search for `Custom liquid` and add it.
 5. Open the `Custom liquid` editor and paste your widget code into the `Liquid code` field.
5. Open the `Custom liquid` editor and paste your widget code into the `Liquid code` field.
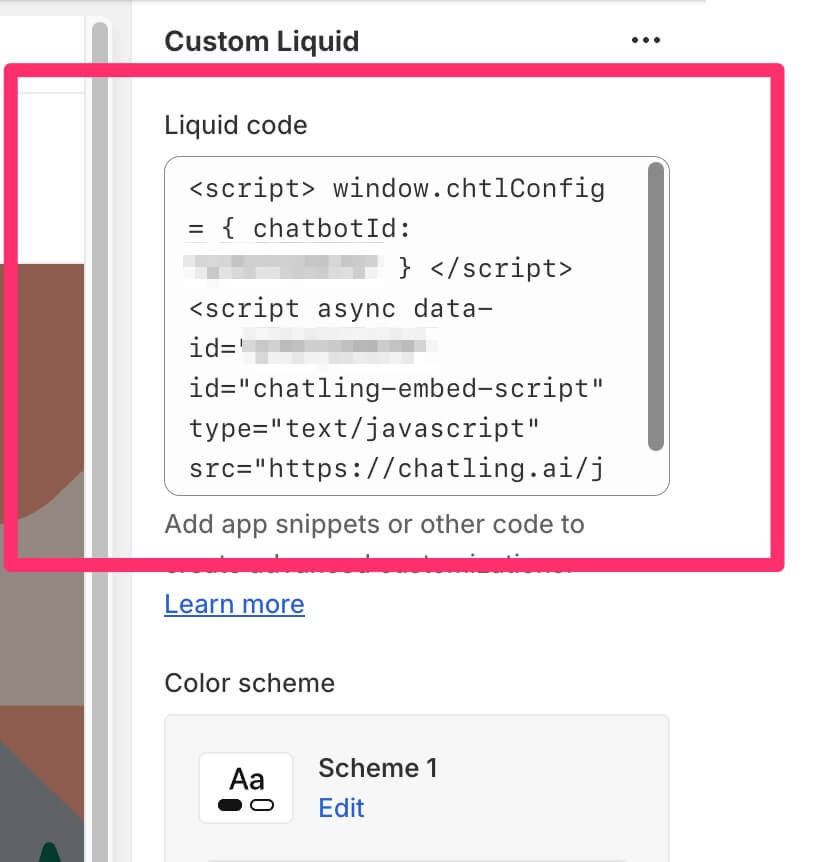 6. Set the `Top padding` and `Bottom padding` to `0` so the section doesn't create a blank space in your site's header.
6. Set the `Top padding` and `Bottom padding` to `0` so the section doesn't create a blank space in your site's header.
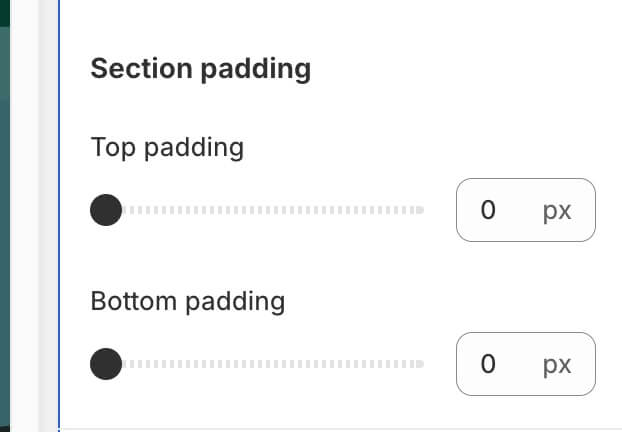 7. Click the `Save` button.
The widget will be live on your website and should appear across all your store's pages.
7. Click the `Save` button.
The widget will be live on your website and should appear across all your store's pages.
 ---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/sidebar.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Sidebar
> Learn about the Sidebar and its functionalities in the Builder.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/sidebar.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Sidebar
> Learn about the Sidebar and its functionalities in the Builder.
 The sidebar contains four menus:
* Blocks
* Variables
* AI Configuration
* Settings
## Sidebar Menus
### Blocks
The Blocks menu contains all the blocks you can add to your flow. [Blocks](/chatbot/builder/blocks/overview) build up the conversational flow of your chatbot.
You can drag and drop blocks onto the canvas to add them to your flow.

Here are the different categories of blocks that are available:
* **Send message**: Display a message to the user.
* **Capture response**: Capture answers from the user, such as text, email, form submission, and more.
* **AI**: Use AI to generate responses to user's questions.
* **Logic**: Add conditions and logic to your flow.
* **Integration**: Connect your chatbot to external services.
### Variables
Variables are placeholders that store information during the conversation. You can use variables to store user inputs, API responses, and more. These variables can be used to personalize the conversation and make it more dynamic.
The sidebar contains four menus:
* Blocks
* Variables
* AI Configuration
* Settings
## Sidebar Menus
### Blocks
The Blocks menu contains all the blocks you can add to your flow. [Blocks](/chatbot/builder/blocks/overview) build up the conversational flow of your chatbot.
You can drag and drop blocks onto the canvas to add them to your flow.

Here are the different categories of blocks that are available:
* **Send message**: Display a message to the user.
* **Capture response**: Capture answers from the user, such as text, email, form submission, and more.
* **AI**: Use AI to generate responses to user's questions.
* **Logic**: Add conditions and logic to your flow.
* **Integration**: Connect your chatbot to external services.
### Variables
Variables are placeholders that store information during the conversation. You can use variables to store user inputs, API responses, and more. These variables can be used to personalize the conversation and make it more dynamic.
 There are two types of variables:
* **System variables**: These are predefined variables that store system information or can be used to perform a specific action. For example, the `contact_email` variable can be used to store the user's email address and save them as a lead.
If you click on a system variable, you can view its purpose.
There are also additional system variables that aren't imported by default. To view and import them, click the `Import system variables` button.
* **Custom variables**: These are variables you create to store information specific to your chatbot. For example, you can create a custom variable to store the user's question and use it in the `AI Response` block to generate a response from the AI.
### AI Configuration
The AI Configuration menu allows you to configure the default AI settings for your chatbot. These settings are used when the chatbot generates AI responses using the Knowledge Base.
There are two types of variables:
* **System variables**: These are predefined variables that store system information or can be used to perform a specific action. For example, the `contact_email` variable can be used to store the user's email address and save them as a lead.
If you click on a system variable, you can view its purpose.
There are also additional system variables that aren't imported by default. To view and import them, click the `Import system variables` button.
* **Custom variables**: These are variables you create to store information specific to your chatbot. For example, you can create a custom variable to store the user's question and use it in the `AI Response` block to generate a response from the AI.
### AI Configuration
The AI Configuration menu allows you to configure the default AI settings for your chatbot. These settings are used when the chatbot generates AI responses using the Knowledge Base.
 You can configure the following settings:
* **Instructions**: Provide instructions to the AI to tailor its responses. For example, you can instruct the AI to provide more detailed responses or to use a specific tone. You can click the `View examples` button to see examples of instructions you can provide.
* **Settings**:
* **Business, product, or brand name**: This will be used by the AI to generate more relevant responses and avoids answering off-topics questions that aren't related to your business, product, or brand, such as questions related to your competitors, weather, etc.
* **AI Model**: The AI model to use for generating responses. Every model uses a different amount of credits per response. We recommend testing with different models to see which one works best for your chatbot.
* **Language**: The language in which the AI should generate responses. If you set it to Auto, the AI will detect the language of the user's question and generate a response in the same language.
* **Temperature**: Controls the randomness of the responses. A higher temperature will generate more creative responses, while a lower temperature will generate more accurate responses.
### Settings
The Settings menu allows you to configure the chatbot's general settings. Here's what you can configure:
* **Message Delay**: The time delay in seconds between chatbot's messages.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/web-widget/installation/squarespace.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Squarespace
> Learn how to add Chatling to your Squarespace website
1. Go to your dashboard.
2. Click `Deploy` button in the sidebar menu.
You can configure the following settings:
* **Instructions**: Provide instructions to the AI to tailor its responses. For example, you can instruct the AI to provide more detailed responses or to use a specific tone. You can click the `View examples` button to see examples of instructions you can provide.
* **Settings**:
* **Business, product, or brand name**: This will be used by the AI to generate more relevant responses and avoids answering off-topics questions that aren't related to your business, product, or brand, such as questions related to your competitors, weather, etc.
* **AI Model**: The AI model to use for generating responses. Every model uses a different amount of credits per response. We recommend testing with different models to see which one works best for your chatbot.
* **Language**: The language in which the AI should generate responses. If you set it to Auto, the AI will detect the language of the user's question and generate a response in the same language.
* **Temperature**: Controls the randomness of the responses. A higher temperature will generate more creative responses, while a lower temperature will generate more accurate responses.
### Settings
The Settings menu allows you to configure the chatbot's general settings. Here's what you can configure:
* **Message Delay**: The time delay in seconds between chatbot's messages.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/web-widget/installation/squarespace.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Squarespace
> Learn how to add Chatling to your Squarespace website
1. Go to your dashboard.
2. Click `Deploy` button in the sidebar menu.
 3. Click the `Manage` button under the `Website Widget` option.
3. Click the `Manage` button under the `Website Widget` option.
 4. Design the appearance of the widget by clicking the `Open widget designer` button.
4. Design the appearance of the widget by clicking the `Open widget designer` button.
 5. Select the display mode for your chatbot, such as "Floating Chat", "Inline", or "Fullscreen".
5. Select the display mode for your chatbot, such as "Floating Chat", "Inline", or "Fullscreen".
 6. Copy the widget code.
6. Copy the widget code.
 7. Sign in to your Squarespace account and open the website where you want to add the widget.
7. Sign in to your Squarespace account and open the website where you want to add the widget.
 8. From the sidebar menu, select `Website`.
8. From the sidebar menu, select `Website`.
 9. Scroll to the bottom of the sidebar menu and choose `Website Tools`.
9. Scroll to the bottom of the sidebar menu and choose `Website Tools`.
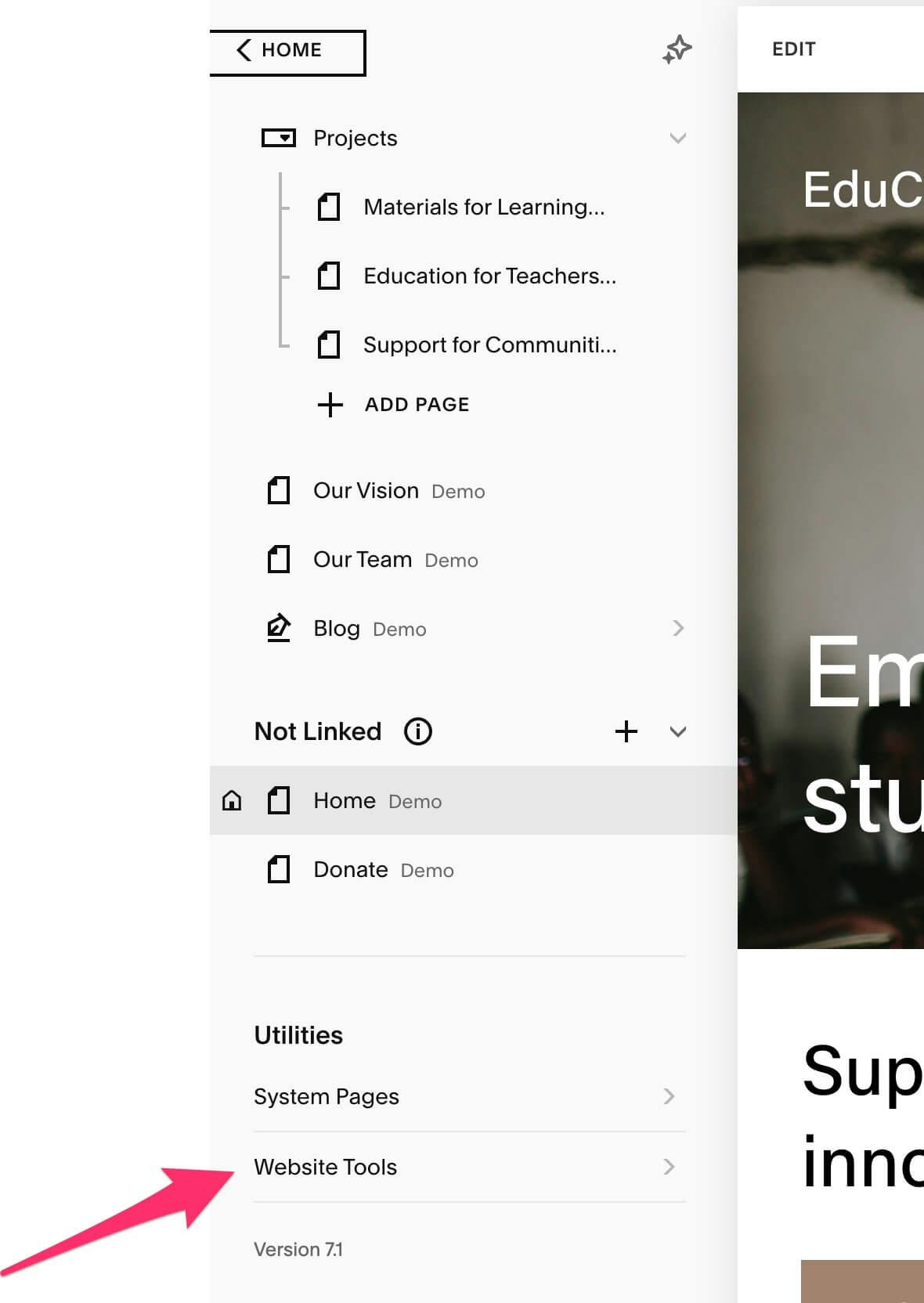 10. Open `Code Injection`.
* If you're on an older version of Squarespace, such as v7.0, code injection is located in `Settings` > `Developer Tools` > `Code Injection`.
10. Open `Code Injection`.
* If you're on an older version of Squarespace, such as v7.0, code injection is located in `Settings` > `Developer Tools` > `Code Injection`.
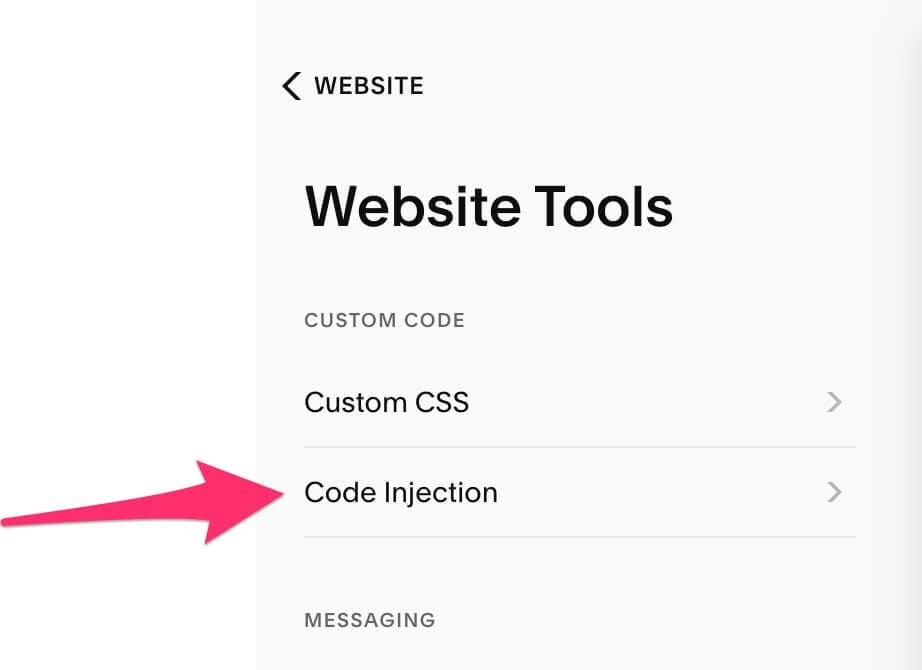 11. Paste the widget code in the `Header` section, and click `Save`.
11. Paste the widget code in the `Header` section, and click `Save`.
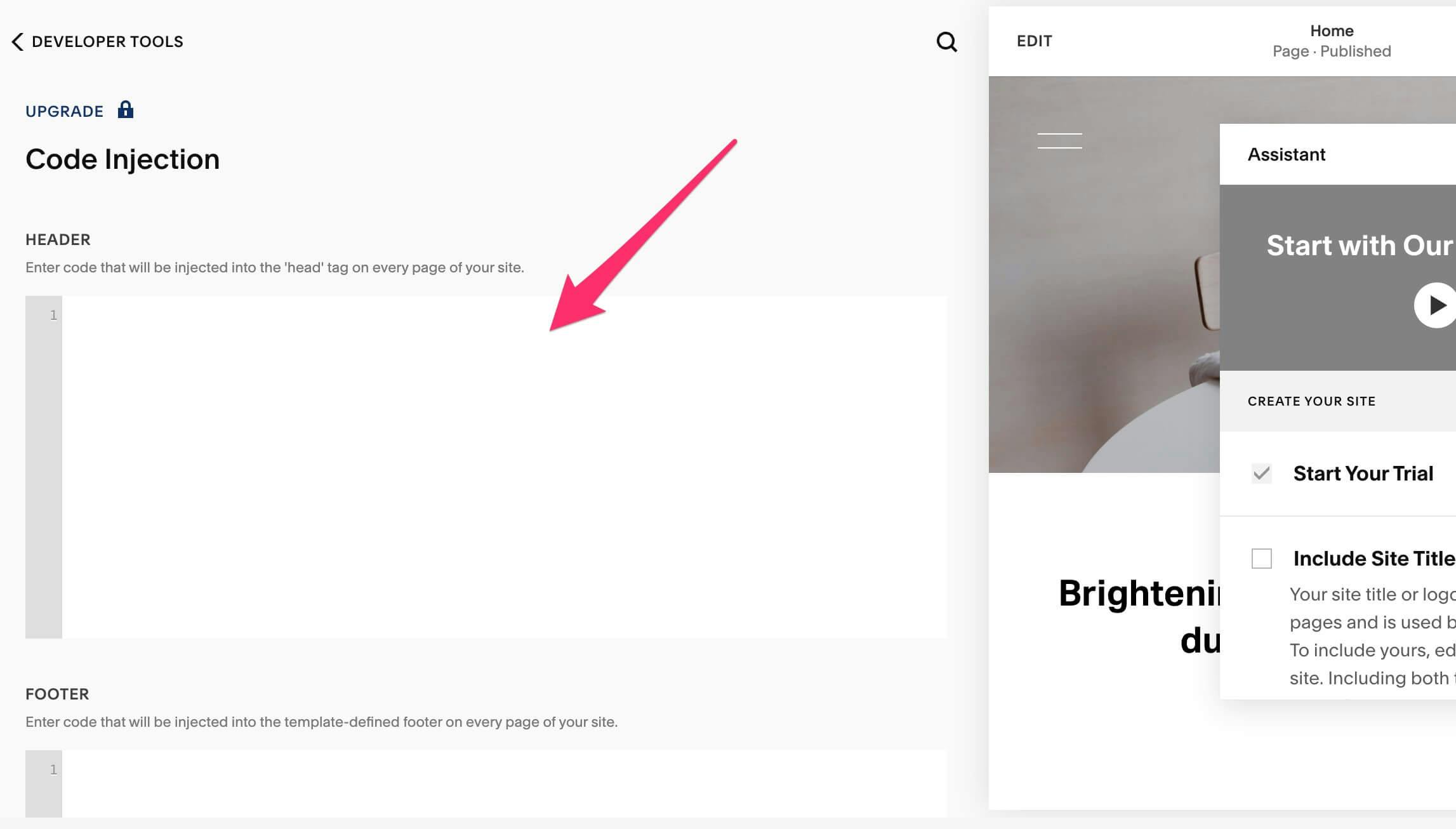 12. The widget is now live on your website, and visitors can interact with it.
12. The widget is now live on your website, and visitors can interact with it.
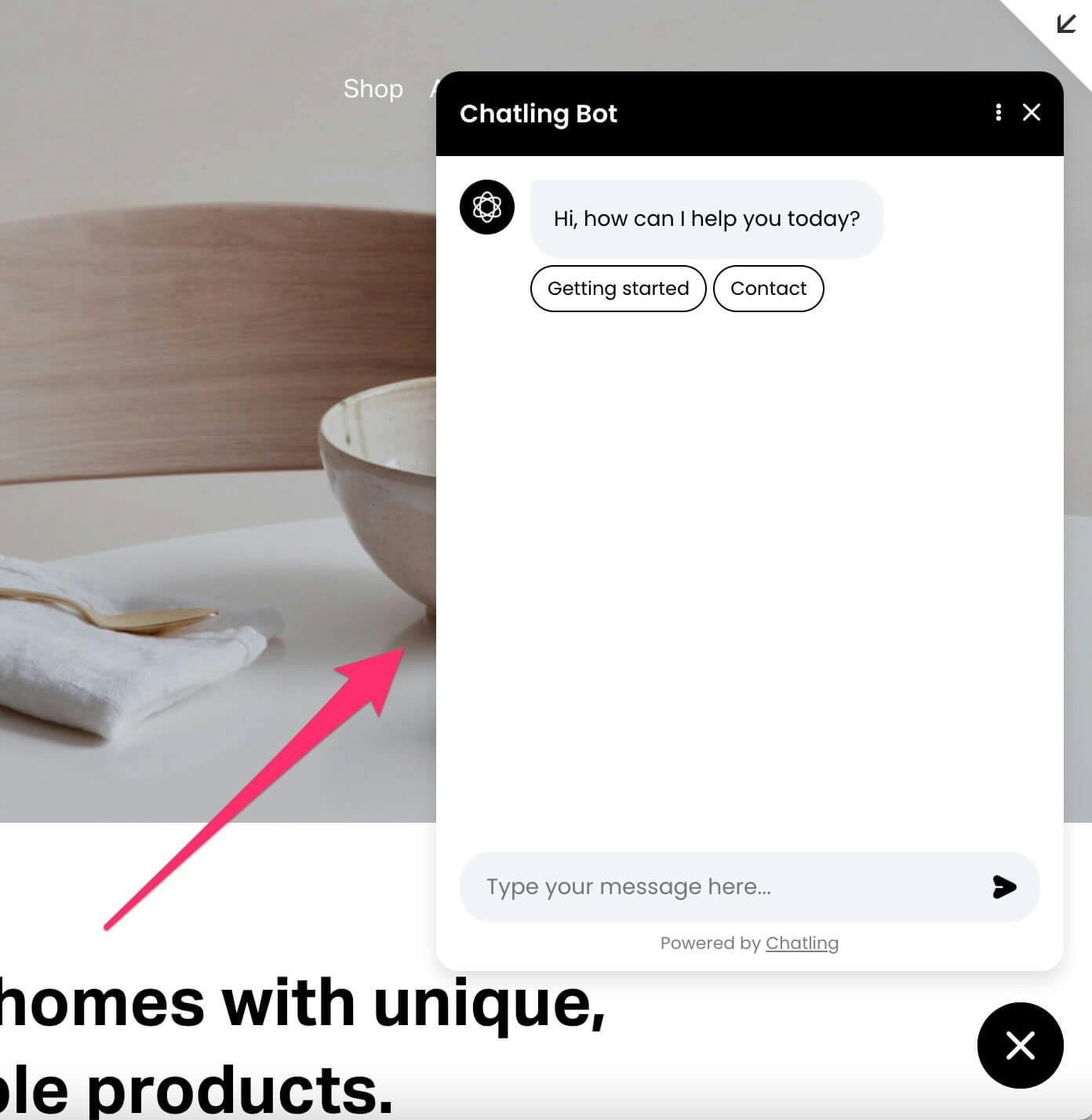 ---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/ai/supported-ai-models.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Supported AI models
> A list of supported AI models in Chatling.
Chatling supports the following LLMs:
* GPT-5.1
* GPT-5
* GPT-5 Mini
* GPT-5 Nano
* GPT-4.1
* GPT-4.1 Mini
* GPT-4.1 Nano
* GPT-4o
* GPT-4o Mini
* o4 Mini
* o3 Mini
* Claude Opus 4
* Claude Opus 3
* Claude Sonnet 4
* Claude Sonnet 3.7
* Claude Sonnet 3.5
* Claude Haiku 3.5
* Claude Haiku 3
* Gemini 2.5 Pro
* Gemini 2.5 Flash
* Gemini 2.0 Flash
To request a new AI model, please [contact us](mailto:support@chatling.ai).
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/test-your-chatbot.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Test your chatbot
> Learn how to test your chatbot to see how it works.
While you're building the chatbot, you can test it to see how it works. This allows you to identify any issues and make improvements before publishing it.
Click the `Preview bot` button in the top right corner of the Builder to launch the chatbot for testing.

---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/blocks/send/text.md
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/blocks/inputs/text.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Text Block
> Learn about the Text input block and how to set it up in the Builder.
The Text block is used to capture user input in the form of text. You can use this block to prompt users for answers and collect the necessary information.
## Configuration
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/ai/supported-ai-models.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Supported AI models
> A list of supported AI models in Chatling.
Chatling supports the following LLMs:
* GPT-5.1
* GPT-5
* GPT-5 Mini
* GPT-5 Nano
* GPT-4.1
* GPT-4.1 Mini
* GPT-4.1 Nano
* GPT-4o
* GPT-4o Mini
* o4 Mini
* o3 Mini
* Claude Opus 4
* Claude Opus 3
* Claude Sonnet 4
* Claude Sonnet 3.7
* Claude Sonnet 3.5
* Claude Haiku 3.5
* Claude Haiku 3
* Gemini 2.5 Pro
* Gemini 2.5 Flash
* Gemini 2.0 Flash
To request a new AI model, please [contact us](mailto:support@chatling.ai).
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/test-your-chatbot.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Test your chatbot
> Learn how to test your chatbot to see how it works.
While you're building the chatbot, you can test it to see how it works. This allows you to identify any issues and make improvements before publishing it.
Click the `Preview bot` button in the top right corner of the Builder to launch the chatbot for testing.

---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/blocks/send/text.md
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/blocks/inputs/text.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Text Block
> Learn about the Text input block and how to set it up in the Builder.
The Text block is used to capture user input in the form of text. You can use this block to prompt users for answers and collect the necessary information.
## Configuration
 You can configure the following settings for the Text block:
* **Store answer in variable**: Choose a variable to store the user's response. You can use the stored data in other blocks to personalize the conversation.
* **Input required**: Determine whether the user must provide an answer to proceed. If this option is disabled, a Skip button will appear, allowing users to skip the input.
* **[Voice Input](/chatbot/builder/block-options/voice-input)**: Toggle on the Voice Input option to allow users to send messages using voice.
* **Min. characters**: The minimum number of characters the user must enter.
* **Max. characters**: The maximum number of characters the user can enter.
* **[Quick replies](/chatbot/builder/block-options/quick-replies)**
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/api-reference/v2/chatbots/update-chatbot-settings.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Update chatbot settings
> Update the settings of a chatbot.
## Request parameters
### Path
The chatbot ID.
### Body
The chatbot name.
The visibility of the chatbot. Possible values are `public` and `private`.
## Response
The status of the request. Will be `success` if the request was successful, otherwise `error`.
The unique identifier of the chatbot.
The name of the chatbot.
The version of the chatbot.
The visibility of the chatbot.
The date and time when the chatbot was created.
```json theme={null}
{
"status": "success",
"data": {
"id": "9761342719",
"name": "My chatbot",
"version": "2.0",
"visibility": "public",
"created_at": "2024-06-17T12:00:00+00:00"
}
}
```
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/blocks/hubspot/update-company.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Update Company
> Update companies in HubSpot from your chatbot.
Easily update companies in HubSpot through your chatbot to keep your CRM up to date automatically.
## Configuration
1. Click the `Connect account` button under the Account field to connect your HubSpot account to Chatling or select an existing connection.
2. The `Search method` determines how the contact is found in HubSpot. Currently, only searching by company ID is supported.
3. Add the properties you want to update for the company. You can enter variables in certain fields for dynamic values.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/blocks/hubspot/update-contact.md
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/blocks/action/update-contact.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Update Contact Block
> Learn about the Update Contact block and how to set it up in the Builder.
The `Update Contact` block can be used to update an existing contact.
The block consists of the following components:
* **Search**: Specify the field and value to use to look up the contact. You can enter a variable to search dynamically.
* **Contact details**: Define the properties you want to update.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/api-reference/v2/conversations/update-conversation.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Update conversation
> Update a conversation's properties.
## Request parameters
### Path
The chatbot ID.
The conversation ID.
### Body
At least one of the following properties is required.
Whether to archive the conversation.
Whether to mark the conversation as important.
The ID of the contact to associate with the conversation.
## Response
The status of the request. Will be `success` if the request was successful, otherwise `error`.
The unique identifier of the conversation.
The unique identifier of the contact associated with the conversation.
Whether the conversation is archived (by the admin).
Whether the conversation is marked as important.
The date and time when the conversation was created.
The unique identifier of the message.
The text content of the message.
The role of the sender of the message (bot, user, or system).
Whether the message is generated by the AI using the knowledge base.
The data of the message. Varies depending on the message type.
(AI response) Whether the AI's response was marked as helpful by the user. Possible values are `1` for helpful, `0` for not helpful, and `null` for not rated.
(AI response) The sources used by the AI to generate the response.
The date and time when the message was created.
```json theme={null}
{
"status": "success",
"data": {
"id": "8977617953",
"contact_id": "qtr89df0-112d-d197-b541-3f8674663246",
"archived": 0,
"important": 1,
"created_at": "2024-06-14T15:45:34+00:00",
"messages": [
{
"text": "System variables are predefined variables that contain system information or can be used to perform specific actions. These variables are automatically created by the Builder.",
"role": "bot",
"is_ai_kb_response": true,
"data": {
"helpful_value": null,
"sources": [
{
"type": "webpage",
"title": "Types of variables - Chatling Documentation",
"url": "https://docs.chatling.ai/builder/variables/variable-types"
},
{
"type": "webpage",
"title": "Sidebar - Chatling Documentation",
"url": "https://docs.chatling.ai/builder/sidebar"
},
{
"type": "webpage",
"title": "What are variables? - Chatling Documentation",
"url": "https://docs.chatling.ai/builder/variables/what-are-variables"
}
]
},
"created_at": "2024-06-17T16:09:52+00:00"
},
{
"text": "What are system variables",
"role": "user",
"created_at": "2024-06-17T16:09:45+00:00"
},
{
"text": "**Hello! How can I assist you today?**\n\nIf you have any questions related to our chatbot or services, please feel free to ask. I'm here to help!",
"role": "bot",
"is_ai_kb_response": true,
"data": {
"helpful_value": null,
"sources": []
},
"created_at": "2024-06-14T15:45:39+00:00"
},
{
"text": "Hello!",
"role": "user",
"created_at": "2024-06-14T15:45:34+00:00"
}
]
}
}
```
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/api-reference/v2/project/update-settings.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Update settings
> Update the project settings.
## Request parameters
### Body
The project name.
## Response
The status of the request. Will be `success` if the request was successful, otherwise `error`.
The unique identifier of the project.
The name of the project.
```json Response theme={null}
{
"status": "success",
"data": {
"project_id": "8917794239",
"name": "My project"
}
}
```
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/blocks/send/url-button.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# URL Button Block
> Learn about the URL Button block and how to set it up in the builder
The URL Button block displays buttons that redirect users to other pages.
You can configure the following settings for the Text block:
* **Store answer in variable**: Choose a variable to store the user's response. You can use the stored data in other blocks to personalize the conversation.
* **Input required**: Determine whether the user must provide an answer to proceed. If this option is disabled, a Skip button will appear, allowing users to skip the input.
* **[Voice Input](/chatbot/builder/block-options/voice-input)**: Toggle on the Voice Input option to allow users to send messages using voice.
* **Min. characters**: The minimum number of characters the user must enter.
* **Max. characters**: The maximum number of characters the user can enter.
* **[Quick replies](/chatbot/builder/block-options/quick-replies)**
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/api-reference/v2/chatbots/update-chatbot-settings.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Update chatbot settings
> Update the settings of a chatbot.
## Request parameters
### Path
The chatbot ID.
### Body
The chatbot name.
The visibility of the chatbot. Possible values are `public` and `private`.
## Response
The status of the request. Will be `success` if the request was successful, otherwise `error`.
The unique identifier of the chatbot.
The name of the chatbot.
The version of the chatbot.
The visibility of the chatbot.
The date and time when the chatbot was created.
```json theme={null}
{
"status": "success",
"data": {
"id": "9761342719",
"name": "My chatbot",
"version": "2.0",
"visibility": "public",
"created_at": "2024-06-17T12:00:00+00:00"
}
}
```
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/blocks/hubspot/update-company.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Update Company
> Update companies in HubSpot from your chatbot.
Easily update companies in HubSpot through your chatbot to keep your CRM up to date automatically.
## Configuration
1. Click the `Connect account` button under the Account field to connect your HubSpot account to Chatling or select an existing connection.
2. The `Search method` determines how the contact is found in HubSpot. Currently, only searching by company ID is supported.
3. Add the properties you want to update for the company. You can enter variables in certain fields for dynamic values.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/blocks/hubspot/update-contact.md
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/blocks/action/update-contact.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Update Contact Block
> Learn about the Update Contact block and how to set it up in the Builder.
The `Update Contact` block can be used to update an existing contact.
The block consists of the following components:
* **Search**: Specify the field and value to use to look up the contact. You can enter a variable to search dynamically.
* **Contact details**: Define the properties you want to update.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/api-reference/v2/conversations/update-conversation.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Update conversation
> Update a conversation's properties.
## Request parameters
### Path
The chatbot ID.
The conversation ID.
### Body
At least one of the following properties is required.
Whether to archive the conversation.
Whether to mark the conversation as important.
The ID of the contact to associate with the conversation.
## Response
The status of the request. Will be `success` if the request was successful, otherwise `error`.
The unique identifier of the conversation.
The unique identifier of the contact associated with the conversation.
Whether the conversation is archived (by the admin).
Whether the conversation is marked as important.
The date and time when the conversation was created.
The unique identifier of the message.
The text content of the message.
The role of the sender of the message (bot, user, or system).
Whether the message is generated by the AI using the knowledge base.
The data of the message. Varies depending on the message type.
(AI response) Whether the AI's response was marked as helpful by the user. Possible values are `1` for helpful, `0` for not helpful, and `null` for not rated.
(AI response) The sources used by the AI to generate the response.
The date and time when the message was created.
```json theme={null}
{
"status": "success",
"data": {
"id": "8977617953",
"contact_id": "qtr89df0-112d-d197-b541-3f8674663246",
"archived": 0,
"important": 1,
"created_at": "2024-06-14T15:45:34+00:00",
"messages": [
{
"text": "System variables are predefined variables that contain system information or can be used to perform specific actions. These variables are automatically created by the Builder.",
"role": "bot",
"is_ai_kb_response": true,
"data": {
"helpful_value": null,
"sources": [
{
"type": "webpage",
"title": "Types of variables - Chatling Documentation",
"url": "https://docs.chatling.ai/builder/variables/variable-types"
},
{
"type": "webpage",
"title": "Sidebar - Chatling Documentation",
"url": "https://docs.chatling.ai/builder/sidebar"
},
{
"type": "webpage",
"title": "What are variables? - Chatling Documentation",
"url": "https://docs.chatling.ai/builder/variables/what-are-variables"
}
]
},
"created_at": "2024-06-17T16:09:52+00:00"
},
{
"text": "What are system variables",
"role": "user",
"created_at": "2024-06-17T16:09:45+00:00"
},
{
"text": "**Hello! How can I assist you today?**\n\nIf you have any questions related to our chatbot or services, please feel free to ask. I'm here to help!",
"role": "bot",
"is_ai_kb_response": true,
"data": {
"helpful_value": null,
"sources": []
},
"created_at": "2024-06-14T15:45:39+00:00"
},
{
"text": "Hello!",
"role": "user",
"created_at": "2024-06-14T15:45:34+00:00"
}
]
}
}
```
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/api-reference/v2/project/update-settings.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Update settings
> Update the project settings.
## Request parameters
### Body
The project name.
## Response
The status of the request. Will be `success` if the request was successful, otherwise `error`.
The unique identifier of the project.
The name of the project.
```json Response theme={null}
{
"status": "success",
"data": {
"project_id": "8917794239",
"name": "My project"
}
}
```
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/blocks/send/url-button.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# URL Button Block
> Learn about the URL Button block and how to set it up in the builder
The URL Button block displays buttons that redirect users to other pages.
 ## Adding URL buttons
1. Drag and drop the URL Button block on the canvas.
## Adding URL buttons
1. Drag and drop the URL Button block on the canvas.
 2. Click on the block to edit it.
3. Click `Add button` button to add a new button.
2. Click on the block to edit it.
3. Click `Add button` button to add a new button.
 4. Enter the button label and URL. The label is the text that will be displayed on the button.
4. Enter the button label and URL. The label is the text that will be displayed on the button.
 5. To add more buttons, click the `+` icon.
5. To add more buttons, click the `+` icon.
 ---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/blocks/inputs/url.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# URL Block
> Learn about the URL input block and how to set it up in the Builder.
The URL block is used to collect URLs from users. It validates the user's input to ensure that it is a valid URL.
You can use this block to ask users for website URLs, social media profiles, or any other web addresses.
## Configuration
The URL block has the following configuration options:
* **Store answer in variable**: The variable where the user's input will be stored.
* **Input required**: Whether the user's input is mandatory. If disabled, a Skip button will appear, allowing users to skip the input.
* **[Quick replies](/chatbot/builder/block-options/quick-replies)**
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/blocks/inputs/url.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# URL Block
> Learn about the URL input block and how to set it up in the Builder.
The URL block is used to collect URLs from users. It validates the user's input to ensure that it is a valid URL.
You can use this block to ask users for website URLs, social media profiles, or any other web addresses.
## Configuration
The URL block has the following configuration options:
* **Store answer in variable**: The variable where the user's input will be stored.
* **Input required**: Whether the user's input is mandatory. If disabled, a Skip button will appear, allowing users to skip the input.
* **[Quick replies](/chatbot/builder/block-options/quick-replies)**
 ---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/api-reference/v2/usage/user-seats.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# User Seats
> Get the user seats usage for the project.
## Response
The status of the request. Will be `success` if the request was successful, otherwise `error`.
The number of seats used.
The maximum number of seats allowed for the project.
```json Response theme={null}
{
"status": "success",
"data": {
"used": 3,
"max": 10
}
}
```
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/intents/using-intents.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Using intents
> Learn how to use intents to create more complex chatbot flows
To make your intents work, there are two essential steps:
1. Enable intent matching in blocks to tell the chatbot which intents to look for in user messages.
2. Define the flow of the chatbot when an intent is matched.
## 1. Intent matching
Currently, intent matching can be enabled in [Text input blocks](/chatbot/builder/blocks/inputs/text).
When users send messages using the Text block, you can configure whether these messages should be checked against one or more defined intents. This allows you to control when intent matching occurs and trigger appropriate flows based on the matches.
### Enabling intent matching
1. Open the editor for a text block.
2. Next to the `Match intent` option, click the `+` button.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/api-reference/v2/usage/user-seats.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# User Seats
> Get the user seats usage for the project.
## Response
The status of the request. Will be `success` if the request was successful, otherwise `error`.
The number of seats used.
The maximum number of seats allowed for the project.
```json Response theme={null}
{
"status": "success",
"data": {
"used": 3,
"max": 10
}
}
```
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/intents/using-intents.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Using intents
> Learn how to use intents to create more complex chatbot flows
To make your intents work, there are two essential steps:
1. Enable intent matching in blocks to tell the chatbot which intents to look for in user messages.
2. Define the flow of the chatbot when an intent is matched.
## 1. Intent matching
Currently, intent matching can be enabled in [Text input blocks](/chatbot/builder/blocks/inputs/text).
When users send messages using the Text block, you can configure whether these messages should be checked against one or more defined intents. This allows you to control when intent matching occurs and trigger appropriate flows based on the matches.
### Enabling intent matching
1. Open the editor for a text block.
2. Next to the `Match intent` option, click the `+` button.
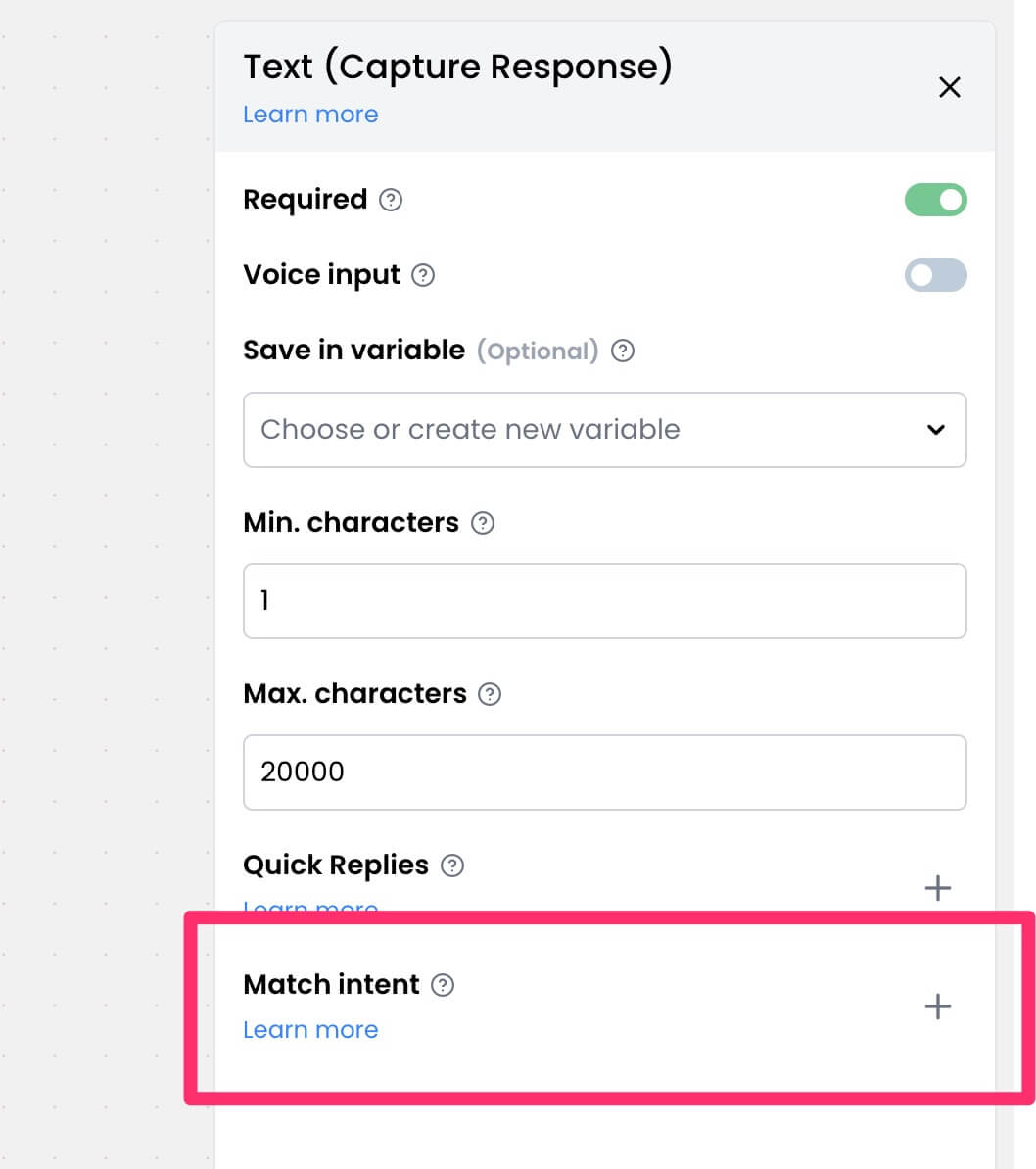 3. Select the intents you want user messages to be checked against.
3. Select the intents you want user messages to be checked against.
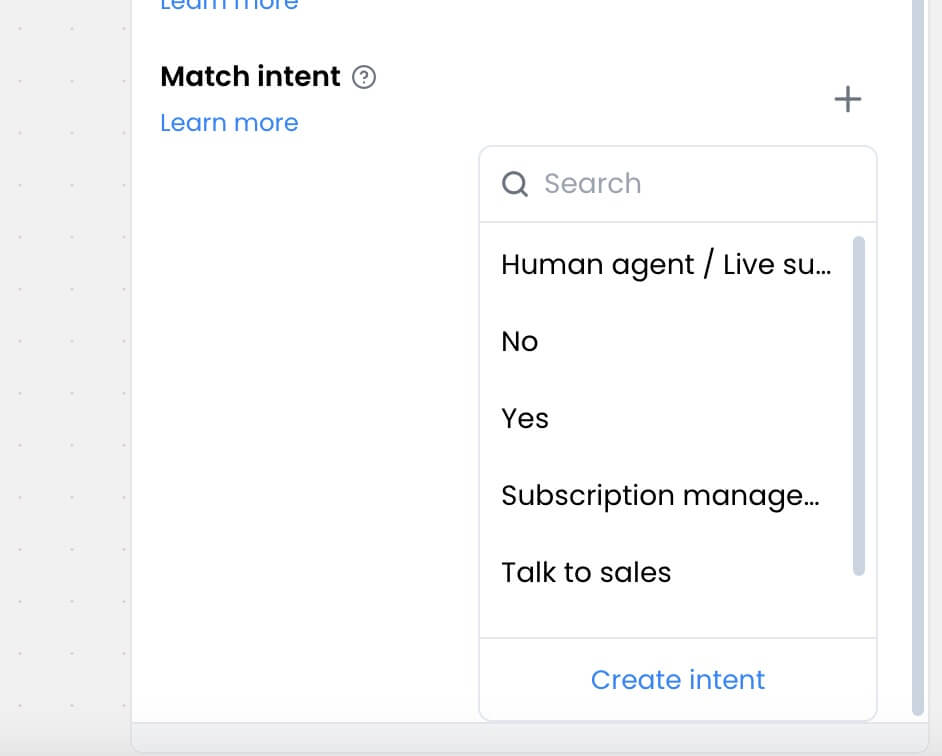 When a user sends a message, the chatbot will check if the message matches any of the selected intents and trigger the appropriate flow. If there are no matches, the flow will continue normally.
## 2. Defining intent flows
There are two ways to define the actions for an intent:
1. Intent trigger block (global)
2. Local trigger
### Intent trigger block
Intent triggers are flows that will be executed when an intent is matched. These triggers are global, meaning that they will be executed by any block that matches the intent. This is useful if you want to create a standard response for an intent that can be used in multiple places in your chatbot.
For example, if you create an Intent trigger for `Order Tracking`:
* Any block that matches this intent will start this flow.
* The same flow runs whether matched in a welcome message or support conversation.
* Flow can include actions like fetching order status, asking for order number, etc.
This provides a consistent response when users ask about order tracking anywhere in your chatbot.
**To add the trigger:**
1. Open `Blocks` from the sidebar.
When a user sends a message, the chatbot will check if the message matches any of the selected intents and trigger the appropriate flow. If there are no matches, the flow will continue normally.
## 2. Defining intent flows
There are two ways to define the actions for an intent:
1. Intent trigger block (global)
2. Local trigger
### Intent trigger block
Intent triggers are flows that will be executed when an intent is matched. These triggers are global, meaning that they will be executed by any block that matches the intent. This is useful if you want to create a standard response for an intent that can be used in multiple places in your chatbot.
For example, if you create an Intent trigger for `Order Tracking`:
* Any block that matches this intent will start this flow.
* The same flow runs whether matched in a welcome message or support conversation.
* Flow can include actions like fetching order status, asking for order number, etc.
This provides a consistent response when users ask about order tracking anywhere in your chatbot.
**To add the trigger:**
1. Open `Blocks` from the sidebar.
 2. Under the `Triggers` section, drag and drop the `Intent` block onto the canvas.
2. Under the `Triggers` section, drag and drop the `Intent` block onto the canvas.
 3. Click on the block to open the editor.
4. Select an intent this trigger belongs to.
3. Click on the block to open the editor.
4. Select an intent this trigger belongs to.
 5. Define the flow to run when the intent is triggered.
5. Define the flow to run when the intent is triggered.
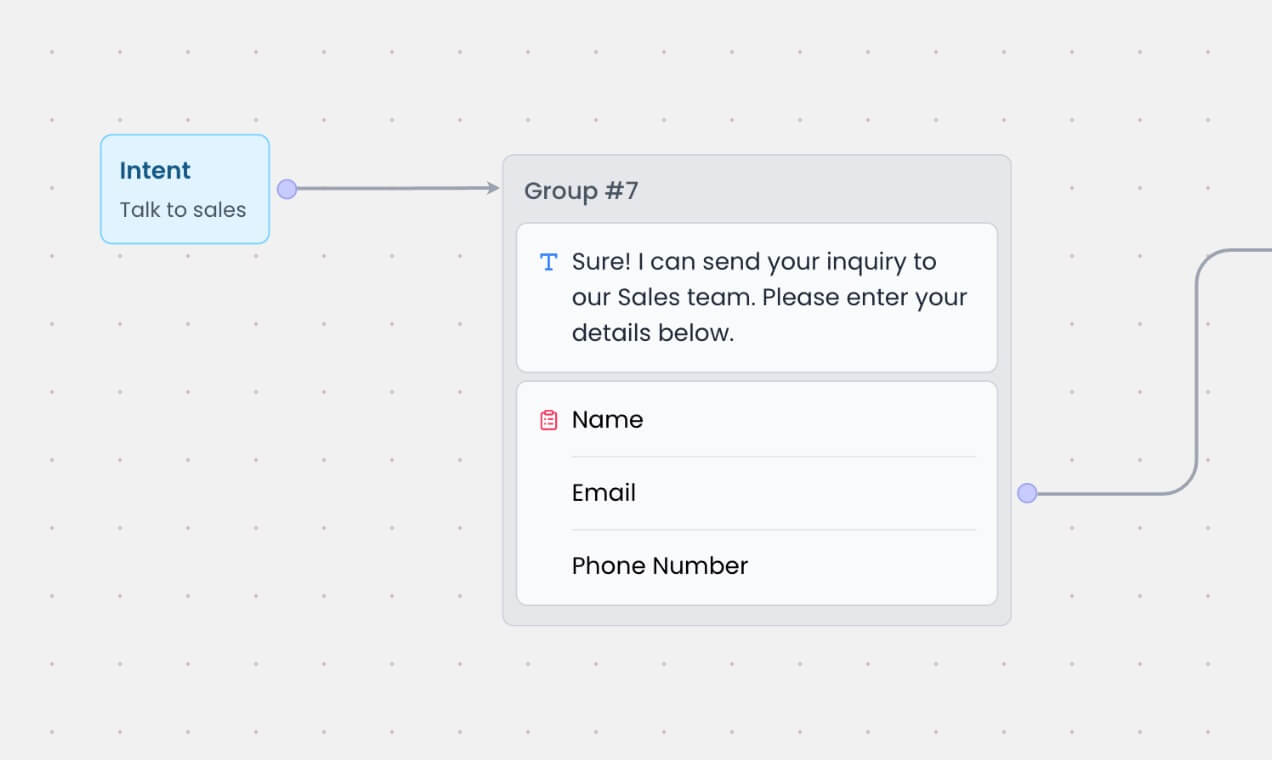 ### Local trigger
Sometimes you want different flows for the same intent depending on where in the conversation it was matched. This is where local triggers come in.
* Open the block where you want to enable local trigger for an intent.
* Find the intent under the `Match intent` option and click the `Local trigger` icon as shown below. For example, we will enable local trigger for the `Order status` intent.
### Local trigger
Sometimes you want different flows for the same intent depending on where in the conversation it was matched. This is where local triggers come in.
* Open the block where you want to enable local trigger for an intent.
* Find the intent under the `Match intent` option and click the `Local trigger` icon as shown below. For example, we will enable local trigger for the `Order status` intent.
 * Define the specific flow for this intent. For example, we will ask the user for their order number before fetching the order status. As such, whenever the input in this block matches the `Order status` intent, the flow defined here will be executed instead of the global trigger.
* Define the specific flow for this intent. For example, we will ask the user for their order number before fetching the order status. As such, whenever the input in this block matches the `Order status` intent, the flow defined here will be executed instead of the global trigger.
 Note that the local trigger takes precedence over the global trigger when enabled.
### Using both triggers
You can have both global and local triggers for intents:
* Use global triggers for standard responses
* Override with local triggers where context-specific flows are needed
This flexibility allows you to:
* Maintain consistent base responses
* Customize flows for specific conversation stages
* Create more dynamic user experiences
## What happens when no intents match?
If no intent is matched, the chatbot will continue with the flow as normal.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/variables/variable-types.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Types of variables
> There are two types of variables: System Variable and Custom Variable. Learn how to use them in your chatbot.
Variables in the Builder are of two types:
* System Variable
* Custom Variable
## System Variable
Note that the local trigger takes precedence over the global trigger when enabled.
### Using both triggers
You can have both global and local triggers for intents:
* Use global triggers for standard responses
* Override with local triggers where context-specific flows are needed
This flexibility allows you to:
* Maintain consistent base responses
* Customize flows for specific conversation stages
* Create more dynamic user experiences
## What happens when no intents match?
If no intent is matched, the chatbot will continue with the flow as normal.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/variables/variable-types.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Types of variables
> There are two types of variables: System Variable and Custom Variable. Learn how to use them in your chatbot.
Variables in the Builder are of two types:
* System Variable
* Custom Variable
## System Variable
 System variables are predefined variables that contain system information or which can be used to perform specific actions. These variables are automatically created by the Builder.
To learn what a specific system variable does, you can open it from the Variables menu in the [sidebar](/chatbot/builder/sidebar) and read its description.
There are also additional system variables that aren't imported by default. To view and import them, go to the Variables menu from the [Sidebar](/chatbot/builder/sidebar) and click the `Import system variables` button.
System variables are predefined variables that contain system information or which can be used to perform specific actions. These variables are automatically created by the Builder.
To learn what a specific system variable does, you can open it from the Variables menu in the [sidebar](/chatbot/builder/sidebar) and read its description.
There are also additional system variables that aren't imported by default. To view and import them, go to the Variables menu from the [Sidebar](/chatbot/builder/sidebar) and click the `Import system variables` button.
 ## Custom Variable
These are variables that you create to store information specific to your chatbot.
For example, you can create a custom variable to store the user's query and pass it to the AI for generating a response from the knowledge base.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/blocks/condition/variable.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Variable
> Learn how to use the Variable condition block in Chatling
The Variable condition block is used to compare a variable with a value or another variable. You can use it to create conditional logic in your bot based on user inputs, stored values, or system variables.
## Components of a variable condition
## Custom Variable
These are variables that you create to store information specific to your chatbot.
For example, you can create a custom variable to store the user's query and pass it to the AI for generating a response from the knowledge base.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/blocks/condition/variable.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Variable
> Learn how to use the Variable condition block in Chatling
The Variable condition block is used to compare a variable with a value or another variable. You can use it to create conditional logic in your bot based on user inputs, stored values, or system variables.
## Components of a variable condition
 * **Label**: A descriptive label for the condition, which will be displayed in the block on the canvas. This is optional and can be skipped.
* **Variable**: The variable or value that the block will evaluate. The variable can be a user input, a stored value, or a system variable.
* **Comparison operator**: The operator that the block will use to compare the variable with the value you specify. You can choose from a list of comparison operators, such as "equals," "greater than," "contains," etc.
* **Value**: The value that the block will compare with the variable. This can be a static value or a variable for dynamic comparisons.
## Examples
### 1. Real estate bot
In a real estate bot, you can use conditions to check if the user is looking to buy or rent a property and display properties accordingly.
You can create two conditions:
* Condition 1: User input contains "buy"
* Condition 2: User input contains "rent"
Here's how to set it up in the editor:
* **Label**: A descriptive label for the condition, which will be displayed in the block on the canvas. This is optional and can be skipped.
* **Variable**: The variable or value that the block will evaluate. The variable can be a user input, a stored value, or a system variable.
* **Comparison operator**: The operator that the block will use to compare the variable with the value you specify. You can choose from a list of comparison operators, such as "equals," "greater than," "contains," etc.
* **Value**: The value that the block will compare with the variable. This can be a static value or a variable for dynamic comparisons.
## Examples
### 1. Real estate bot
In a real estate bot, you can use conditions to check if the user is looking to buy or rent a property and display properties accordingly.
You can create two conditions:
* Condition 1: User input contains "buy"
* Condition 2: User input contains "rent"
Here's how to set it up in the editor:
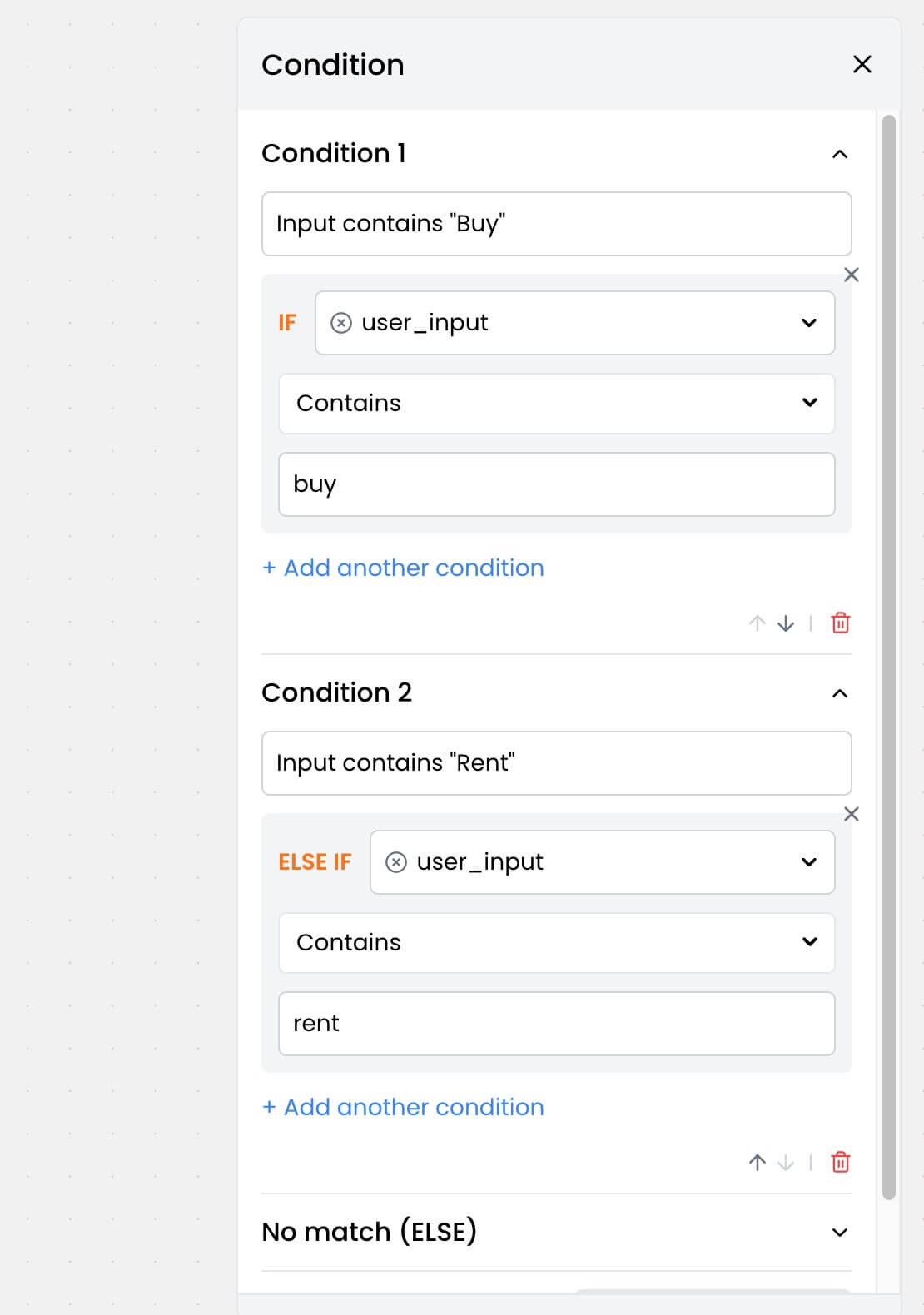 Once you have set up the conditions, you can define the paths for each condition. Here's an example:
Once you have set up the conditions, you can define the paths for each condition. Here's an example:
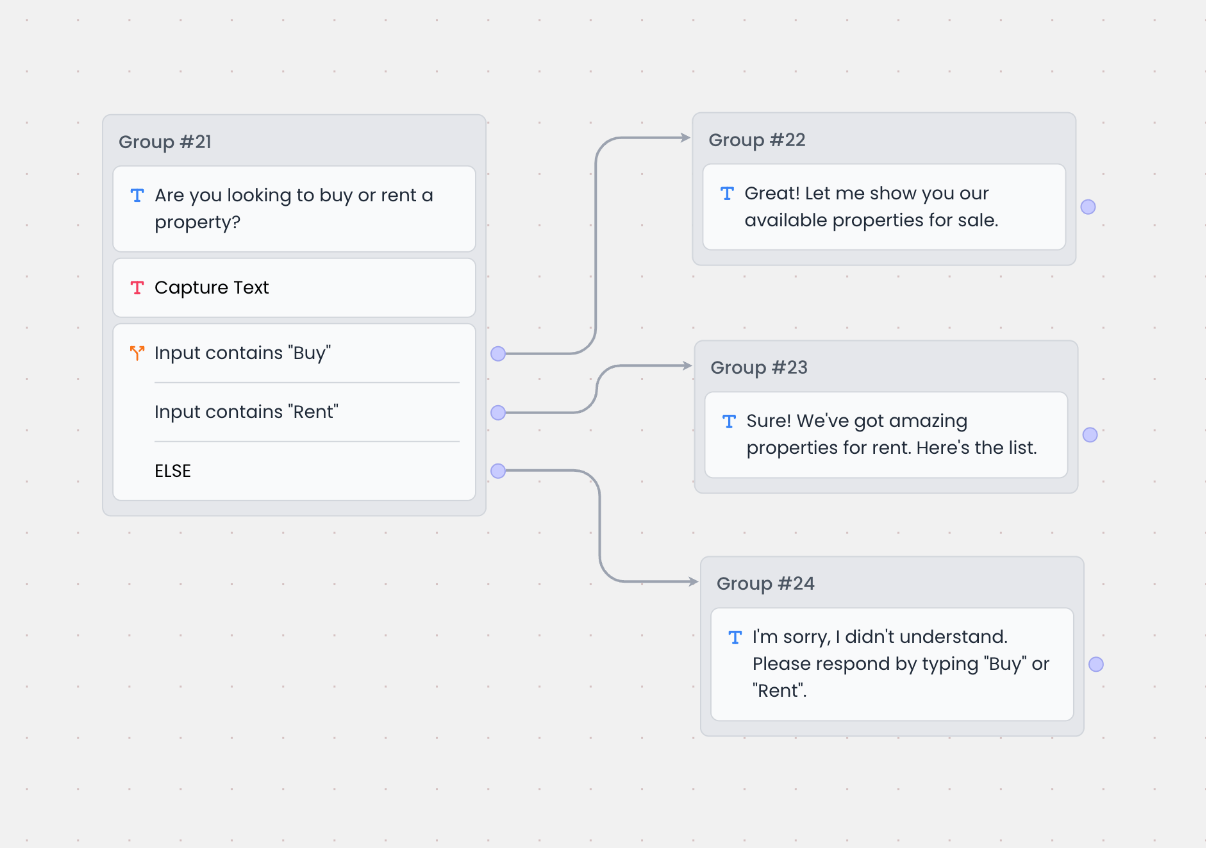 Based on the above, here's how the bot will respond:
* If the user input contains "buy," the bot will respond with `Great! Let me show you our available properties for sale`.
* If the user input contains "rent," the bot will respond with `Sure! We've got amazing properties for rent. Here's the list`.
* Else if none of the conditions are met, the bot will respond with `I'm sorry, I didn't understand. Please respond by typing "Buy" or "Rent"`.
### 2. Filtering job application candidates
Let's say a candidate is applying for a job through the bot and you want to qualify them based on the following criteria:
* Location: New York
* Willing to relocate: Yes
* Years of experience: 3 or more
You can set up the following conditions:
Based on the above, here's how the bot will respond:
* If the user input contains "buy," the bot will respond with `Great! Let me show you our available properties for sale`.
* If the user input contains "rent," the bot will respond with `Sure! We've got amazing properties for rent. Here's the list`.
* Else if none of the conditions are met, the bot will respond with `I'm sorry, I didn't understand. Please respond by typing "Buy" or "Rent"`.
### 2. Filtering job application candidates
Let's say a candidate is applying for a job through the bot and you want to qualify them based on the following criteria:
* Location: New York
* Willing to relocate: Yes
* Years of experience: 3 or more
You can set up the following conditions:
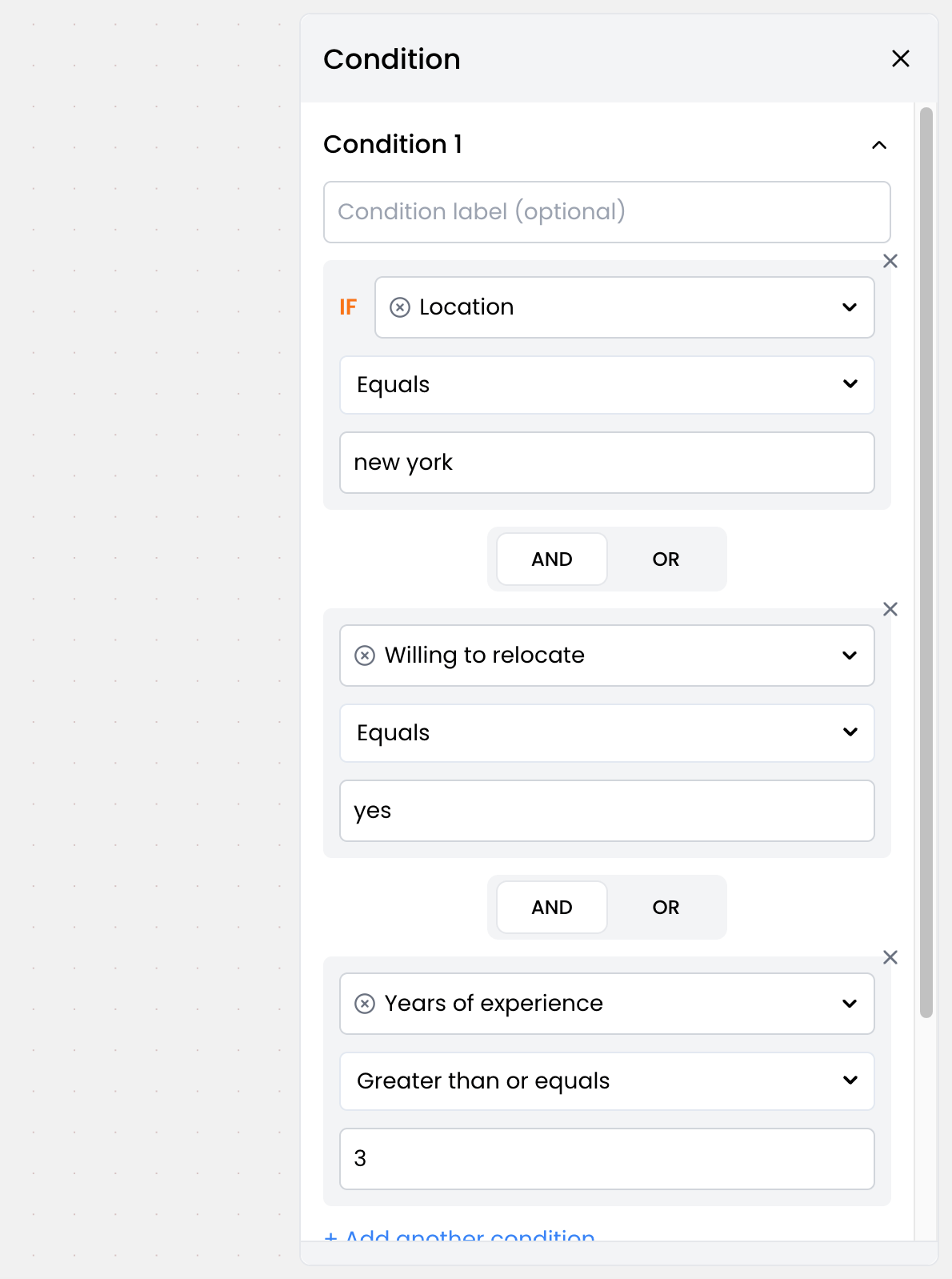 Once you have set up the conditions, you can define the paths for each condition. Here's an example:
Once you have set up the conditions, you can define the paths for each condition. Here's an example:
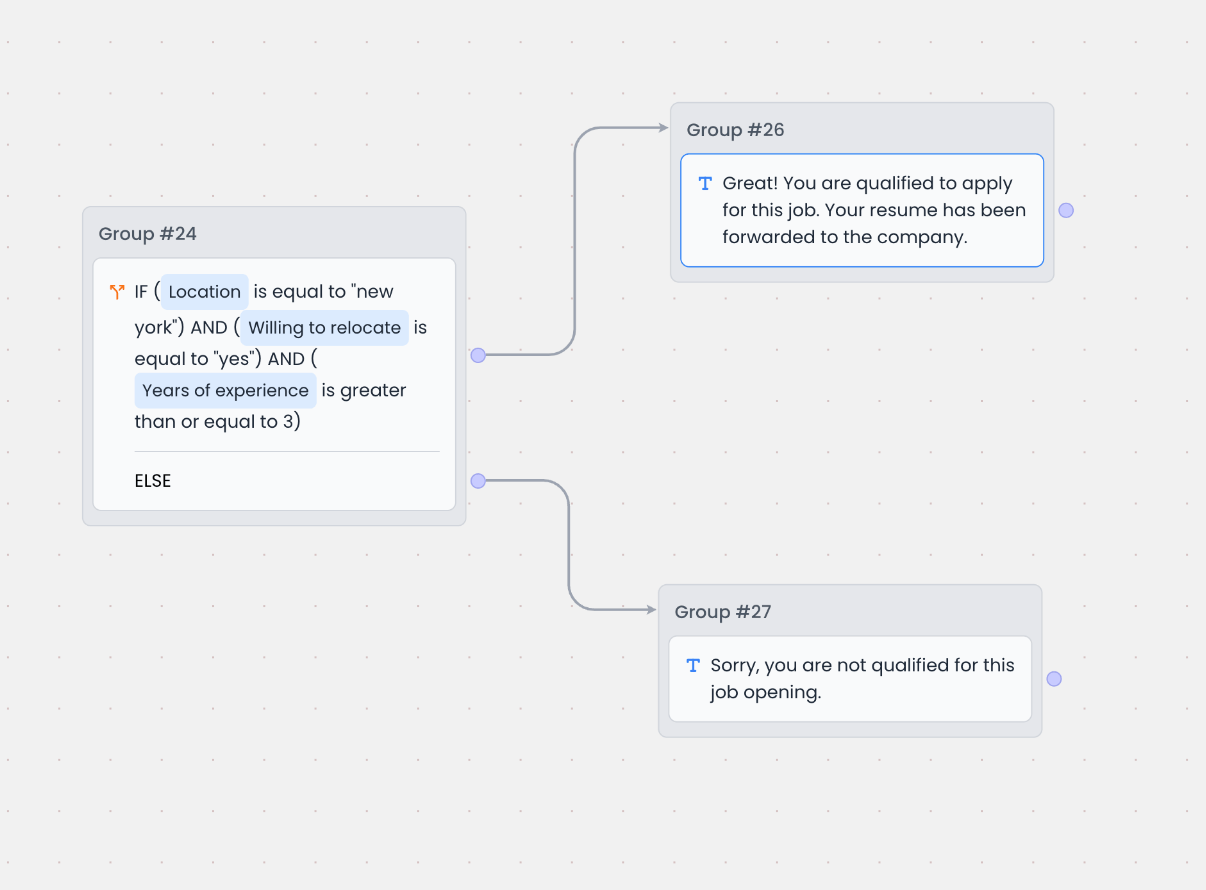 Based on the above, here's how the bot will respond:
* If the candidate is from New York, willing to relocate, and has 3 or more years of experience, the bot will respond with `Congratulations! You've been shortlisted for the next round of interviews`.
* Otherwise, the bot will respond with `Sorry, you are not qualified for this job opening. We'll keep your application on file for future opportunities`.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/blocks/send/video.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Video Block
> Learn about the Video block and how to set it up in the builder
The Video block allows you to display a video to the user in the conversation. You can add a video from YouTube, Vimeo, or any other video hosting platform, or you can paste the direct link to a video file.
For video platforms that support embedding, Chatling will automatically embed the video in the conversation. Here's an example:
Based on the above, here's how the bot will respond:
* If the candidate is from New York, willing to relocate, and has 3 or more years of experience, the bot will respond with `Congratulations! You've been shortlisted for the next round of interviews`.
* Otherwise, the bot will respond with `Sorry, you are not qualified for this job opening. We'll keep your application on file for future opportunities`.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/blocks/send/video.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Video Block
> Learn about the Video block and how to set it up in the builder
The Video block allows you to display a video to the user in the conversation. You can add a video from YouTube, Vimeo, or any other video hosting platform, or you can paste the direct link to a video file.
For video platforms that support embedding, Chatling will automatically embed the video in the conversation. Here's an example:
 ## Adding a video
Adding a video is simple. Just paste the URL to the video in the block editor and the chatbot will automatically embed it in the conversation.
## Adding a video
Adding a video is simple. Just paste the URL to the video in the block editor and the chatbot will automatically embed it in the conversation.
 ---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/general-settings/visibility.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Visibility
> A guide on how to make your chatbot public or private.
You can set the visibility of your chatbot to be public or private. Setting to Public will make your chatbot visible to all users, while setting to Private will make it accessible from your account only.
## How to set the visibility
1. From the chatbot dashboard, go to `Settings`.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/general-settings/visibility.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Visibility
> A guide on how to make your chatbot public or private.
You can set the visibility of your chatbot to be public or private. Setting to Public will make your chatbot visible to all users, while setting to Private will make it accessible from your account only.
## How to set the visibility
1. From the chatbot dashboard, go to `Settings`.
 2. Click the `Visibility` tab.
3. Set the visibility to `Public` or `Private`.
4. Click `Save` to apply the changes.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/block-options/voice-input.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Voice Input
> Allow users to speak to your chatbot using Voice Input.
Voice Input is a speech-to-text feature that allows users to record voice messages and transcribes them into text. Rather than typing their message, users can speak to your chatbot and it will automatically be converted to text.
2. Click the `Visibility` tab.
3. Set the visibility to `Public` or `Private`.
4. Click `Save` to apply the changes.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/block-options/voice-input.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Voice Input
> Allow users to speak to your chatbot using Voice Input.
Voice Input is a speech-to-text feature that allows users to record voice messages and transcribes them into text. Rather than typing their message, users can speak to your chatbot and it will automatically be converted to text.
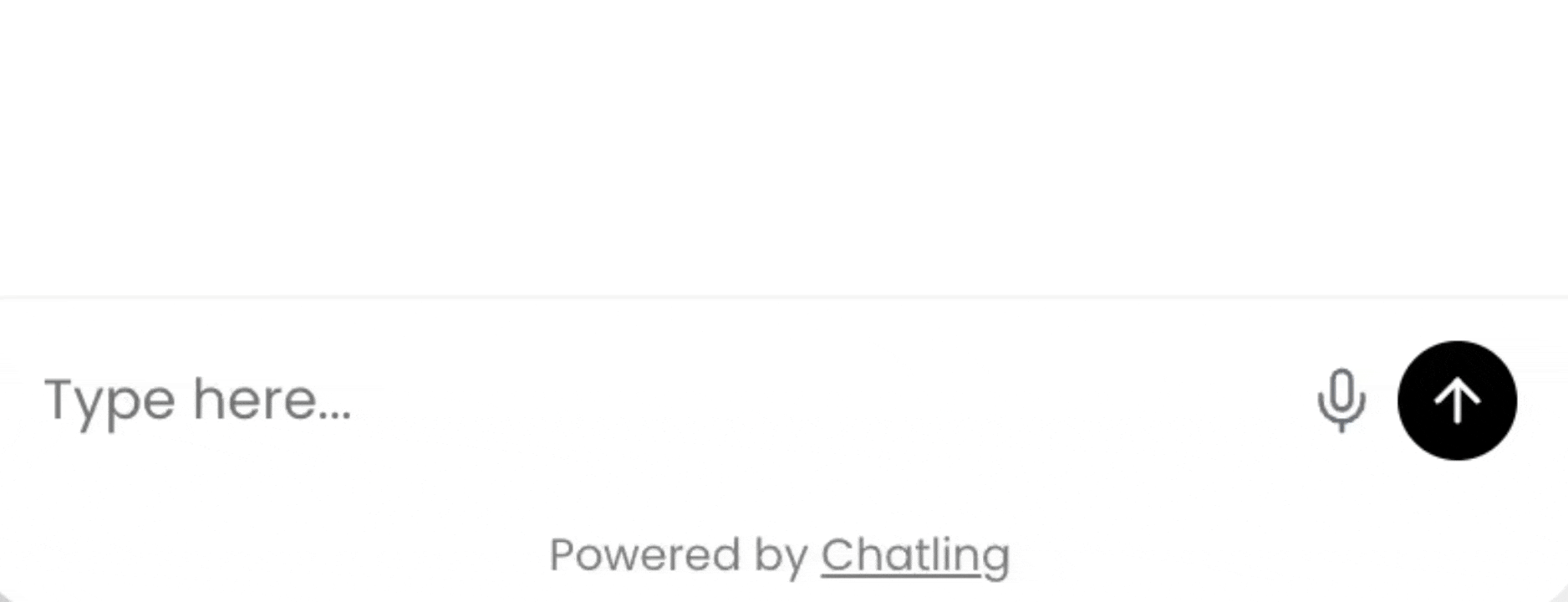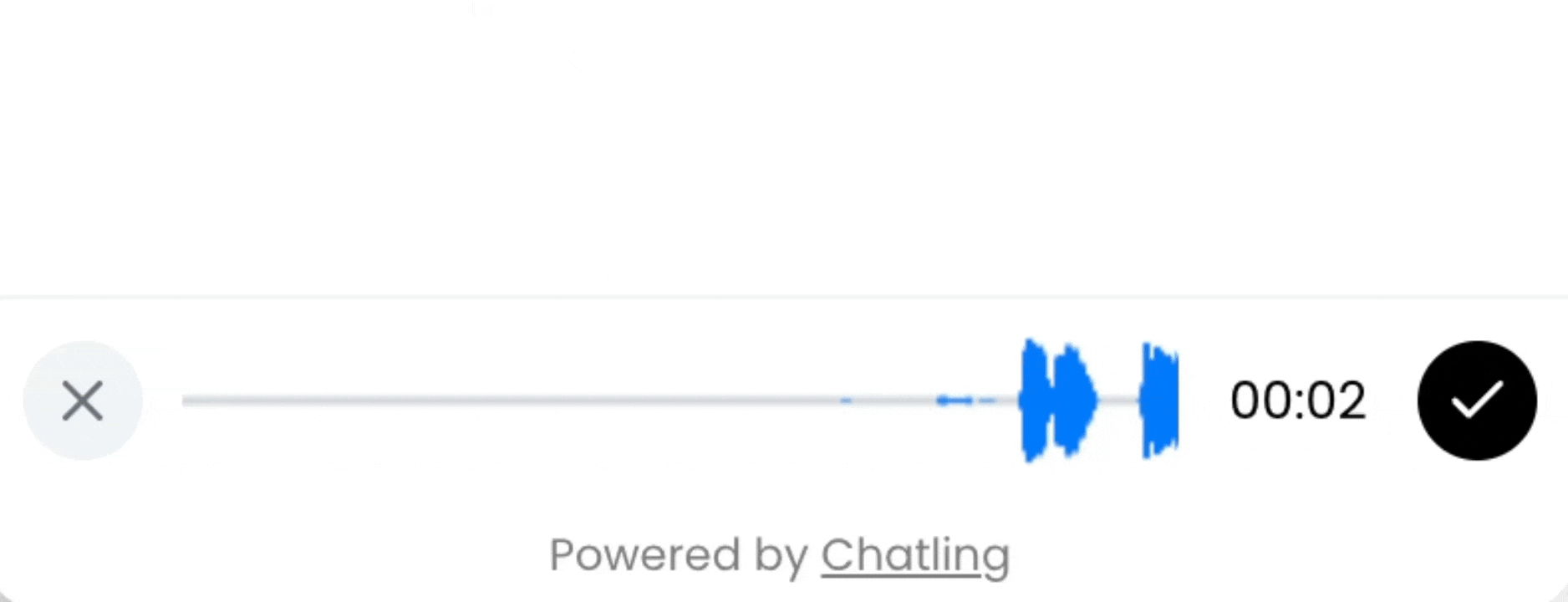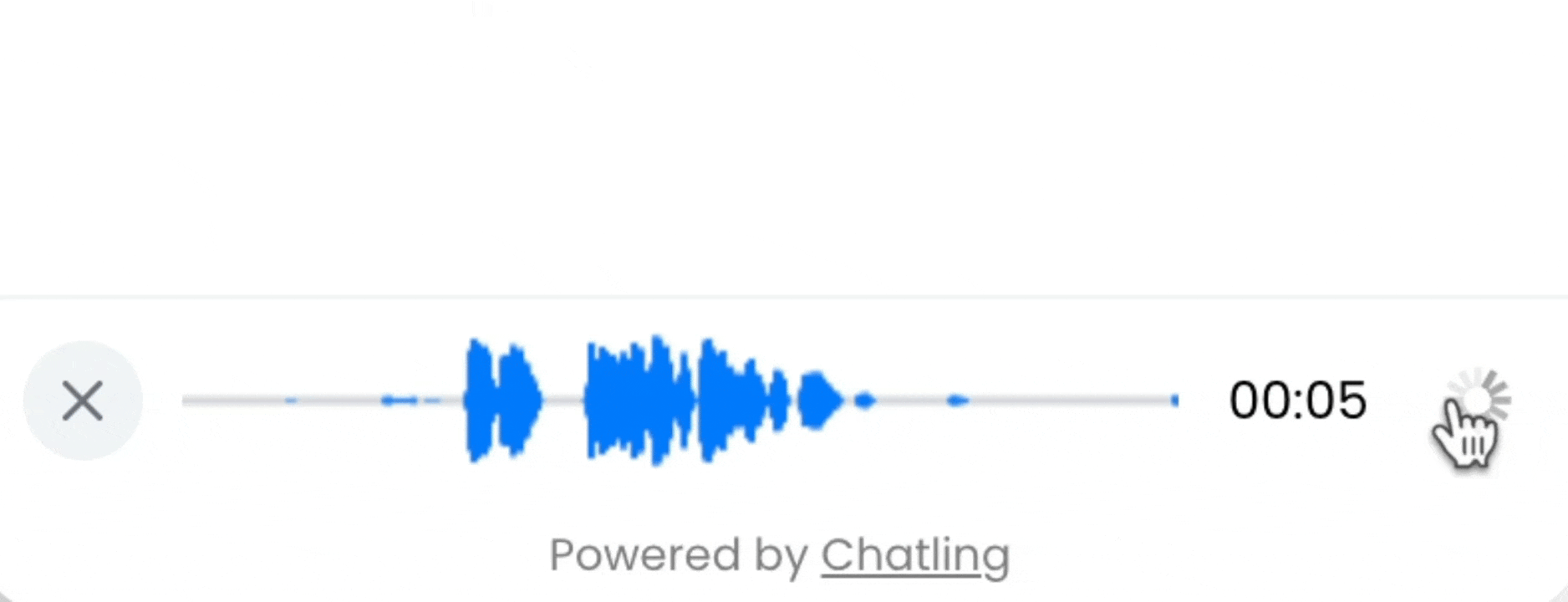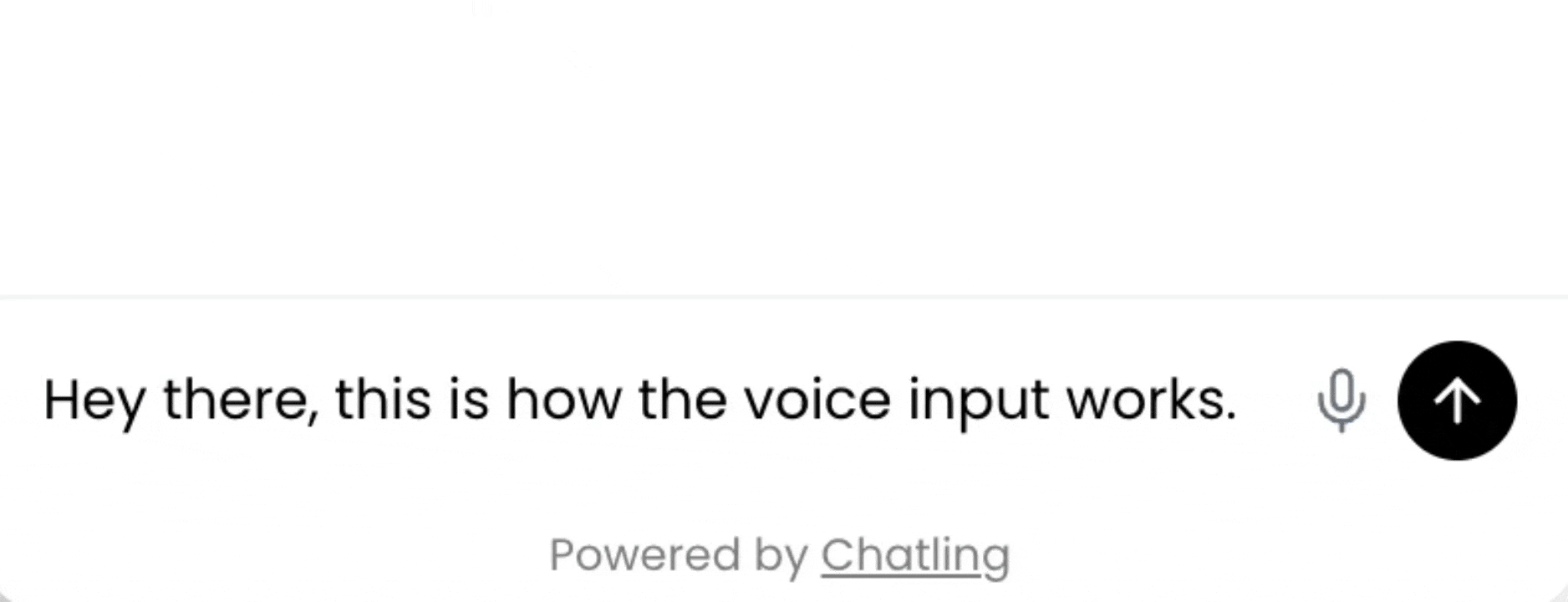 ## Supported blocks
Currently, Voice Input is available for the Text input block only.
## How to enable Voice Input
Open the block editor for a Text input block and toggle on the "Voice Input" option.
## Supported blocks
Currently, Voice Input is available for the Text input block only.
## How to enable Voice Input
Open the block editor for a Text input block and toggle on the "Voice Input" option.
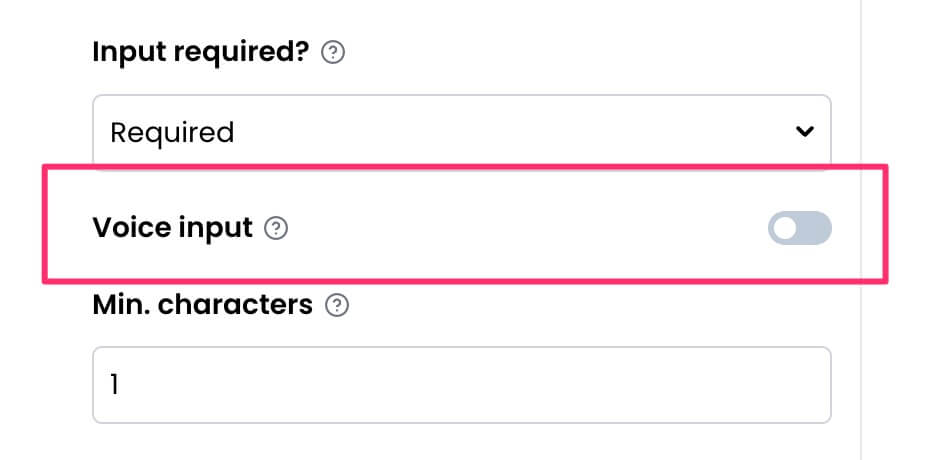 The chatbot will then display a microphone icon when the block is displayed. Users can click on the microphone icon to record a voice message.
The chatbot will then display a microphone icon when the block is displayed. Users can click on the microphone icon to record a voice message.
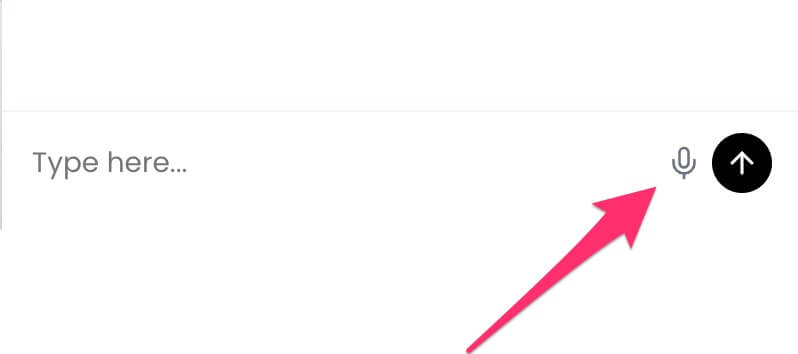 ## What happens when I run out of Speech to Text credits?
When you're out of credits, the voice recording icon will be removed and users will not be able to access the feature. You can upgrade your plan to increase the credits limit or wait until the next billing cycle for the credits to reset.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/web-widget/installation/webflow.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Webflow
> Learn how to add Chatling to your Webflow website
1. Go to your dashboard.
2. Click `Deploy` button in the sidebar menu.
## What happens when I run out of Speech to Text credits?
When you're out of credits, the voice recording icon will be removed and users will not be able to access the feature. You can upgrade your plan to increase the credits limit or wait until the next billing cycle for the credits to reset.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/web-widget/installation/webflow.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Webflow
> Learn how to add Chatling to your Webflow website
1. Go to your dashboard.
2. Click `Deploy` button in the sidebar menu.
 3. Click the `Manage` button under the `Website Widget` option.
3. Click the `Manage` button under the `Website Widget` option.
 4. Design the appearance of the widget by clicking the `Open widget designer` button.
4. Design the appearance of the widget by clicking the `Open widget designer` button.
 5. Select the display mode for your chatbot, such as "Floating Chat", "Inline", or "Fullscreen".
5. Select the display mode for your chatbot, such as "Floating Chat", "Inline", or "Fullscreen".
 6. Copy the widget code.
6. Copy the widget code.
 7. Go to your Webflow dashboard and open the website where you want to add the widget.
7. Go to your Webflow dashboard and open the website where you want to add the widget.
 8. Click the webflow icon in the top left and select `Site settings`.
8. Click the webflow icon in the top left and select `Site settings`.
 9. Click on `Custom code` from the sidebar.
9. Click on `Custom code` from the sidebar.
 10. Paste the widget code in the `Head code` textbox and click `Save`.
10. Paste the widget code in the `Head code` textbox and click `Save`.
 11. Publish the website. The widget will now be appear on your Webflow website.
11. Publish the website. The widget will now be appear on your Webflow website.
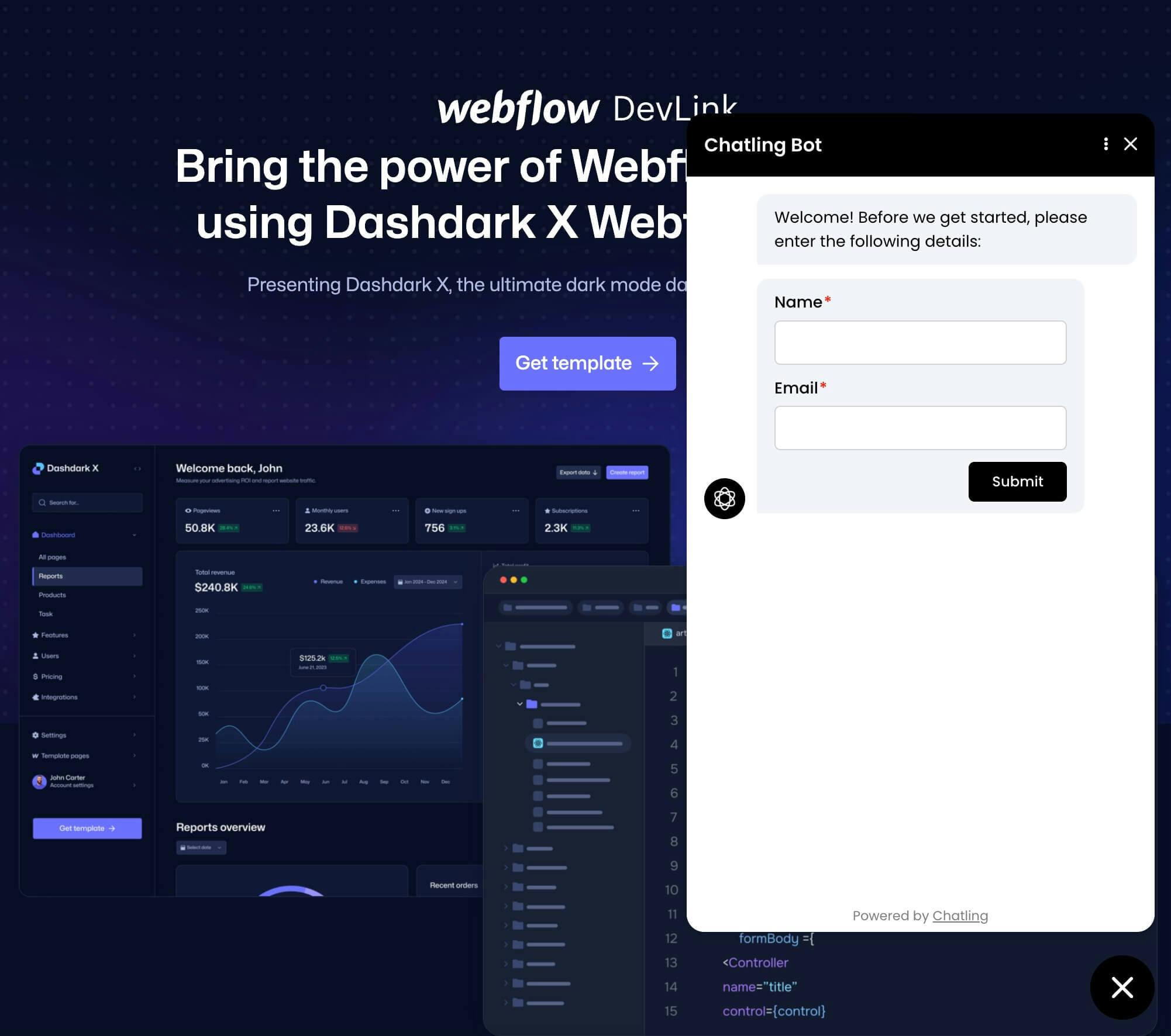 ---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/variables/what-are-variables.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# What are variables?
> Learn about Variables, the different types, and how to use them
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/variables/what-are-variables.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# What are variables?
> Learn about Variables, the different types, and how to use them
 Variables are placeholders that store information during the conversation. You can use variables to store user inputs, API responses, and more. These variables can be used to personalize the conversation and make it more dynamic.
For example, you can store the user's name in a variable and use it to greet the user. This way, you can make the conversation more engaging and interactive.
In the next section, you will learn about the different types of variables and how to use them in your chatbot.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/faq/what-happens-when-ai-credits-exhausted.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# What happens when AI credits are exhausted?
When your AI credits are exhausted, users can still interact with the chatbot and send messages, but an error will be displayed saying "Insufficient AI credits".
When the usage exceeds the limit, you must top up your AI credits by purchasing the **Extra AI Credits** add-on from Billing & Usage > Add-ons page. Alternatively, you can upgrade your plan to get more credits.
You can enable the **AI Credit Usage** notification in your account to be alerted when your usage reaches a threshold such as 50%, 75%, 90% or 100%.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/web-widget/whitelist-domains.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Whitelist domains
> Learn how to whitelist domains for your chatbot to prevent it from being added to unauthorized websites.
If you want to prevent your widget from being added to unauthorized websites, you can whitelist domains.
By adding whitelisted domains, the widget will only appear on websites that match the whitelisted domains.
## How to whitelist domains
1. Open your chatbot's dashboard.
2. Go to Settings.
Variables are placeholders that store information during the conversation. You can use variables to store user inputs, API responses, and more. These variables can be used to personalize the conversation and make it more dynamic.
For example, you can store the user's name in a variable and use it to greet the user. This way, you can make the conversation more engaging and interactive.
In the next section, you will learn about the different types of variables and how to use them in your chatbot.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/faq/what-happens-when-ai-credits-exhausted.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# What happens when AI credits are exhausted?
When your AI credits are exhausted, users can still interact with the chatbot and send messages, but an error will be displayed saying "Insufficient AI credits".
When the usage exceeds the limit, you must top up your AI credits by purchasing the **Extra AI Credits** add-on from Billing & Usage > Add-ons page. Alternatively, you can upgrade your plan to get more credits.
You can enable the **AI Credit Usage** notification in your account to be alerted when your usage reaches a threshold such as 50%, 75%, 90% or 100%.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/web-widget/whitelist-domains.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Whitelist domains
> Learn how to whitelist domains for your chatbot to prevent it from being added to unauthorized websites.
If you want to prevent your widget from being added to unauthorized websites, you can whitelist domains.
By adding whitelisted domains, the widget will only appear on websites that match the whitelisted domains.
## How to whitelist domains
1. Open your chatbot's dashboard.
2. Go to Settings.
 3. Click the `Security` tab.
4. Under the `Whitelist domains` section, type in a domain you want to whitelist and click the `+ Add` button. You can add multiple domains.
5. Click `Save`.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/web-widget/widget-sdk.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Widget SDK
## Configuration
You can configure the widget during launch by setting the `window.chtlConfig` object, as shown below.
```javascript theme={null}
window.chtlConfig = {
// Configuration options
};
```
Below are the available properties you can set.
### `chatIconVisible`
Whether to display the chat icon (open and close buttons).
* Possible values: `true`, `false`
* Default: `true`
```javascript theme={null}
window.chtlConfig = {
chatIconVisible: true,
// ... other config options
};
```
### `displayType`
The type of widget to display.
* Possible values: `floating`, `fullscreen`, `page_inline`
* Default: `floating`
```javascript theme={null}
window.chtlConfig = {
displayType: 'floating',
// ... other config options
};
```
### `language`
The language of the widget in ISO 639-1 format. This will override the language set in your chatbot's appearance settings.
* Possible values: `en`, `ar`, `az`, `bg`, `bn`, `bs`, `ca`, `cs`, `da`, `de`, `el`, `en`, `es`, `et`, `fa`, `fi`, `fr`, `he`, `hi`, `hr`, `hu`, `hy`, `id`, `it`, `ja`, `ko`, `lt`, `lv`, `mn`, `ms`, `nl`, `no`, `pl`, `pt`, `pt-br`, `ro`, `ru`, `sk`, `sl`, `sq`, `sr`, `sv`, `th`, `tr`, `uk`, `ur`, `vi`, `zh-cn`, `zh-tw`
```javascript theme={null}
window.chtlConfig = {
language: 'en',
// ... other config options
};
```
## Methods
Below are the SDK methods you can call to interact with the widget.
You must wait for the widget script to load before calling these methods.
### `open()`
Opens the chatbot, similar to when a user clicks the chat icon.
```javascript theme={null}
window.Chatling.open();
```
### `minimize()`
Minimizes the chatbot, similar to when a user clicks the minimize button in the widget.
```javascript theme={null}
window.Chatling.minimize();
```
### `hideChatIcon()`
Hides the chat icon.
```javascript theme={null}
window.Chatling.hideChatIcon();
```
### `showChatIcon()`
Shows the chat icon.
```javascript theme={null}
window.Chatling.showChatIcon();
```
### `setVariables()`
You can pass custom values to the chatbot at any point after it's loaded.
The method takes an object containing the variable names and values. You must make sure that the variables [have been created](/chatbot/builder/variables/how-to-create-variables) in the builder and that the names match exactly.
To pass custom data during launch, read [this guide](/web-widget/pass-custom-data#pass-custom-data-during-launch).
```javascript theme={null}
window.Chatling.setVariables({
"contact_name": "Rick Astley",
"contact_email": "rick.astley@example.com",
"age": 30
}, function(success, errorMessage) {
if (!success) {
// handle error
}
});
```
### `destroy()`
Permanently removes the chatbot from the page.
```javascript theme={null}
window.Chatling.destroy();
```
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/web-widget/installation/wix.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Wix
> Learn how to add Chatling to your Wix website
1. Go to your dashboard.
2. Click `Deploy` button in the sidebar menu.
3. Click the `Security` tab.
4. Under the `Whitelist domains` section, type in a domain you want to whitelist and click the `+ Add` button. You can add multiple domains.
5. Click `Save`.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/web-widget/widget-sdk.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Widget SDK
## Configuration
You can configure the widget during launch by setting the `window.chtlConfig` object, as shown below.
```javascript theme={null}
window.chtlConfig = {
// Configuration options
};
```
Below are the available properties you can set.
### `chatIconVisible`
Whether to display the chat icon (open and close buttons).
* Possible values: `true`, `false`
* Default: `true`
```javascript theme={null}
window.chtlConfig = {
chatIconVisible: true,
// ... other config options
};
```
### `displayType`
The type of widget to display.
* Possible values: `floating`, `fullscreen`, `page_inline`
* Default: `floating`
```javascript theme={null}
window.chtlConfig = {
displayType: 'floating',
// ... other config options
};
```
### `language`
The language of the widget in ISO 639-1 format. This will override the language set in your chatbot's appearance settings.
* Possible values: `en`, `ar`, `az`, `bg`, `bn`, `bs`, `ca`, `cs`, `da`, `de`, `el`, `en`, `es`, `et`, `fa`, `fi`, `fr`, `he`, `hi`, `hr`, `hu`, `hy`, `id`, `it`, `ja`, `ko`, `lt`, `lv`, `mn`, `ms`, `nl`, `no`, `pl`, `pt`, `pt-br`, `ro`, `ru`, `sk`, `sl`, `sq`, `sr`, `sv`, `th`, `tr`, `uk`, `ur`, `vi`, `zh-cn`, `zh-tw`
```javascript theme={null}
window.chtlConfig = {
language: 'en',
// ... other config options
};
```
## Methods
Below are the SDK methods you can call to interact with the widget.
You must wait for the widget script to load before calling these methods.
### `open()`
Opens the chatbot, similar to when a user clicks the chat icon.
```javascript theme={null}
window.Chatling.open();
```
### `minimize()`
Minimizes the chatbot, similar to when a user clicks the minimize button in the widget.
```javascript theme={null}
window.Chatling.minimize();
```
### `hideChatIcon()`
Hides the chat icon.
```javascript theme={null}
window.Chatling.hideChatIcon();
```
### `showChatIcon()`
Shows the chat icon.
```javascript theme={null}
window.Chatling.showChatIcon();
```
### `setVariables()`
You can pass custom values to the chatbot at any point after it's loaded.
The method takes an object containing the variable names and values. You must make sure that the variables [have been created](/chatbot/builder/variables/how-to-create-variables) in the builder and that the names match exactly.
To pass custom data during launch, read [this guide](/web-widget/pass-custom-data#pass-custom-data-during-launch).
```javascript theme={null}
window.Chatling.setVariables({
"contact_name": "Rick Astley",
"contact_email": "rick.astley@example.com",
"age": 30
}, function(success, errorMessage) {
if (!success) {
// handle error
}
});
```
### `destroy()`
Permanently removes the chatbot from the page.
```javascript theme={null}
window.Chatling.destroy();
```
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/web-widget/installation/wix.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Wix
> Learn how to add Chatling to your Wix website
1. Go to your dashboard.
2. Click `Deploy` button in the sidebar menu.
 3. Click the `Manage` button under the `Website Widget` option.
3. Click the `Manage` button under the `Website Widget` option.
 4. Design the appearance of the widget by clicking the `Open widget designer` button.
4. Design the appearance of the widget by clicking the `Open widget designer` button.
 5. Select the display mode for your chatbot, such as "Floating Chat", "Inline", or "Fullscreen".
5. Select the display mode for your chatbot, such as "Floating Chat", "Inline", or "Fullscreen".
 6. Copy the widget code.
6. Copy the widget code.
 7. Go to your Wix dashboard and click `Settings` from the sidebar menu.
7. Go to your Wix dashboard and click `Settings` from the sidebar menu.
 8. Scroll down to the Advanced section and click `Custom code`.
8. Scroll down to the Advanced section and click `Custom code`.
 9. Under the Head section, click `Add Code`.
9. Under the Head section, click `Add Code`.
 10. Paste the widget code into the text box that appears and click `Apply`.
10. Paste the widget code into the text box that appears and click `Apply`.
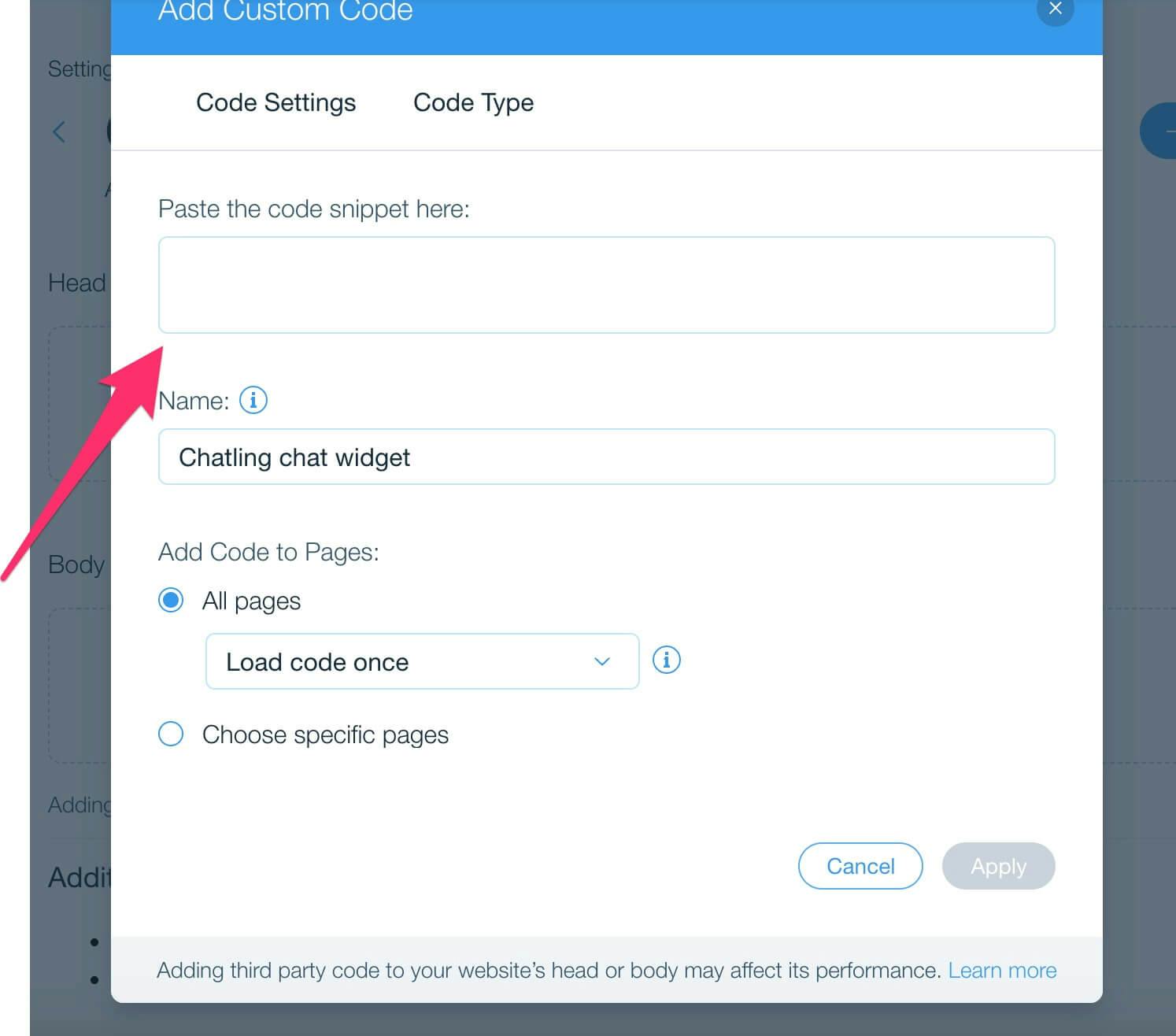 11. The widget is now live on your Wix website and visitors can interact with it.
11. The widget is now live on your Wix website and visitors can interact with it.
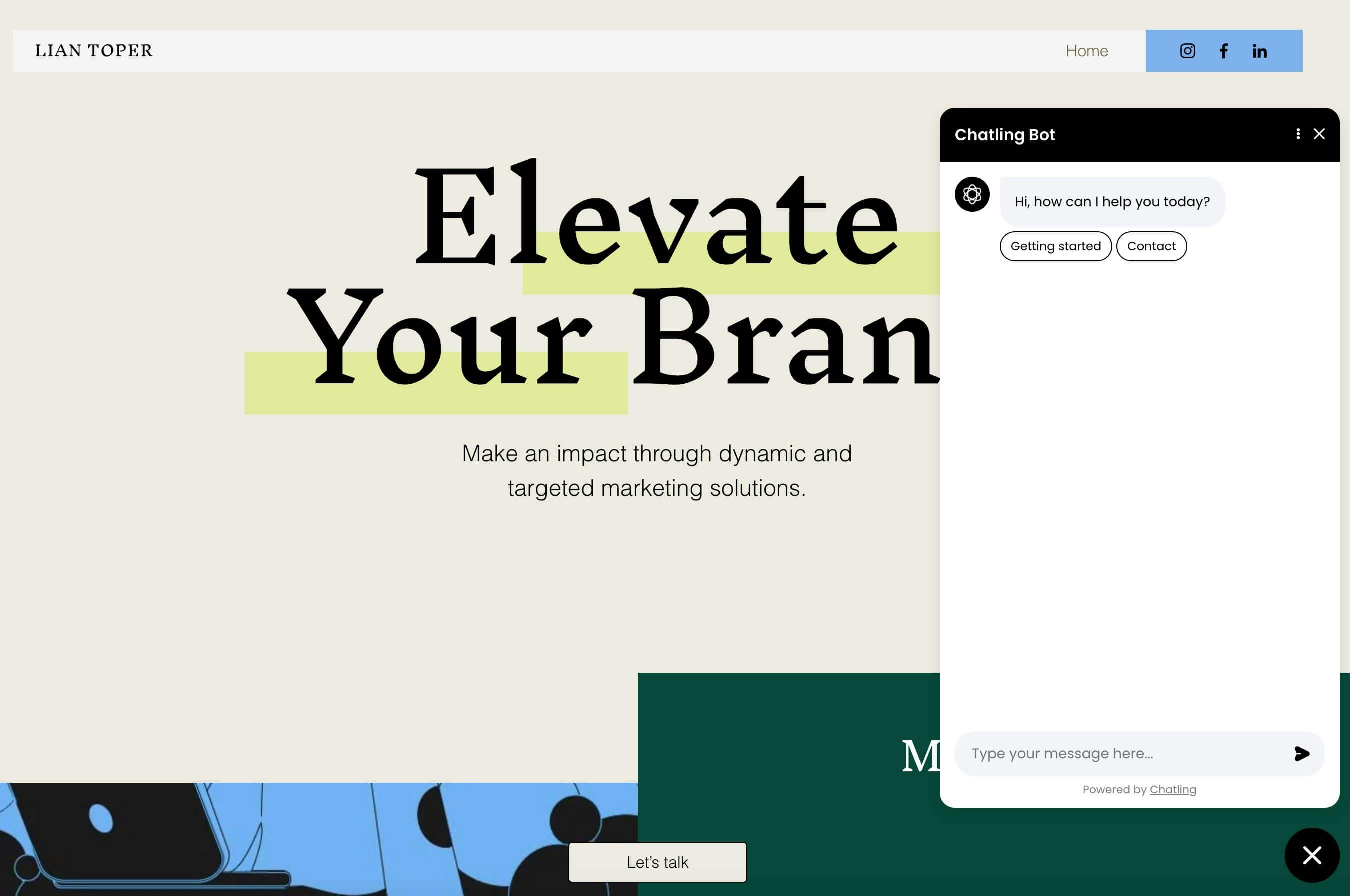 ---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/web-widget/installation/wordpress.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# WordPress
> Learn how to add Chatling to your WordPress website
## Method 1: Install using a plugin
1. Go to your dashboard.
2. Click `Deploy` button in the sidebar menu.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/web-widget/installation/wordpress.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# WordPress
> Learn how to add Chatling to your WordPress website
## Method 1: Install using a plugin
1. Go to your dashboard.
2. Click `Deploy` button in the sidebar menu.
 3. Click the `Manage` button under the `Website Widget` option.
3. Click the `Manage` button under the `Website Widget` option.
 4. Design the appearance of the widget by clicking the `Open widget designer` button.
4. Design the appearance of the widget by clicking the `Open widget designer` button.
 5. Select the display mode for your chatbot, such as "Floating Chat", "Inline", or "Fullscreen".
5. Select the display mode for your chatbot, such as "Floating Chat", "Inline", or "Fullscreen".
 6. Copy the widget code.
6. Copy the widget code.
 7. In your WordPress dashboard, go to `Plugins` > `Add new plugin`.
7. In your WordPress dashboard, go to `Plugins` > `Add new plugin`.
 8. Search for the `Insert Headers And Footers` plugin and install the one by WPBrigade.
8. Search for the `Insert Headers And Footers` plugin and install the one by WPBrigade.
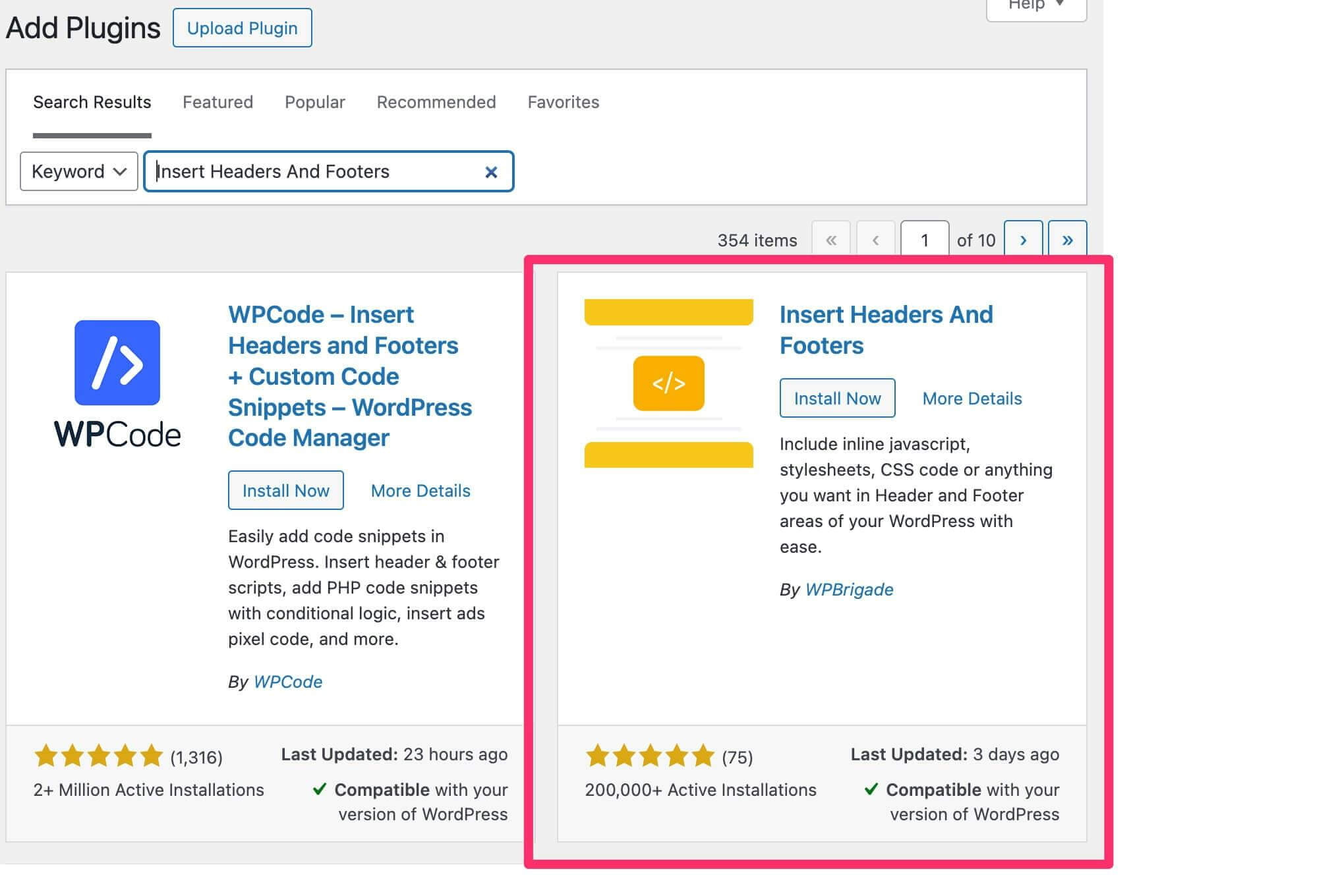 9. Once installed, activate the plugin.
10. Go to `Settings` > `WP Headers and Footers` from the sidebar.
9. Once installed, activate the plugin.
10. Go to `Settings` > `WP Headers and Footers` from the sidebar.
 11. Paste the chatbot widget code in the header section.
11. Paste the chatbot widget code in the header section.
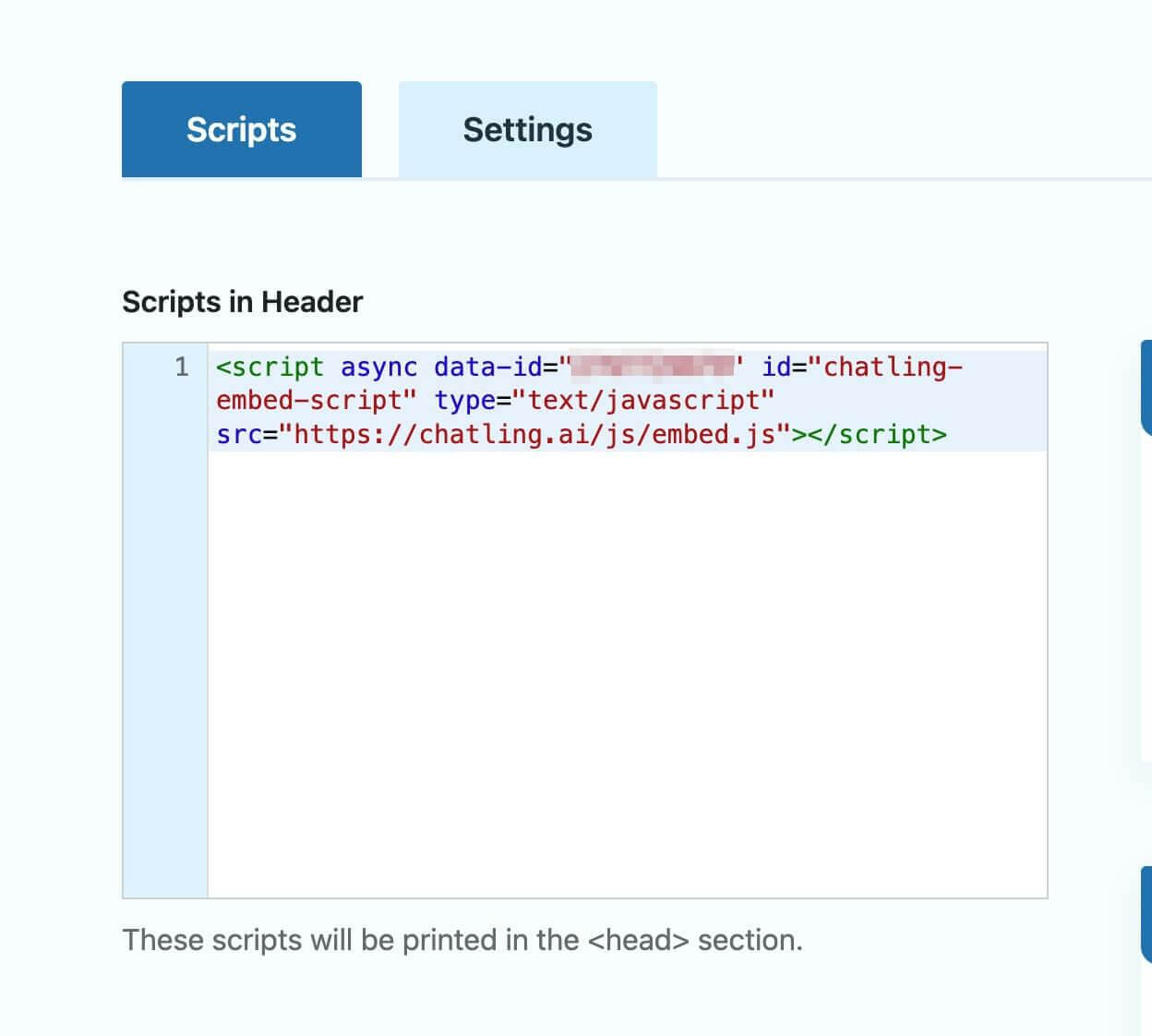 12. Click `Save Changes`.
## Method 2: Install using the theme editor
1. Follow steps 1-6 from Method 1 to copy the widget code.
2. Open your WordPress dashboard.
3. From the sidebar menu, select `Appearance` > `Theme File Editor`.
12. Click `Save Changes`.
## Method 2: Install using the theme editor
1. Follow steps 1-6 from Method 1 to copy the widget code.
2. Open your WordPress dashboard.
3. From the sidebar menu, select `Appearance` > `Theme File Editor`.
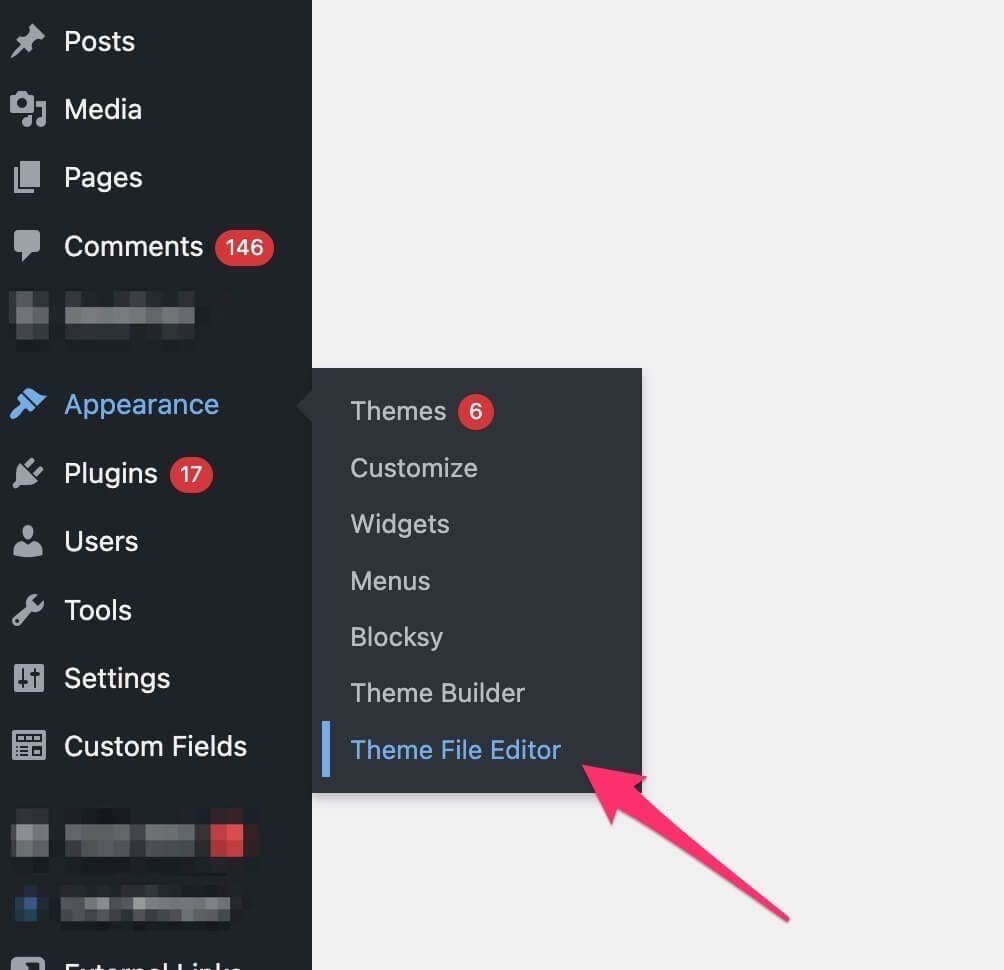 4. Under the `Theme Files` section (right side of the screen), search and open the `header.php` file.
4. Under the `Theme Files` section (right side of the screen), search and open the `header.php` file.
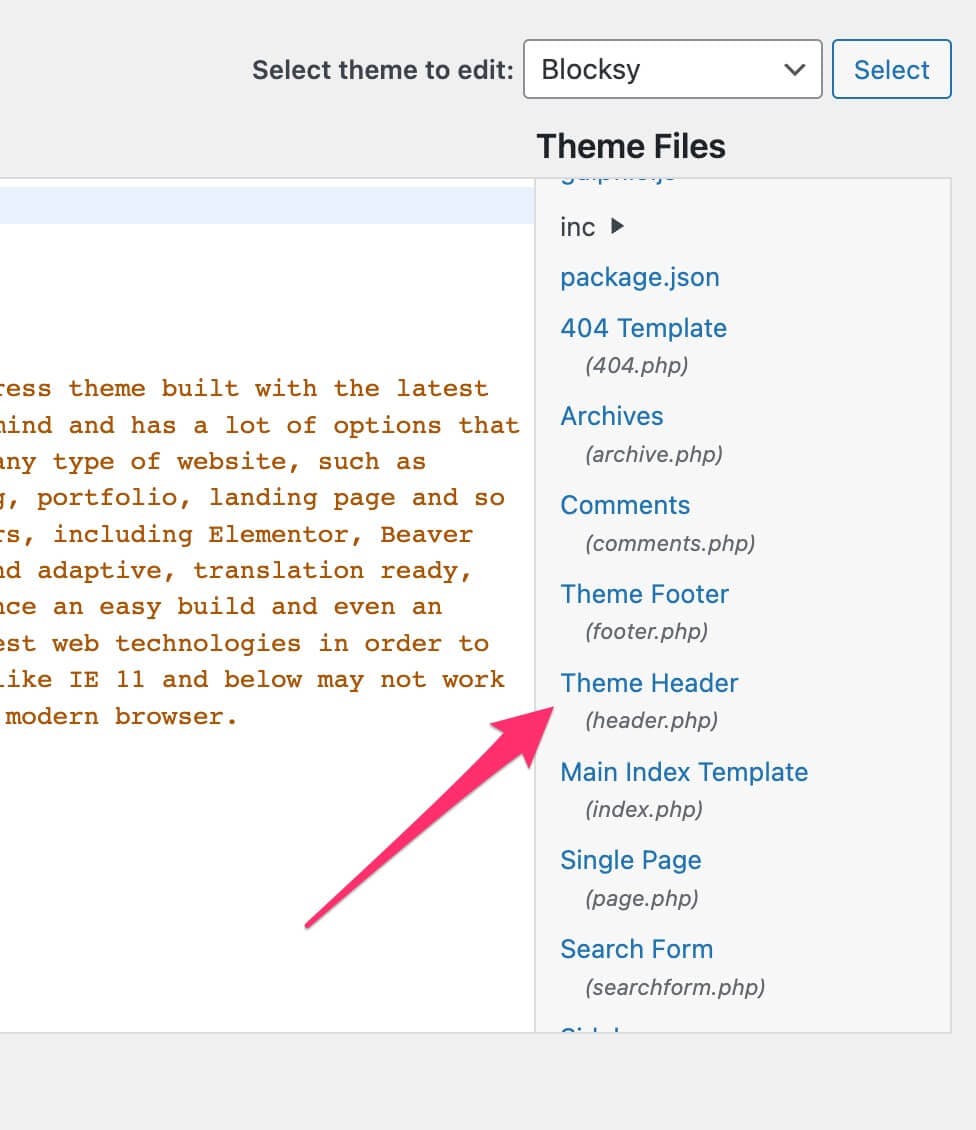 5. Paste the widget code before the closing `` tag.
5. Paste the widget code before the closing `` tag.
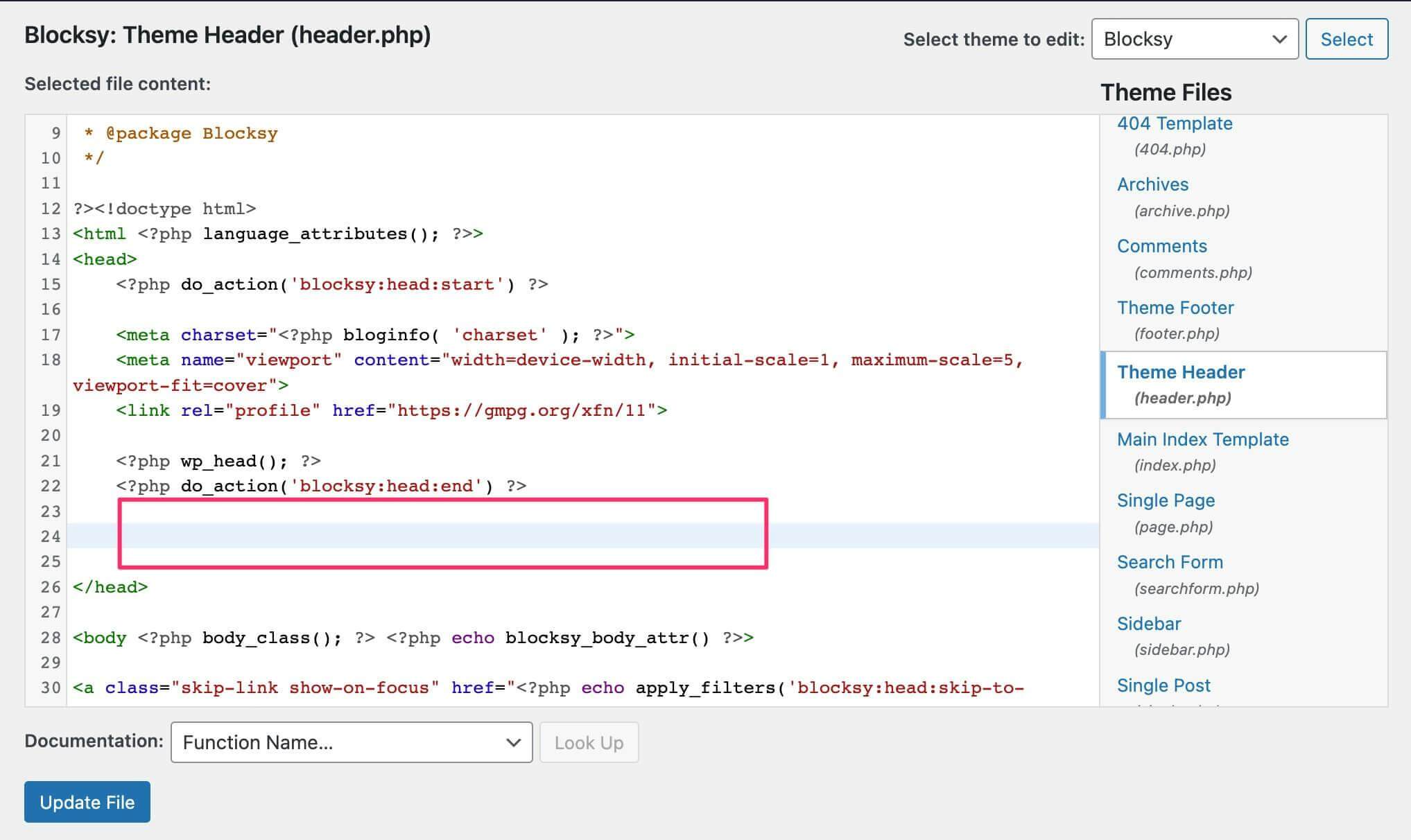 6. Click `Update File` to save.
6. Click `Update File` to save.
 Next, add the variable values to your widget's code snippet. You must make sure that the variable names match exactly as they are in the builder.
```javascript theme={null}
window.chtlConfig = {
chatbotId: "
Next, add the variable values to your widget's code snippet. You must make sure that the variable names match exactly as they are in the builder.
```javascript theme={null}
window.chtlConfig = {
chatbotId: " ## Pass custom data after launch
If at any point after launching the chatbot, you want to pass some data to it, you can do so by calling the `window.Chatling.setVariables` function.
```javascript theme={null}
window.Chatling.setVariables({
"contact_name": "Rick Astley",
"contact_email": "rick.astley@example.com",
"age": 30
}, function(success, errorMessage) {
if (!success) {
// handle error
}
});
```
**Note:**
* The `setVariables` function must be called after the chatbot widget has loaded.
- Variables must be present in the builder and the names must match exactly.
- This will overwrite any existing values for the variables.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/blocks/inputs/phone.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Phone Block
> Learn about the Phone input block and how to set it up in the Builder.
The Phone block is used to collect phone numbers from users.
At the moment, the Phone block is not fully developed and doesn't have the ability to validate phone numbers or provide option for users to select their country code. We are working on improving this block and will update this documentation once the changes are live.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/ai-agent/playground.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Playground
The Playground is your sandbox to experiment with your AI agent in real time. You can tweak core settings—like AI model, enabled actions, temperature, and instructions—then chat with the agent to see exactly how those changes affect behavior.
You can also run side-by-side comparisons of up to 5 instances of your agent, each with different settings, to quickly identify the configuration that performs best.
## Pass custom data after launch
If at any point after launching the chatbot, you want to pass some data to it, you can do so by calling the `window.Chatling.setVariables` function.
```javascript theme={null}
window.Chatling.setVariables({
"contact_name": "Rick Astley",
"contact_email": "rick.astley@example.com",
"age": 30
}, function(success, errorMessage) {
if (!success) {
// handle error
}
});
```
**Note:**
* The `setVariables` function must be called after the chatbot widget has loaded.
- Variables must be present in the builder and the names must match exactly.
- This will overwrite any existing values for the variables.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/blocks/inputs/phone.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Phone Block
> Learn about the Phone input block and how to set it up in the Builder.
The Phone block is used to collect phone numbers from users.
At the moment, the Phone block is not fully developed and doesn't have the ability to validate phone numbers or provide option for users to select their country code. We are working on improving this block and will update this documentation once the changes are live.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/ai-agent/playground.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Playground
The Playground is your sandbox to experiment with your AI agent in real time. You can tweak core settings—like AI model, enabled actions, temperature, and instructions—then chat with the agent to see exactly how those changes affect behavior.
You can also run side-by-side comparisons of up to 5 instances of your agent, each with different settings, to quickly identify the configuration that performs best.
 ## How to compare multiple variations of your agent?
To test with different variations of your agent, click the `Compare` button in the top right corner of the playground. A new instance of your agent will be created with default settings.
## How to compare multiple variations of your agent?
To test with different variations of your agent, click the `Compare` button in the top right corner of the playground. A new instance of your agent will be created with default settings.
 You can then tweak the settings of the new instance and chat with it to see how it performs.
You can then tweak the settings of the new instance and chat with it to see how it performs.
 All inputs to agents are synced between the instances, so you can see how the agent behaves with different settings. If you want to disable this, you can toggle the `Sync` button above one of the agents.
All inputs to agents are synced between the instances, so you can see how the agent behaves with different settings. If you want to disable this, you can toggle the `Sync` button above one of the agents.
 To remove an agent, click the `X` button above it.
To remove an agent, click the `X` button above it.
 ---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/web-widget/installation/prestashop.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# PrestaShop
> Learn how to add Chatling to your PrestaShop website
1. Go to your dashboard.
2. Click `Deploy` button in the sidebar menu.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/web-widget/installation/prestashop.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# PrestaShop
> Learn how to add Chatling to your PrestaShop website
1. Go to your dashboard.
2. Click `Deploy` button in the sidebar menu.
 3. Click the `Manage` button under the `Website Widget` option.
3. Click the `Manage` button under the `Website Widget` option.
 4. Design the appearance of the widget by clicking the `Open widget designer` button.
4. Design the appearance of the widget by clicking the `Open widget designer` button.
 5. Select the display mode for your chatbot, such as "Floating Chat", "Inline", or "Fullscreen".
5. Select the display mode for your chatbot, such as "Floating Chat", "Inline", or "Fullscreen".
 6. Copy the widget code.
6. Copy the widget code.
 7. Download our [PrestaShop module](https://static.chatling.ai/files/chatling-prestashop-v1-0.zip).
8. Extract the zip file and open the `chatling` folder.
7. Download our [PrestaShop module](https://static.chatling.ai/files/chatling-prestashop-v1-0.zip).
8. Extract the zip file and open the `chatling` folder.
 9. Inside the folder, open the `chatling.php` file using a text editor of your choice, such as Notepad on Windows or TextEdit on macOS.
9. Inside the folder, open the `chatling.php` file using a text editor of your choice, such as Notepad on Windows or TextEdit on macOS.
 10. Go to the bottom of the file and find the line that says `Paste code snippet here`.
10. Go to the bottom of the file and find the line that says `Paste code snippet here`.
 Replace it with the code snippet you copied in step #2, as shown below.
Replace it with the code snippet you copied in step #2, as shown below.
 11. Save the file and close it.
12. Zip the `chatling` folder. Do not rename the folder to anything else otherwise the module won't work.
11. Save the file and close it.
12. Zip the `chatling` folder. Do not rename the folder to anything else otherwise the module won't work.
 13. Go to your PrestaShop admin panel. From the sidebar menu, click `Module` > `Module Manager`.
13. Go to your PrestaShop admin panel. From the sidebar menu, click `Module` > `Module Manager`.
 14. Click the `Upload a module` button in the top right. Browse and select the module's zip file.
14. Click the `Upload a module` button in the top right. Browse and select the module's zip file.
 15. Once the module is uploaded, the widget will be live on your website.
15. Once the module is uploaded, the widget will be live on your website.
 ---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/publish-your-chatbot.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Publish your chatbot
> Learn how to publish your chatbot and make it live.
Once you've built your chatbot and tested it thoroughly, you can publish it to make it live.
By publishing, any changes you've made to the chatbot will become available to users where the chatbot is embedded.
To publish your chatbot, click the `Publish` button in the top right corner of the Builder.

---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/block-options/quick-replies.md
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/ai-agent/quick-replies.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Adding Quick Replies to AI Agents
Quick replies are buttons displayed above the input field that allow users to ask common questions without typing.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/publish-your-chatbot.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Publish your chatbot
> Learn how to publish your chatbot and make it live.
Once you've built your chatbot and tested it thoroughly, you can publish it to make it live.
By publishing, any changes you've made to the chatbot will become available to users where the chatbot is embedded.
To publish your chatbot, click the `Publish` button in the top right corner of the Builder.

---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/block-options/quick-replies.md
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/ai-agent/quick-replies.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Adding Quick Replies to AI Agents
Quick replies are buttons displayed above the input field that allow users to ask common questions without typing.

 2. Under the `Website Widget` option, click the brush icon to open the widget editor.
2. Under the `Website Widget` option, click the brush icon to open the widget editor.
 3. Click `Texts` from the sidebar and go to the `Quick Replies` section.
3. Click `Texts` from the sidebar and go to the `Quick Replies` section.
 4. Click the `Add` button to add a new quick reply. Each quick reply will have a label and a message. The label will be displayed on the button and the message will be sent when the user clicks on the button.
4. Click the `Add` button to add a new quick reply. Each quick reply will have a label and a message. The label will be displayed on the button and the message will be sent when the user clicks on the button.
 5. You can also add translations for the quick replies, which will be displayed automatically based on the user's language.
6. The `Auto-hide quick replies` option allows you to automatically hide the quick replies after a certain number of messages are sent by the user. This is useful to prevent the quick replies from being displayed at all times.
5. You can also add translations for the quick replies, which will be displayed automatically based on the user's language.
6. The `Auto-hide quick replies` option allows you to automatically hide the quick replies after a certain number of messages are sent by the user. This is useful to prevent the quick replies from being displayed at all times.
 7. Once you are done, click the `Save` button to save the changes.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/api-reference/v2/conversations/rate-ai-answer.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Rate AI answer
Use this endpoint to rate an AI answer as helpful or not helpful. You can only rate AI answers generated using the Knowledge Base.
## Request parameters
### Path
7. Once you are done, click the `Save` button to save the changes.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/api-reference/v2/conversations/rate-ai-answer.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Rate AI answer
Use this endpoint to rate an AI answer as helpful or not helpful. You can only rate AI answers generated using the Knowledge Base.
## Request parameters
### Path
 3. Click the `Security` tab.
4. Under the `Rate limiting` section, add a rate limit, e.g. 10 messages per minute. You can add multiple rate limits for different periods of time, such as per minute, per hour, or per day.
3. Click the `Security` tab.
4. Under the `Rate limiting` section, add a rate limit, e.g. 10 messages per minute. You can add multiple rate limits for different periods of time, such as per minute, per hour, or per day.
 ## Re-sync data sources in bulk
To re-sync multiple data sources at once, click on the checkbox next to the links you want to re-sync. Then, click on the `Bulk action` dropdown and select `Re-sync links`.
## Re-sync data sources in bulk
To re-sync multiple data sources at once, click on the checkbox next to the links you want to re-sync. Then, click on the `Bulk action` dropdown and select `Re-sync links`.
 ---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/whatsapp/reconnect-account.md
# Reconnect WhatsApp account
> Learn how to reconnect your WhatsApp account to your chatbot in Chatling.
If you want to restart the connection between your WhatsApp account and your chatbot, you can disconnect and reconnect your account.
1. From your chatbot's dashboard, click the `Settings` button under the Chatbot menu.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/whatsapp/reconnect-account.md
# Reconnect WhatsApp account
> Learn how to reconnect your WhatsApp account to your chatbot in Chatling.
If you want to restart the connection between your WhatsApp account and your chatbot, you can disconnect and reconnect your account.
1. From your chatbot's dashboard, click the `Settings` button under the Chatbot menu.
 2. Go to the `WhatsApp` tab.
2. Go to the `WhatsApp` tab.
 3. Click the `Disconnect` button.
3. Click the `Disconnect` button.
 4. An onboarding will be displayed to reconnect your account. Follow the on-screen instructions to reconnect your account. You can also check [this guide](/chatbot/whatsapp/setup) for the steps to connect your account.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/web-widget/remove-powered-by-chatling-branding.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Remove "Powered by Chatling" branding
> Learn how to remove the Chatling branding from your chatbot widget.
## Which plans can remove the branding?
The branding can be removed if you're on the **Ultimate** plan or by purchasing the [Remove "Powered by Chatling" branding add-on](https://chatling.com/pricing).
## How to remove the branding
1. Open the widget designer. To learn how to access it, see [this guide](/web-widget/customize#how-to-customize-the-widget).
2. Go to `Configure`.
4. An onboarding will be displayed to reconnect your account. Follow the on-screen instructions to reconnect your account. You can also check [this guide](/chatbot/whatsapp/setup) for the steps to connect your account.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/web-widget/remove-powered-by-chatling-branding.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Remove "Powered by Chatling" branding
> Learn how to remove the Chatling branding from your chatbot widget.
## Which plans can remove the branding?
The branding can be removed if you're on the **Ultimate** plan or by purchasing the [Remove "Powered by Chatling" branding add-on](https://chatling.com/pricing).
## How to remove the branding
1. Open the widget designer. To learn how to access it, see [this guide](/web-widget/customize#how-to-customize-the-widget).
2. Go to `Configure`.
 2. Find the member you want to remove and click the ellipsis icon next to them.
2. Find the member you want to remove and click the ellipsis icon next to them.
 3. Click **Remove member**.
The member will be removed from the project immediately and will no longer have access to it.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/faq/reset-chat-on-page-load.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# How to reset the chat on page load?
By default, chat history is retained when users navigate away from the chatbot and return to it, refresh the page, or go to a different page. This means that when users return to the chatbot, they can see their existing chat and continue from where they left off.
If you want to disable this so that the chat is reset on page load, you can do so by following these steps:
1. From your chatbot dashboard, go to `Builder`.
3. Click **Remove member**.
The member will be removed from the project immediately and will no longer have access to it.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/faq/reset-chat-on-page-load.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# How to reset the chat on page load?
By default, chat history is retained when users navigate away from the chatbot and return to it, refresh the page, or go to a different page. This means that when users return to the chatbot, they can see their existing chat and continue from where they left off.
If you want to disable this so that the chat is reset on page load, you can do so by following these steps:
1. From your chatbot dashboard, go to `Builder`.
 2. Click the settings icon in the sidebar.
2. Click the settings icon in the sidebar.
 3. Enable the the `Reset chat on page load` option.
3. Enable the the `Reset chat on page load` option.
 ---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/api-reference/v2/knowledge-base/resync-source.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Resync data source
> Resync a data source.
**The following limitations apply:**
* The supported sources are links and Zoho articles.
* You can have up to 50 data sources queued for resync. If you exceed this limit, you will receive an error and must wait until some of the queued resyncs are complete.
* You can only resync data sources that are in the `processed` state.
## Request parameters
### Path
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/api-reference/v2/knowledge-base/resync-source.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Resync data source
> Resync a data source.
**The following limitations apply:**
* The supported sources are links and Zoho articles.
* You can have up to 50 data sources queued for resync. If you exceed this limit, you will receive an error and must wait until some of the queued resyncs are complete.
* You can only resync data sources that are in the `processed` state.
## Request parameters
### Path
 2. Click the `Satisfaction Survey` tab.
2. Click the `Satisfaction Survey` tab.
 3. Toggle on the `Show survey` option.
3. Toggle on the `Show survey` option.
 4. Customize the survey by selecting the rating type, questions to display, and more.
4. Customize the survey by selecting the rating type, questions to display, and more.
 5. Click `Save` to apply the changes.
5. Click `Save` to apply the changes.
 ## View survey responses
You can view survey responses from the `Conversations` page of your chatbot dashboard. If a conversation has a survey response, the result will appear within the conversation thread as well as on the `Details` section in the sidebar.
## View survey responses
You can view survey responses from the `Conversations` page of your chatbot dashboard. If a conversation has a survey response, the result will appear within the conversation thread as well as on the `Details` section in the sidebar.
 ---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/save-your-work.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Save your work
> Learn how to save your changes in the Builder.
Any changes you make to your chatbot's flow in the [Builder](/chatbot/builder/introduction) is saved automatically. You can also save it manually by clicking the `Save` button in the top right side of the screen.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/save-your-work.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Save your work
> Learn how to save your changes in the Builder.
Any changes you make to your chatbot's flow in the [Builder](/chatbot/builder/introduction) is saved automatically. You can also save it manually by clicking the `Save` button in the top right side of the screen.
 When you save your changes, it will be saved as a draft and will not be published. This allows you to work on the chatbot and test it without affecting the live version.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/blocks/action/send-email.md
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/ai-agent/actions/send-email.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Send Email
The Send Email action allows the AI Agent to send emails to one or more recipients. You can use it to send notifications, follow ups, order confirmations, transactional emails and other types of emails.
When you save your changes, it will be saved as a draft and will not be published. This allows you to work on the chatbot and test it without affecting the live version.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/blocks/action/send-email.md
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/ai-agent/actions/send-email.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Send Email
The Send Email action allows the AI Agent to send emails to one or more recipients. You can use it to send notifications, follow ups, order confirmations, transactional emails and other types of emails.
 ## Configuration
### `Action Name`
A short, specific identifier that tells the Agent what this action does (e.g. best\_sellers\_buttons, support\_button).
### `When to Use`
A detailed description of what the action does and when it must be used.
When applicable, you can specify one or more of the following:
* **Positive cues/phrases**: Example utterances and keywords that signal this action (include a few variations).
* **Preconditions**: What must be true before running.
* **Do not use when**: Explicit exclusions to avoid false triggers.
## Configuration
### `Action Name`
A short, specific identifier that tells the Agent what this action does (e.g. best\_sellers\_buttons, support\_button).
### `When to Use`
A detailed description of what the action does and when it must be used.
When applicable, you can specify one or more of the following:
* **Positive cues/phrases**: Example utterances and keywords that signal this action (include a few variations).
* **Preconditions**: What must be true before running.
* **Do not use when**: Explicit exclusions to avoid false triggers.
 ### `Frequency`
Specify how often the Agent can invoke this action to avoid overusing it, e.g `Once per chat` or `Whenever applicable`.
### `Frequency`
Specify how often the Agent can invoke this action to avoid overusing it, e.g `Once per chat` or `Whenever applicable`.
 ### `Input parameters`
Define the parameters the Agent must gather before sending the request. The Agent can capture these from user input, existing chat context, or saved contact data.
For each parameter, you can specify the following:
* **Name**: The name of the parameter. Must start with a letter and contain only letters, numbers, and underscores.
* **Description** (optional): A description of the parameter to indicate what it is and if applicable, the formatting rules and min/max length.
* **Save to variable** (optional): The variable where the data can be saved. Useful when you want to use the data in the email setup, such as the recipient's email address.
### `Email Setup`
Configure the email setup.
* **Sender Name**: The name of the sender.
* **To**: The email addresses of the recipients (max 5).
* **Reply-to**: The email addresses to reply to (max 5).
* **CC**: The email addresses of the recipients who will receive a copy of the email (max 5).
* **Subject**: The subject of the email.
* **Message**: The content of the email.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/ai/set-ai-model.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Setting the AI model
> Learn how to set the LLM model used by the AI.
There are various [AI models](/ai/supported-ai-models) available in Chatling that you can use to generate responses for your chatbot.
We recommend testing with different models to see which one works best for your chatbot and provides the most accurate responses. Each model uses a different amount of credits per response.
## How to set the AI model?
The method for choosing the AI model depends on the [Response Source](/chatbot/builder/blocks/ai/ai-response#what-is-the-response-source) that you've set for the [AI Response](/chatbot/builder/blocks/ai/ai-response) block.
Below are the instructions based on the response source you've selected.
### 1. Response Source: Knowledge Base
If you are using the Knowledge Base as the response source, you can set the AI model using the [AI Configuration menu](/chatbot/builder/sidebar#ai-configuration) in the Builder's sidebar.
1. Click on the AI Configuration menu in the sidebar.
### `Input parameters`
Define the parameters the Agent must gather before sending the request. The Agent can capture these from user input, existing chat context, or saved contact data.
For each parameter, you can specify the following:
* **Name**: The name of the parameter. Must start with a letter and contain only letters, numbers, and underscores.
* **Description** (optional): A description of the parameter to indicate what it is and if applicable, the formatting rules and min/max length.
* **Save to variable** (optional): The variable where the data can be saved. Useful when you want to use the data in the email setup, such as the recipient's email address.
### `Email Setup`
Configure the email setup.
* **Sender Name**: The name of the sender.
* **To**: The email addresses of the recipients (max 5).
* **Reply-to**: The email addresses to reply to (max 5).
* **CC**: The email addresses of the recipients who will receive a copy of the email (max 5).
* **Subject**: The subject of the email.
* **Message**: The content of the email.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/ai/set-ai-model.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Setting the AI model
> Learn how to set the LLM model used by the AI.
There are various [AI models](/ai/supported-ai-models) available in Chatling that you can use to generate responses for your chatbot.
We recommend testing with different models to see which one works best for your chatbot and provides the most accurate responses. Each model uses a different amount of credits per response.
## How to set the AI model?
The method for choosing the AI model depends on the [Response Source](/chatbot/builder/blocks/ai/ai-response#what-is-the-response-source) that you've set for the [AI Response](/chatbot/builder/blocks/ai/ai-response) block.
Below are the instructions based on the response source you've selected.
### 1. Response Source: Knowledge Base
If you are using the Knowledge Base as the response source, you can set the AI model using the [AI Configuration menu](/chatbot/builder/sidebar#ai-configuration) in the Builder's sidebar.
1. Click on the AI Configuration menu in the sidebar.
 2. Go to `Settings`.
2. Go to `Settings`.
 3. Select the AI model you want to use from the dropdown list.
3. Select the AI model you want to use from the dropdown list.
 Once you've selected the AI model, all AI Response blocks that use the Knowledge Base as the response source will use this model to generate responses.
#### Setting the model on a per-block basis
If you want to set the AI model on a per-block basis, you can do so by opening the AI Response block's editor and settings the `Model` option. This will override the default model set in the AI Configuration settings.
Once you've selected the AI model, all AI Response blocks that use the Knowledge Base as the response source will use this model to generate responses.
#### Setting the model on a per-block basis
If you want to set the AI model on a per-block basis, you can do so by opening the AI Response block's editor and settings the `Model` option. This will override the default model set in the AI Configuration settings.
 ### 2. Response Source: AI Model
If you are using the "AI Model" as the response source, you can set the AI model from the block's editor using the `Model` option.
### 2. Response Source: AI Model
If you are using the "AI Model" as the response source, you can set the AI model from the block's editor using the `Model` option.
 ---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/blocks/action/set-variable.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Set Variable
> Learn about the Set Variable block and how to set it up in the Builder.
The Set Variable block is used to set the value of one or more variables. With it, you can modify variable values dynamically at any point in the flow.
## How to configure
1. Click on the Set Variable block in the canvas to open its settings.
2. Select the variable you want to modify.
3. Select the type of the modification:
* **Value**: Set the variable to a specific value. You can also insert variables to make the value dynamic.
* **Add/Subtract/Multiply/Divide**: Perform a mathematical operation on the variable. You can add, subtract, multiply, or divide the variable by a specific value. The value must be a number.
4. Enter the value.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/blocks/action/set-variable.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Set Variable
> Learn about the Set Variable block and how to set it up in the Builder.
The Set Variable block is used to set the value of one or more variables. With it, you can modify variable values dynamically at any point in the flow.
## How to configure
1. Click on the Set Variable block in the canvas to open its settings.
2. Select the variable you want to modify.
3. Select the type of the modification:
* **Value**: Set the variable to a specific value. You can also insert variables to make the value dynamic.
* **Add/Subtract/Multiply/Divide**: Perform a mathematical operation on the variable. You can add, subtract, multiply, or divide the variable by a specific value. The value must be a number.
4. Enter the value.
 ## Multiple variables
You can set multiple variables at once by clicking on the **Add variable** button. This will add a new row where you can select another variable and set its value.
## Multiple variables
You can set multiple variables at once by clicking on the **Add variable** button. This will add a new row where you can select another variable and set its value.
 ## Example
Let's say you're building a lead generation chatbot for a real estate brokerage. You want to prompt the AI to ask the customer three questions about their requirements and forward the answers to the team. You can do this by using a counter variable that increments each time the user answers a question.
Below is a sample flow that demonstrates how to use the Set Variable block.
## Example
Let's say you're building a lead generation chatbot for a real estate brokerage. You want to prompt the AI to ask the customer three questions about their requirements and forward the answers to the team. You can do this by using a counter variable that increments each time the user answers a question.
Below is a sample flow that demonstrates how to use the Set Variable block.
 We're using a variable called `counter` to keep track of the number of questions that have been asked. This variable is incremented by 1 each time the user answers a question.
Then, we're using the Condition block to check if the counter is greater or equal to 3. If it is, a message is displayed to inform the user that their inquiry has been forwarded to the team. Else, the AI asks the next question.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/whatsapp/setup.md
# How to connect your WhatsApp Business account
When you create a WhatsApp chatbot, an onboarding is displayed to guide you through the process of connecting your WhatsApp Business account to Chatling. We'll walk you through the steps below.
## Before you start
The phone number you connect must not be in use by a WhatsApp account. If it's in use, you must delete the account from WhatsApp before continuing.
Here's how to delete a WhatsApp account:
1. Open the WhatsApp app.
2. Go to `Settings` > `Account` > `Delete my account`.
3. Type in your phone number for confirmation and tap on `Delete my account`.
Once deleted, the phone number can be used to connect a new WhatsApp Business account.
## How to connect your WhatsApp Business account
1. Click the `Login with Facebook` button.
We're using a variable called `counter` to keep track of the number of questions that have been asked. This variable is incremented by 1 each time the user answers a question.
Then, we're using the Condition block to check if the counter is greater or equal to 3. If it is, a message is displayed to inform the user that their inquiry has been forwarded to the team. Else, the AI asks the next question.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/whatsapp/setup.md
# How to connect your WhatsApp Business account
When you create a WhatsApp chatbot, an onboarding is displayed to guide you through the process of connecting your WhatsApp Business account to Chatling. We'll walk you through the steps below.
## Before you start
The phone number you connect must not be in use by a WhatsApp account. If it's in use, you must delete the account from WhatsApp before continuing.
Here's how to delete a WhatsApp account:
1. Open the WhatsApp app.
2. Go to `Settings` > `Account` > `Delete my account`.
3. Type in your phone number for confirmation and tap on `Delete my account`.
Once deleted, the phone number can be used to connect a new WhatsApp Business account.
## How to connect your WhatsApp Business account
1. Click the `Login with Facebook` button.
 2. A Facebook authentication window will open. Click the `Continue` button.
2. A Facebook authentication window will open. Click the `Continue` button.
 3. Select `Get started` to continue.
3. Select `Get started` to continue.
 4. Select a business profile or create a new one.
4. Select a business profile or create a new one.
 5. Choose or create a new WhatsApp Business account and profile.
5. Choose or create a new WhatsApp Business account and profile.
 6. Enter the required information to create a new business profile.
* *Skip this step if you selected an existing business profile.*
7. Add and verify your phone number.
* *Skip this step if you selected an existing business profile.*
6. Enter the required information to create a new business profile.
* *Skip this step if you selected an existing business profile.*
7. Add and verify your phone number.
* *Skip this step if you selected an existing business profile.*
 8. Click the `Continue` button.
8. Click the `Continue` button.
 9. Facebook begins verifying the information you provided. Once it's completed successfully, you should see a message similar to below. Click the `Finish` button.
9. Facebook begins verifying the information you provided. Once it's completed successfully, you should see a message similar to below. Click the `Finish` button.
 10. Go back to Chatling and a message will be displayed that your authentication is being processed. If successful, you should see a message similar to below.
10. Go back to Chatling and a message will be displayed that your authentication is being processed. If successful, you should see a message similar to below.
 11. Next, you must enter a six digit code for two-factor authentication so that your phone number can be registered with WhatsApp. If the number already has 2FA enabled, enter the same code you had set up.
11. Next, you must enter a six digit code for two-factor authentication so that your phone number can be registered with WhatsApp. If the number already has 2FA enabled, enter the same code you had set up.
 12. Once the phone number is registered successfully, you're all set and your WhatsApp Business account is connected to Chatling. Click the `Open Dashboard` button to continue.
12. Once the phone number is registered successfully, you're all set and your WhatsApp Business account is connected to Chatling. Click the `Open Dashboard` button to continue.

 2. Click `Generate Link`.
2. Click `Generate Link`.
 3. To password protect the link, enable `Require password` and type in a password.
3. To password protect the link, enable `Require password` and type in a password.
 4. Copy the link and share it with others.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/web-widget/installation/shopify.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Shopify
> Learn how to add Chatling to your Shopify store
## Method 1: Using theme.liquid
1. Go to your dashboard.
2. Click `Deploy` button in the sidebar menu.
4. Copy the link and share it with others.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/web-widget/installation/shopify.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Shopify
> Learn how to add Chatling to your Shopify store
## Method 1: Using theme.liquid
1. Go to your dashboard.
2. Click `Deploy` button in the sidebar menu.
 3. Click the `Manage` button under the `Website Widget` option.
3. Click the `Manage` button under the `Website Widget` option.
 4. Design the appearance of the widget by clicking the `Open widget designer` button.
4. Design the appearance of the widget by clicking the `Open widget designer` button.
 5. Select the display mode for your chatbot, such as "Floating Chat", "Inline", or "Fullscreen".
5. Select the display mode for your chatbot, such as "Floating Chat", "Inline", or "Fullscreen".
 6. Copy the widget code.
6. Copy the widget code.
 7. Go to your Shopify dashboard and click on `Online Store` from the sidebar.
7. Go to your Shopify dashboard and click on `Online Store` from the sidebar.
 8. Edit your theme by clicking the ellipsis icon next to your current theme and choosing `Edit code`.
8. Edit your theme by clicking the ellipsis icon next to your current theme and choosing `Edit code`.
 9. Find and open the `theme.liquid` file From the sidebar where the list of files is displayed.
9. Find and open the `theme.liquid` file From the sidebar where the list of files is displayed.
 10. Paste the widget code in the `` section. You can paste it anywhere between the opening `` tag and the closing `` tag.
10. Paste the widget code in the `` section. You can paste it anywhere between the opening `` tag and the closing `` tag.
 11. Click the Save button.
The chatbot will be live on your website and should appear across all your store's pages.
11. Click the Save button.
The chatbot will be live on your website and should appear across all your store's pages.
 ## Method 2: Using Customization
1. Follow steps 1-6 from Method 1 to copy the widget code.
2. From your Shopify dashboard, click on `Online Store` and go to `Themes`.
## Method 2: Using Customization
1. Follow steps 1-6 from Method 1 to copy the widget code.
2. From your Shopify dashboard, click on `Online Store` and go to `Themes`.
 3. Click on the `Customize` button next to your current theme.
3. Click on the `Customize` button next to your current theme.
 4. Under the `Header` section, choose `Add section`. Search for `Custom liquid` and add it.
4. Under the `Header` section, choose `Add section`. Search for `Custom liquid` and add it.
 5. Open the `Custom liquid` editor and paste your widget code into the `Liquid code` field.
5. Open the `Custom liquid` editor and paste your widget code into the `Liquid code` field.
 6. Set the `Top padding` and `Bottom padding` to `0` so the section doesn't create a blank space in your site's header.
6. Set the `Top padding` and `Bottom padding` to `0` so the section doesn't create a blank space in your site's header.
 7. Click the `Save` button.
The widget will be live on your website and should appear across all your store's pages.
7. Click the `Save` button.
The widget will be live on your website and should appear across all your store's pages.
 ---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/sidebar.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Sidebar
> Learn about the Sidebar and its functionalities in the Builder.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/sidebar.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Sidebar
> Learn about the Sidebar and its functionalities in the Builder.
 The sidebar contains four menus:
* Blocks
* Variables
* AI Configuration
* Settings
## Sidebar Menus
### Blocks
The Blocks menu contains all the blocks you can add to your flow. [Blocks](/chatbot/builder/blocks/overview) build up the conversational flow of your chatbot.
You can drag and drop blocks onto the canvas to add them to your flow.

Here are the different categories of blocks that are available:
* **Send message**: Display a message to the user.
* **Capture response**: Capture answers from the user, such as text, email, form submission, and more.
* **AI**: Use AI to generate responses to user's questions.
* **Logic**: Add conditions and logic to your flow.
* **Integration**: Connect your chatbot to external services.
### Variables
Variables are placeholders that store information during the conversation. You can use variables to store user inputs, API responses, and more. These variables can be used to personalize the conversation and make it more dynamic.
The sidebar contains four menus:
* Blocks
* Variables
* AI Configuration
* Settings
## Sidebar Menus
### Blocks
The Blocks menu contains all the blocks you can add to your flow. [Blocks](/chatbot/builder/blocks/overview) build up the conversational flow of your chatbot.
You can drag and drop blocks onto the canvas to add them to your flow.

Here are the different categories of blocks that are available:
* **Send message**: Display a message to the user.
* **Capture response**: Capture answers from the user, such as text, email, form submission, and more.
* **AI**: Use AI to generate responses to user's questions.
* **Logic**: Add conditions and logic to your flow.
* **Integration**: Connect your chatbot to external services.
### Variables
Variables are placeholders that store information during the conversation. You can use variables to store user inputs, API responses, and more. These variables can be used to personalize the conversation and make it more dynamic.
 There are two types of variables:
* **System variables**: These are predefined variables that store system information or can be used to perform a specific action. For example, the `contact_email` variable can be used to store the user's email address and save them as a lead.
If you click on a system variable, you can view its purpose.
There are also additional system variables that aren't imported by default. To view and import them, click the `Import system variables` button.
* **Custom variables**: These are variables you create to store information specific to your chatbot. For example, you can create a custom variable to store the user's question and use it in the `AI Response` block to generate a response from the AI.
### AI Configuration
The AI Configuration menu allows you to configure the default AI settings for your chatbot. These settings are used when the chatbot generates AI responses using the Knowledge Base.
There are two types of variables:
* **System variables**: These are predefined variables that store system information or can be used to perform a specific action. For example, the `contact_email` variable can be used to store the user's email address and save them as a lead.
If you click on a system variable, you can view its purpose.
There are also additional system variables that aren't imported by default. To view and import them, click the `Import system variables` button.
* **Custom variables**: These are variables you create to store information specific to your chatbot. For example, you can create a custom variable to store the user's question and use it in the `AI Response` block to generate a response from the AI.
### AI Configuration
The AI Configuration menu allows you to configure the default AI settings for your chatbot. These settings are used when the chatbot generates AI responses using the Knowledge Base.
 You can configure the following settings:
* **Instructions**: Provide instructions to the AI to tailor its responses. For example, you can instruct the AI to provide more detailed responses or to use a specific tone. You can click the `View examples` button to see examples of instructions you can provide.
* **Settings**:
* **Business, product, or brand name**: This will be used by the AI to generate more relevant responses and avoids answering off-topics questions that aren't related to your business, product, or brand, such as questions related to your competitors, weather, etc.
* **AI Model**: The AI model to use for generating responses. Every model uses a different amount of credits per response. We recommend testing with different models to see which one works best for your chatbot.
* **Language**: The language in which the AI should generate responses. If you set it to Auto, the AI will detect the language of the user's question and generate a response in the same language.
* **Temperature**: Controls the randomness of the responses. A higher temperature will generate more creative responses, while a lower temperature will generate more accurate responses.
### Settings
The Settings menu allows you to configure the chatbot's general settings. Here's what you can configure:
* **Message Delay**: The time delay in seconds between chatbot's messages.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/web-widget/installation/squarespace.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Squarespace
> Learn how to add Chatling to your Squarespace website
1. Go to your dashboard.
2. Click `Deploy` button in the sidebar menu.
You can configure the following settings:
* **Instructions**: Provide instructions to the AI to tailor its responses. For example, you can instruct the AI to provide more detailed responses or to use a specific tone. You can click the `View examples` button to see examples of instructions you can provide.
* **Settings**:
* **Business, product, or brand name**: This will be used by the AI to generate more relevant responses and avoids answering off-topics questions that aren't related to your business, product, or brand, such as questions related to your competitors, weather, etc.
* **AI Model**: The AI model to use for generating responses. Every model uses a different amount of credits per response. We recommend testing with different models to see which one works best for your chatbot.
* **Language**: The language in which the AI should generate responses. If you set it to Auto, the AI will detect the language of the user's question and generate a response in the same language.
* **Temperature**: Controls the randomness of the responses. A higher temperature will generate more creative responses, while a lower temperature will generate more accurate responses.
### Settings
The Settings menu allows you to configure the chatbot's general settings. Here's what you can configure:
* **Message Delay**: The time delay in seconds between chatbot's messages.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/web-widget/installation/squarespace.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Squarespace
> Learn how to add Chatling to your Squarespace website
1. Go to your dashboard.
2. Click `Deploy` button in the sidebar menu.
 3. Click the `Manage` button under the `Website Widget` option.
3. Click the `Manage` button under the `Website Widget` option.
 4. Design the appearance of the widget by clicking the `Open widget designer` button.
4. Design the appearance of the widget by clicking the `Open widget designer` button.
 5. Select the display mode for your chatbot, such as "Floating Chat", "Inline", or "Fullscreen".
5. Select the display mode for your chatbot, such as "Floating Chat", "Inline", or "Fullscreen".
 6. Copy the widget code.
6. Copy the widget code.
 7. Sign in to your Squarespace account and open the website where you want to add the widget.
7. Sign in to your Squarespace account and open the website where you want to add the widget.
 8. From the sidebar menu, select `Website`.
8. From the sidebar menu, select `Website`.
 9. Scroll to the bottom of the sidebar menu and choose `Website Tools`.
9. Scroll to the bottom of the sidebar menu and choose `Website Tools`.
 10. Open `Code Injection`.
* If you're on an older version of Squarespace, such as v7.0, code injection is located in `Settings` > `Developer Tools` > `Code Injection`.
10. Open `Code Injection`.
* If you're on an older version of Squarespace, such as v7.0, code injection is located in `Settings` > `Developer Tools` > `Code Injection`.
 11. Paste the widget code in the `Header` section, and click `Save`.
11. Paste the widget code in the `Header` section, and click `Save`.
 12. The widget is now live on your website, and visitors can interact with it.
12. The widget is now live on your website, and visitors can interact with it.
 ---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/ai/supported-ai-models.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Supported AI models
> A list of supported AI models in Chatling.
Chatling supports the following LLMs:
* GPT-5.1
* GPT-5
* GPT-5 Mini
* GPT-5 Nano
* GPT-4.1
* GPT-4.1 Mini
* GPT-4.1 Nano
* GPT-4o
* GPT-4o Mini
* o4 Mini
* o3 Mini
* Claude Opus 4
* Claude Opus 3
* Claude Sonnet 4
* Claude Sonnet 3.7
* Claude Sonnet 3.5
* Claude Haiku 3.5
* Claude Haiku 3
* Gemini 2.5 Pro
* Gemini 2.5 Flash
* Gemini 2.0 Flash
To request a new AI model, please [contact us](mailto:support@chatling.ai).
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/test-your-chatbot.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Test your chatbot
> Learn how to test your chatbot to see how it works.
While you're building the chatbot, you can test it to see how it works. This allows you to identify any issues and make improvements before publishing it.
Click the `Preview bot` button in the top right corner of the Builder to launch the chatbot for testing.

---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/blocks/send/text.md
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/blocks/inputs/text.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Text Block
> Learn about the Text input block and how to set it up in the Builder.
The Text block is used to capture user input in the form of text. You can use this block to prompt users for answers and collect the necessary information.
## Configuration
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/ai/supported-ai-models.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Supported AI models
> A list of supported AI models in Chatling.
Chatling supports the following LLMs:
* GPT-5.1
* GPT-5
* GPT-5 Mini
* GPT-5 Nano
* GPT-4.1
* GPT-4.1 Mini
* GPT-4.1 Nano
* GPT-4o
* GPT-4o Mini
* o4 Mini
* o3 Mini
* Claude Opus 4
* Claude Opus 3
* Claude Sonnet 4
* Claude Sonnet 3.7
* Claude Sonnet 3.5
* Claude Haiku 3.5
* Claude Haiku 3
* Gemini 2.5 Pro
* Gemini 2.5 Flash
* Gemini 2.0 Flash
To request a new AI model, please [contact us](mailto:support@chatling.ai).
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/test-your-chatbot.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Test your chatbot
> Learn how to test your chatbot to see how it works.
While you're building the chatbot, you can test it to see how it works. This allows you to identify any issues and make improvements before publishing it.
Click the `Preview bot` button in the top right corner of the Builder to launch the chatbot for testing.

---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/blocks/send/text.md
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/blocks/inputs/text.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Text Block
> Learn about the Text input block and how to set it up in the Builder.
The Text block is used to capture user input in the form of text. You can use this block to prompt users for answers and collect the necessary information.
## Configuration
 You can configure the following settings for the Text block:
* **Store answer in variable**: Choose a variable to store the user's response. You can use the stored data in other blocks to personalize the conversation.
* **Input required**: Determine whether the user must provide an answer to proceed. If this option is disabled, a Skip button will appear, allowing users to skip the input.
* **[Voice Input](/chatbot/builder/block-options/voice-input)**: Toggle on the Voice Input option to allow users to send messages using voice.
* **Min. characters**: The minimum number of characters the user must enter.
* **Max. characters**: The maximum number of characters the user can enter.
* **[Quick replies](/chatbot/builder/block-options/quick-replies)**
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/api-reference/v2/chatbots/update-chatbot-settings.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Update chatbot settings
> Update the settings of a chatbot.
## Request parameters
### Path
You can configure the following settings for the Text block:
* **Store answer in variable**: Choose a variable to store the user's response. You can use the stored data in other blocks to personalize the conversation.
* **Input required**: Determine whether the user must provide an answer to proceed. If this option is disabled, a Skip button will appear, allowing users to skip the input.
* **[Voice Input](/chatbot/builder/block-options/voice-input)**: Toggle on the Voice Input option to allow users to send messages using voice.
* **Min. characters**: The minimum number of characters the user must enter.
* **Max. characters**: The maximum number of characters the user can enter.
* **[Quick replies](/chatbot/builder/block-options/quick-replies)**
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/api-reference/v2/chatbots/update-chatbot-settings.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Update chatbot settings
> Update the settings of a chatbot.
## Request parameters
### Path
 ## Adding URL buttons
1. Drag and drop the URL Button block on the canvas.
## Adding URL buttons
1. Drag and drop the URL Button block on the canvas.
 2. Click on the block to edit it.
3. Click `Add button` button to add a new button.
2. Click on the block to edit it.
3. Click `Add button` button to add a new button.
 4. Enter the button label and URL. The label is the text that will be displayed on the button.
4. Enter the button label and URL. The label is the text that will be displayed on the button.
 5. To add more buttons, click the `+` icon.
5. To add more buttons, click the `+` icon.
 ---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/blocks/inputs/url.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# URL Block
> Learn about the URL input block and how to set it up in the Builder.
The URL block is used to collect URLs from users. It validates the user's input to ensure that it is a valid URL.
You can use this block to ask users for website URLs, social media profiles, or any other web addresses.
## Configuration
The URL block has the following configuration options:
* **Store answer in variable**: The variable where the user's input will be stored.
* **Input required**: Whether the user's input is mandatory. If disabled, a Skip button will appear, allowing users to skip the input.
* **[Quick replies](/chatbot/builder/block-options/quick-replies)**
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/blocks/inputs/url.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# URL Block
> Learn about the URL input block and how to set it up in the Builder.
The URL block is used to collect URLs from users. It validates the user's input to ensure that it is a valid URL.
You can use this block to ask users for website URLs, social media profiles, or any other web addresses.
## Configuration
The URL block has the following configuration options:
* **Store answer in variable**: The variable where the user's input will be stored.
* **Input required**: Whether the user's input is mandatory. If disabled, a Skip button will appear, allowing users to skip the input.
* **[Quick replies](/chatbot/builder/block-options/quick-replies)**
 ---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/api-reference/v2/usage/user-seats.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# User Seats
> Get the user seats usage for the project.
## Response
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/api-reference/v2/usage/user-seats.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# User Seats
> Get the user seats usage for the project.
## Response
 3. Select the intents you want user messages to be checked against.
3. Select the intents you want user messages to be checked against.
 When a user sends a message, the chatbot will check if the message matches any of the selected intents and trigger the appropriate flow. If there are no matches, the flow will continue normally.
## 2. Defining intent flows
There are two ways to define the actions for an intent:
1. Intent trigger block (global)
2. Local trigger
### Intent trigger block
Intent triggers are flows that will be executed when an intent is matched. These triggers are global, meaning that they will be executed by any block that matches the intent. This is useful if you want to create a standard response for an intent that can be used in multiple places in your chatbot.
For example, if you create an Intent trigger for `Order Tracking`:
* Any block that matches this intent will start this flow.
* The same flow runs whether matched in a welcome message or support conversation.
* Flow can include actions like fetching order status, asking for order number, etc.
This provides a consistent response when users ask about order tracking anywhere in your chatbot.
**To add the trigger:**
1. Open `Blocks` from the sidebar.
When a user sends a message, the chatbot will check if the message matches any of the selected intents and trigger the appropriate flow. If there are no matches, the flow will continue normally.
## 2. Defining intent flows
There are two ways to define the actions for an intent:
1. Intent trigger block (global)
2. Local trigger
### Intent trigger block
Intent triggers are flows that will be executed when an intent is matched. These triggers are global, meaning that they will be executed by any block that matches the intent. This is useful if you want to create a standard response for an intent that can be used in multiple places in your chatbot.
For example, if you create an Intent trigger for `Order Tracking`:
* Any block that matches this intent will start this flow.
* The same flow runs whether matched in a welcome message or support conversation.
* Flow can include actions like fetching order status, asking for order number, etc.
This provides a consistent response when users ask about order tracking anywhere in your chatbot.
**To add the trigger:**
1. Open `Blocks` from the sidebar.
 2. Under the `Triggers` section, drag and drop the `Intent` block onto the canvas.
2. Under the `Triggers` section, drag and drop the `Intent` block onto the canvas.
 3. Click on the block to open the editor.
4. Select an intent this trigger belongs to.
3. Click on the block to open the editor.
4. Select an intent this trigger belongs to.
 5. Define the flow to run when the intent is triggered.
5. Define the flow to run when the intent is triggered.
 ### Local trigger
Sometimes you want different flows for the same intent depending on where in the conversation it was matched. This is where local triggers come in.
* Open the block where you want to enable local trigger for an intent.
* Find the intent under the `Match intent` option and click the `Local trigger` icon as shown below. For example, we will enable local trigger for the `Order status` intent.
### Local trigger
Sometimes you want different flows for the same intent depending on where in the conversation it was matched. This is where local triggers come in.
* Open the block where you want to enable local trigger for an intent.
* Find the intent under the `Match intent` option and click the `Local trigger` icon as shown below. For example, we will enable local trigger for the `Order status` intent.
 * Define the specific flow for this intent. For example, we will ask the user for their order number before fetching the order status. As such, whenever the input in this block matches the `Order status` intent, the flow defined here will be executed instead of the global trigger.
* Define the specific flow for this intent. For example, we will ask the user for their order number before fetching the order status. As such, whenever the input in this block matches the `Order status` intent, the flow defined here will be executed instead of the global trigger.
 Note that the local trigger takes precedence over the global trigger when enabled.
### Using both triggers
You can have both global and local triggers for intents:
* Use global triggers for standard responses
* Override with local triggers where context-specific flows are needed
This flexibility allows you to:
* Maintain consistent base responses
* Customize flows for specific conversation stages
* Create more dynamic user experiences
## What happens when no intents match?
If no intent is matched, the chatbot will continue with the flow as normal.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/variables/variable-types.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Types of variables
> There are two types of variables: System Variable and Custom Variable. Learn how to use them in your chatbot.
Variables in the Builder are of two types:
* System Variable
* Custom Variable
## System Variable
Note that the local trigger takes precedence over the global trigger when enabled.
### Using both triggers
You can have both global and local triggers for intents:
* Use global triggers for standard responses
* Override with local triggers where context-specific flows are needed
This flexibility allows you to:
* Maintain consistent base responses
* Customize flows for specific conversation stages
* Create more dynamic user experiences
## What happens when no intents match?
If no intent is matched, the chatbot will continue with the flow as normal.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/variables/variable-types.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Types of variables
> There are two types of variables: System Variable and Custom Variable. Learn how to use them in your chatbot.
Variables in the Builder are of two types:
* System Variable
* Custom Variable
## System Variable
 System variables are predefined variables that contain system information or which can be used to perform specific actions. These variables are automatically created by the Builder.
To learn what a specific system variable does, you can open it from the Variables menu in the [sidebar](/chatbot/builder/sidebar) and read its description.
There are also additional system variables that aren't imported by default. To view and import them, go to the Variables menu from the [Sidebar](/chatbot/builder/sidebar) and click the `Import system variables` button.
System variables are predefined variables that contain system information or which can be used to perform specific actions. These variables are automatically created by the Builder.
To learn what a specific system variable does, you can open it from the Variables menu in the [sidebar](/chatbot/builder/sidebar) and read its description.
There are also additional system variables that aren't imported by default. To view and import them, go to the Variables menu from the [Sidebar](/chatbot/builder/sidebar) and click the `Import system variables` button.
 ## Custom Variable
These are variables that you create to store information specific to your chatbot.
For example, you can create a custom variable to store the user's query and pass it to the AI for generating a response from the knowledge base.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/blocks/condition/variable.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Variable
> Learn how to use the Variable condition block in Chatling
The Variable condition block is used to compare a variable with a value or another variable. You can use it to create conditional logic in your bot based on user inputs, stored values, or system variables.
## Components of a variable condition
## Custom Variable
These are variables that you create to store information specific to your chatbot.
For example, you can create a custom variable to store the user's query and pass it to the AI for generating a response from the knowledge base.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/blocks/condition/variable.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Variable
> Learn how to use the Variable condition block in Chatling
The Variable condition block is used to compare a variable with a value or another variable. You can use it to create conditional logic in your bot based on user inputs, stored values, or system variables.
## Components of a variable condition
 * **Label**: A descriptive label for the condition, which will be displayed in the block on the canvas. This is optional and can be skipped.
* **Variable**: The variable or value that the block will evaluate. The variable can be a user input, a stored value, or a system variable.
* **Comparison operator**: The operator that the block will use to compare the variable with the value you specify. You can choose from a list of comparison operators, such as "equals," "greater than," "contains," etc.
* **Value**: The value that the block will compare with the variable. This can be a static value or a variable for dynamic comparisons.
## Examples
### 1. Real estate bot
In a real estate bot, you can use conditions to check if the user is looking to buy or rent a property and display properties accordingly.
You can create two conditions:
* Condition 1: User input contains "buy"
* Condition 2: User input contains "rent"
Here's how to set it up in the editor:
* **Label**: A descriptive label for the condition, which will be displayed in the block on the canvas. This is optional and can be skipped.
* **Variable**: The variable or value that the block will evaluate. The variable can be a user input, a stored value, or a system variable.
* **Comparison operator**: The operator that the block will use to compare the variable with the value you specify. You can choose from a list of comparison operators, such as "equals," "greater than," "contains," etc.
* **Value**: The value that the block will compare with the variable. This can be a static value or a variable for dynamic comparisons.
## Examples
### 1. Real estate bot
In a real estate bot, you can use conditions to check if the user is looking to buy or rent a property and display properties accordingly.
You can create two conditions:
* Condition 1: User input contains "buy"
* Condition 2: User input contains "rent"
Here's how to set it up in the editor:
 Once you have set up the conditions, you can define the paths for each condition. Here's an example:
Once you have set up the conditions, you can define the paths for each condition. Here's an example:
 Based on the above, here's how the bot will respond:
* If the user input contains "buy," the bot will respond with `Great! Let me show you our available properties for sale`.
* If the user input contains "rent," the bot will respond with `Sure! We've got amazing properties for rent. Here's the list`.
* Else if none of the conditions are met, the bot will respond with `I'm sorry, I didn't understand. Please respond by typing "Buy" or "Rent"`.
### 2. Filtering job application candidates
Let's say a candidate is applying for a job through the bot and you want to qualify them based on the following criteria:
* Location: New York
* Willing to relocate: Yes
* Years of experience: 3 or more
You can set up the following conditions:
Based on the above, here's how the bot will respond:
* If the user input contains "buy," the bot will respond with `Great! Let me show you our available properties for sale`.
* If the user input contains "rent," the bot will respond with `Sure! We've got amazing properties for rent. Here's the list`.
* Else if none of the conditions are met, the bot will respond with `I'm sorry, I didn't understand. Please respond by typing "Buy" or "Rent"`.
### 2. Filtering job application candidates
Let's say a candidate is applying for a job through the bot and you want to qualify them based on the following criteria:
* Location: New York
* Willing to relocate: Yes
* Years of experience: 3 or more
You can set up the following conditions:
 Once you have set up the conditions, you can define the paths for each condition. Here's an example:
Once you have set up the conditions, you can define the paths for each condition. Here's an example:
 Based on the above, here's how the bot will respond:
* If the candidate is from New York, willing to relocate, and has 3 or more years of experience, the bot will respond with `Congratulations! You've been shortlisted for the next round of interviews`.
* Otherwise, the bot will respond with `Sorry, you are not qualified for this job opening. We'll keep your application on file for future opportunities`.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/blocks/send/video.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Video Block
> Learn about the Video block and how to set it up in the builder
The Video block allows you to display a video to the user in the conversation. You can add a video from YouTube, Vimeo, or any other video hosting platform, or you can paste the direct link to a video file.
For video platforms that support embedding, Chatling will automatically embed the video in the conversation. Here's an example:
Based on the above, here's how the bot will respond:
* If the candidate is from New York, willing to relocate, and has 3 or more years of experience, the bot will respond with `Congratulations! You've been shortlisted for the next round of interviews`.
* Otherwise, the bot will respond with `Sorry, you are not qualified for this job opening. We'll keep your application on file for future opportunities`.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/blocks/send/video.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Video Block
> Learn about the Video block and how to set it up in the builder
The Video block allows you to display a video to the user in the conversation. You can add a video from YouTube, Vimeo, or any other video hosting platform, or you can paste the direct link to a video file.
For video platforms that support embedding, Chatling will automatically embed the video in the conversation. Here's an example:
 ## Adding a video
Adding a video is simple. Just paste the URL to the video in the block editor and the chatbot will automatically embed it in the conversation.
## Adding a video
Adding a video is simple. Just paste the URL to the video in the block editor and the chatbot will automatically embed it in the conversation.
 ---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/general-settings/visibility.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Visibility
> A guide on how to make your chatbot public or private.
You can set the visibility of your chatbot to be public or private. Setting to Public will make your chatbot visible to all users, while setting to Private will make it accessible from your account only.
## How to set the visibility
1. From the chatbot dashboard, go to `Settings`.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/general-settings/visibility.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Visibility
> A guide on how to make your chatbot public or private.
You can set the visibility of your chatbot to be public or private. Setting to Public will make your chatbot visible to all users, while setting to Private will make it accessible from your account only.
## How to set the visibility
1. From the chatbot dashboard, go to `Settings`.
 2. Click the `Visibility` tab.
3. Set the visibility to `Public` or `Private`.
4. Click `Save` to apply the changes.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/block-options/voice-input.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Voice Input
> Allow users to speak to your chatbot using Voice Input.
Voice Input is a speech-to-text feature that allows users to record voice messages and transcribes them into text. Rather than typing their message, users can speak to your chatbot and it will automatically be converted to text.
2. Click the `Visibility` tab.
3. Set the visibility to `Public` or `Private`.
4. Click `Save` to apply the changes.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/block-options/voice-input.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Voice Input
> Allow users to speak to your chatbot using Voice Input.
Voice Input is a speech-to-text feature that allows users to record voice messages and transcribes them into text. Rather than typing their message, users can speak to your chatbot and it will automatically be converted to text.
 ## Supported blocks
Currently, Voice Input is available for the Text input block only.
## How to enable Voice Input
Open the block editor for a Text input block and toggle on the "Voice Input" option.
## Supported blocks
Currently, Voice Input is available for the Text input block only.
## How to enable Voice Input
Open the block editor for a Text input block and toggle on the "Voice Input" option.
 The chatbot will then display a microphone icon when the block is displayed. Users can click on the microphone icon to record a voice message.
The chatbot will then display a microphone icon when the block is displayed. Users can click on the microphone icon to record a voice message.
 3. Click the `Manage` button under the `Website Widget` option.
3. Click the `Manage` button under the `Website Widget` option.
 4. Design the appearance of the widget by clicking the `Open widget designer` button.
4. Design the appearance of the widget by clicking the `Open widget designer` button.
 5. Select the display mode for your chatbot, such as "Floating Chat", "Inline", or "Fullscreen".
5. Select the display mode for your chatbot, such as "Floating Chat", "Inline", or "Fullscreen".
 6. Copy the widget code.
6. Copy the widget code.
 7. Go to your Webflow dashboard and open the website where you want to add the widget.
7. Go to your Webflow dashboard and open the website where you want to add the widget.
 8. Click the webflow icon in the top left and select `Site settings`.
8. Click the webflow icon in the top left and select `Site settings`.
 9. Click on `Custom code` from the sidebar.
9. Click on `Custom code` from the sidebar.
 10. Paste the widget code in the `Head code` textbox and click `Save`.
10. Paste the widget code in the `Head code` textbox and click `Save`.
 11. Publish the website. The widget will now be appear on your Webflow website.
11. Publish the website. The widget will now be appear on your Webflow website.
 ---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/variables/what-are-variables.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# What are variables?
> Learn about Variables, the different types, and how to use them
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/variables/what-are-variables.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# What are variables?
> Learn about Variables, the different types, and how to use them
 Variables are placeholders that store information during the conversation. You can use variables to store user inputs, API responses, and more. These variables can be used to personalize the conversation and make it more dynamic.
For example, you can store the user's name in a variable and use it to greet the user. This way, you can make the conversation more engaging and interactive.
In the next section, you will learn about the different types of variables and how to use them in your chatbot.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/faq/what-happens-when-ai-credits-exhausted.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# What happens when AI credits are exhausted?
When your AI credits are exhausted, users can still interact with the chatbot and send messages, but an error will be displayed saying "Insufficient AI credits".
When the usage exceeds the limit, you must top up your AI credits by purchasing the **Extra AI Credits** add-on from Billing & Usage > Add-ons page. Alternatively, you can upgrade your plan to get more credits.
You can enable the **AI Credit Usage** notification in your account to be alerted when your usage reaches a threshold such as 50%, 75%, 90% or 100%.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/web-widget/whitelist-domains.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Whitelist domains
> Learn how to whitelist domains for your chatbot to prevent it from being added to unauthorized websites.
If you want to prevent your widget from being added to unauthorized websites, you can whitelist domains.
By adding whitelisted domains, the widget will only appear on websites that match the whitelisted domains.
## How to whitelist domains
1. Open your chatbot's dashboard.
2. Go to Settings.
Variables are placeholders that store information during the conversation. You can use variables to store user inputs, API responses, and more. These variables can be used to personalize the conversation and make it more dynamic.
For example, you can store the user's name in a variable and use it to greet the user. This way, you can make the conversation more engaging and interactive.
In the next section, you will learn about the different types of variables and how to use them in your chatbot.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/faq/what-happens-when-ai-credits-exhausted.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# What happens when AI credits are exhausted?
When your AI credits are exhausted, users can still interact with the chatbot and send messages, but an error will be displayed saying "Insufficient AI credits".
When the usage exceeds the limit, you must top up your AI credits by purchasing the **Extra AI Credits** add-on from Billing & Usage > Add-ons page. Alternatively, you can upgrade your plan to get more credits.
You can enable the **AI Credit Usage** notification in your account to be alerted when your usage reaches a threshold such as 50%, 75%, 90% or 100%.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/web-widget/whitelist-domains.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Whitelist domains
> Learn how to whitelist domains for your chatbot to prevent it from being added to unauthorized websites.
If you want to prevent your widget from being added to unauthorized websites, you can whitelist domains.
By adding whitelisted domains, the widget will only appear on websites that match the whitelisted domains.
## How to whitelist domains
1. Open your chatbot's dashboard.
2. Go to Settings.
 3. Click the `Security` tab.
4. Under the `Whitelist domains` section, type in a domain you want to whitelist and click the `+ Add` button. You can add multiple domains.
5. Click `Save`.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/web-widget/widget-sdk.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Widget SDK
## Configuration
You can configure the widget during launch by setting the `window.chtlConfig` object, as shown below.
```javascript theme={null}
window.chtlConfig = {
// Configuration options
};
```
Below are the available properties you can set.
### `chatIconVisible`
Whether to display the chat icon (open and close buttons).
* Possible values: `true`, `false`
* Default: `true`
```javascript theme={null}
window.chtlConfig = {
chatIconVisible: true,
// ... other config options
};
```
### `displayType`
The type of widget to display.
* Possible values: `floating`, `fullscreen`, `page_inline`
* Default: `floating`
```javascript theme={null}
window.chtlConfig = {
displayType: 'floating',
// ... other config options
};
```
### `language`
The language of the widget in ISO 639-1 format. This will override the language set in your chatbot's appearance settings.
* Possible values: `en`, `ar`, `az`, `bg`, `bn`, `bs`, `ca`, `cs`, `da`, `de`, `el`, `en`, `es`, `et`, `fa`, `fi`, `fr`, `he`, `hi`, `hr`, `hu`, `hy`, `id`, `it`, `ja`, `ko`, `lt`, `lv`, `mn`, `ms`, `nl`, `no`, `pl`, `pt`, `pt-br`, `ro`, `ru`, `sk`, `sl`, `sq`, `sr`, `sv`, `th`, `tr`, `uk`, `ur`, `vi`, `zh-cn`, `zh-tw`
```javascript theme={null}
window.chtlConfig = {
language: 'en',
// ... other config options
};
```
## Methods
Below are the SDK methods you can call to interact with the widget.
3. Click the `Security` tab.
4. Under the `Whitelist domains` section, type in a domain you want to whitelist and click the `+ Add` button. You can add multiple domains.
5. Click `Save`.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/web-widget/widget-sdk.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Widget SDK
## Configuration
You can configure the widget during launch by setting the `window.chtlConfig` object, as shown below.
```javascript theme={null}
window.chtlConfig = {
// Configuration options
};
```
Below are the available properties you can set.
### `chatIconVisible`
Whether to display the chat icon (open and close buttons).
* Possible values: `true`, `false`
* Default: `true`
```javascript theme={null}
window.chtlConfig = {
chatIconVisible: true,
// ... other config options
};
```
### `displayType`
The type of widget to display.
* Possible values: `floating`, `fullscreen`, `page_inline`
* Default: `floating`
```javascript theme={null}
window.chtlConfig = {
displayType: 'floating',
// ... other config options
};
```
### `language`
The language of the widget in ISO 639-1 format. This will override the language set in your chatbot's appearance settings.
* Possible values: `en`, `ar`, `az`, `bg`, `bn`, `bs`, `ca`, `cs`, `da`, `de`, `el`, `en`, `es`, `et`, `fa`, `fi`, `fr`, `he`, `hi`, `hr`, `hu`, `hy`, `id`, `it`, `ja`, `ko`, `lt`, `lv`, `mn`, `ms`, `nl`, `no`, `pl`, `pt`, `pt-br`, `ro`, `ru`, `sk`, `sl`, `sq`, `sr`, `sv`, `th`, `tr`, `uk`, `ur`, `vi`, `zh-cn`, `zh-tw`
```javascript theme={null}
window.chtlConfig = {
language: 'en',
// ... other config options
};
```
## Methods
Below are the SDK methods you can call to interact with the widget.
 3. Click the `Manage` button under the `Website Widget` option.
3. Click the `Manage` button under the `Website Widget` option.
 4. Design the appearance of the widget by clicking the `Open widget designer` button.
4. Design the appearance of the widget by clicking the `Open widget designer` button.
 5. Select the display mode for your chatbot, such as "Floating Chat", "Inline", or "Fullscreen".
5. Select the display mode for your chatbot, such as "Floating Chat", "Inline", or "Fullscreen".
 6. Copy the widget code.
6. Copy the widget code.
 7. Go to your Wix dashboard and click `Settings` from the sidebar menu.
7. Go to your Wix dashboard and click `Settings` from the sidebar menu.
 8. Scroll down to the Advanced section and click `Custom code`.
8. Scroll down to the Advanced section and click `Custom code`.
 9. Under the Head section, click `Add Code`.
9. Under the Head section, click `Add Code`.
 10. Paste the widget code into the text box that appears and click `Apply`.
10. Paste the widget code into the text box that appears and click `Apply`.
 11. The widget is now live on your Wix website and visitors can interact with it.
11. The widget is now live on your Wix website and visitors can interact with it.
 ---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/web-widget/installation/wordpress.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# WordPress
> Learn how to add Chatling to your WordPress website
## Method 1: Install using a plugin
1. Go to your dashboard.
2. Click `Deploy` button in the sidebar menu.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/web-widget/installation/wordpress.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# WordPress
> Learn how to add Chatling to your WordPress website
## Method 1: Install using a plugin
1. Go to your dashboard.
2. Click `Deploy` button in the sidebar menu.
 3. Click the `Manage` button under the `Website Widget` option.
3. Click the `Manage` button under the `Website Widget` option.
 4. Design the appearance of the widget by clicking the `Open widget designer` button.
4. Design the appearance of the widget by clicking the `Open widget designer` button.
 5. Select the display mode for your chatbot, such as "Floating Chat", "Inline", or "Fullscreen".
5. Select the display mode for your chatbot, such as "Floating Chat", "Inline", or "Fullscreen".
 6. Copy the widget code.
6. Copy the widget code.
 7. In your WordPress dashboard, go to `Plugins` > `Add new plugin`.
7. In your WordPress dashboard, go to `Plugins` > `Add new plugin`.
 8. Search for the `Insert Headers And Footers` plugin and install the one by WPBrigade.
8. Search for the `Insert Headers And Footers` plugin and install the one by WPBrigade.
 9. Once installed, activate the plugin.
10. Go to `Settings` > `WP Headers and Footers` from the sidebar.
9. Once installed, activate the plugin.
10. Go to `Settings` > `WP Headers and Footers` from the sidebar.
 11. Paste the chatbot widget code in the header section.
11. Paste the chatbot widget code in the header section.
 12. Click `Save Changes`.
## Method 2: Install using the theme editor
1. Follow steps 1-6 from Method 1 to copy the widget code.
2. Open your WordPress dashboard.
3. From the sidebar menu, select `Appearance` > `Theme File Editor`.
12. Click `Save Changes`.
## Method 2: Install using the theme editor
1. Follow steps 1-6 from Method 1 to copy the widget code.
2. Open your WordPress dashboard.
3. From the sidebar menu, select `Appearance` > `Theme File Editor`.
 4. Under the `Theme Files` section (right side of the screen), search and open the `header.php` file.
4. Under the `Theme Files` section (right side of the screen), search and open the `header.php` file.
 5. Paste the widget code before the closing `` tag.
5. Paste the widget code before the closing `` tag.
 6. Click `Update File` to save.
6. Click `Update File` to save.
 ## How to add data to the knowledge base
To add data to the Knowledge Base, follow these steps:
1. From the dashboard, go to `Knowledge Base`.
## How to add data to the knowledge base
To add data to the Knowledge Base, follow these steps:
1. From the dashboard, go to `Knowledge Base`.
 2. Click on the `Add new` or `New Data Source` button.
2. Click on the `Add new` or `New Data Source` button.
 3. Select the type of data source you want to add.
3. Select the type of data source you want to add.
 4. Follow the on-screen instructions to add the data source to the knowledge base.
Once added, it will take a few minutes for the data to be processed. The status of the data source will be displayed in the Knowledge Base page and will change to "Processed" once the AI has extracted the information.
4. Follow the on-screen instructions to add the data source to the knowledge base.
Once added, it will take a few minutes for the data to be processed. The status of the data source will be displayed in the Knowledge Base page and will change to "Processed" once the AI has extracted the information.
 ---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/api-reference/v2/knowledge-base/add-faq.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Add FAQ
> Add new FAQ data sources to the knowledge base.
## Request parameters
### Path
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/api-reference/v2/knowledge-base/add-faq.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Add FAQ
> Add new FAQ data sources to the knowledge base.
## Request parameters
### Path
 Often times, you may want to display a text in the chatbot's footer, such as a disclaimer, privacy notice, or any other text. Here's how you can do that.
1. Open the `Deploy` page.
Often times, you may want to display a text in the chatbot's footer, such as a disclaimer, privacy notice, or any other text. Here's how you can do that.
1. Open the `Deploy` page.
 4. Under the `Footer` section, you can enter the text you want to display.
4. Under the `Footer` section, you can enter the text you want to display.
 5. Click `Save` to apply the changes.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/api-reference/v2/knowledge-base/add-link.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Add link
> Add new link data sources to the knowledge base.
## Request parameters
### Path
5. Click `Save` to apply the changes.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/api-reference/v2/knowledge-base/add-link.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Add link
> Add new link data sources to the knowledge base.
## Request parameters
### Path
 ---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/blocks/ai/ai-response.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# AI Response Block
> Learn about the AI Response block and how to set it up in the Builder.
The AI Response block is used for generating responses to user input using AI. It can provide answers based on the information you have added to the [Knowledge Base](/knowledge-base/overview) or from the AI's pretrained data.
The AI uses natural language processing (NLP) to understand the user's input and generate relevant responses.
## What is the "Response Source"?
The Response Source determines where the AI will look for answers to user queries. You can choose from the following options:
* **Knowledge Base**: The AI will search the data you've uploaded to the Knowledge Base for the relevant information and return the corresponding answer.
* **AI Model**: The AI will use its pretrained data to generate a response based on the user's query. This is ideal for a general-purpose AI that can answer a wide range of questions without limiting its responses to the data in the knowledge base.
## Configurations for Knowledge Base Response Source
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/blocks/ai/ai-response.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# AI Response Block
> Learn about the AI Response block and how to set it up in the Builder.
The AI Response block is used for generating responses to user input using AI. It can provide answers based on the information you have added to the [Knowledge Base](/knowledge-base/overview) or from the AI's pretrained data.
The AI uses natural language processing (NLP) to understand the user's input and generate relevant responses.
## What is the "Response Source"?
The Response Source determines where the AI will look for answers to user queries. You can choose from the following options:
* **Knowledge Base**: The AI will search the data you've uploaded to the Knowledge Base for the relevant information and return the corresponding answer.
* **AI Model**: The AI will use its pretrained data to generate a response based on the user's query. This is ideal for a general-purpose AI that can answer a wide range of questions without limiting its responses to the data in the knowledge base.
## Configurations for Knowledge Base Response Source
 When you select the "Knowledge Base" as the Response Source, you can configure the following settings:
* **Question**: The user's input or query that the AI will process to generate a response. You can use variables to make the question dynamic. For example, you can capture the user's input using a Text input block and store it in a variable called `user_input`. Then, you can use this variable in the "Question" field to make the AI response dynamic.
* **Store response in variable**: You can store the AI response in a variable to use it in other blocks.
* **Stream**: When enabled, the AI response will be streamed to the user in real-time as it is generated. This provides a more interactive experience for the user.
* When Stream is enabled, some features that require post-processing, such as "Not Found path" will be disabled.
* **Not Found path**: The path to follow if the AI does not find a relevant answer in the Knowledge Base.
* **Model**: The AI model to use for generating responses.
* **Language**: The language in which the AI will respond to the user. If you set it to "Auto," the AI will detect the language of the user's input and respond in the same language.
* If you want the AI to respond in a certain dialect or accent, you can specify it in Instructions section of the [AI Configuration](/chatbot/builder/sidebar#ai-configuration).
* **Temperature**: The randomness of the AI's responses. A higher temperature value will result in more diverse and creative responses, while a lower value will produce more accurate responses.
### What does "Use global AI settings" mean?
When you set an option, such as the AI model, language, or temperature to "Use global AI settings", the AI will use the settings defined in the [AI Configuration](/chatbot/builder/sidebar#ai-configuration) menu in the [sidebar](/chatbot/builder/sidebar). This allows you to define global settings that will be applied to all AI blocks in your bot.
## Configurations for AI Model Response Source
When you set the Response Source to "AI Model", you can configure the following settings:
* **Prompt**: The message or query that the AI will use to generate a response. You can use variables to make the prompt dynamic.
* **Store response in variable**: You can store the AI response in a variable to use it in other blocks.
* **Instructions**: Additional instructions for the AI to follow when generating a response. For example, you can specify its personality, tone, or style, or provide specific context for the response.
* **Model**: The AI model to use for generating responses.
* **Max Length**: Maximum number of tokens to generate, shared between the prompt and the response. One token is roughly 4 characters.
* **Temperature**: Randomness of the AI's responses. A higher temperature value will result in more diverse and creative responses, while a lower value will produce more focused and deterministic responses.
* **Top P**: Controls diversity via nucleus sampling: 0.5 means half of all likelihood-weighted options are considered.
* **Frequency Penalty**: How much to penalize new tokens based on their existing frequency in the text so far. Decreases the model's likelihood to repeat the same line verbatim.
* **Presence Penalty**: How much to penalize new tokens based on whether they appear in the text so far. Increases the model's likelihood to talk about new topics.
## How to set up the AI block to respond from the knowledge base?
Here's a high level overview of how the AI generates responses using the knowledge base:
* The user inputs a question or query, which is saved in a variable of your choice.
* The stored input is passed to the AI which uses natural language processing (NLP) to understand the user's query and the context of the conversation.
* The AI searches the knowledge base for relevant information.
* The AI generates the response and displays it to the user.
To set up the AI block, follow these steps:
1. Add a Text input block to the canvas. We'll use this block to capture the user's input and store it in a variable so it can be passed to the AI block.
When you select the "Knowledge Base" as the Response Source, you can configure the following settings:
* **Question**: The user's input or query that the AI will process to generate a response. You can use variables to make the question dynamic. For example, you can capture the user's input using a Text input block and store it in a variable called `user_input`. Then, you can use this variable in the "Question" field to make the AI response dynamic.
* **Store response in variable**: You can store the AI response in a variable to use it in other blocks.
* **Stream**: When enabled, the AI response will be streamed to the user in real-time as it is generated. This provides a more interactive experience for the user.
* When Stream is enabled, some features that require post-processing, such as "Not Found path" will be disabled.
* **Not Found path**: The path to follow if the AI does not find a relevant answer in the Knowledge Base.
* **Model**: The AI model to use for generating responses.
* **Language**: The language in which the AI will respond to the user. If you set it to "Auto," the AI will detect the language of the user's input and respond in the same language.
* If you want the AI to respond in a certain dialect or accent, you can specify it in Instructions section of the [AI Configuration](/chatbot/builder/sidebar#ai-configuration).
* **Temperature**: The randomness of the AI's responses. A higher temperature value will result in more diverse and creative responses, while a lower value will produce more accurate responses.
### What does "Use global AI settings" mean?
When you set an option, such as the AI model, language, or temperature to "Use global AI settings", the AI will use the settings defined in the [AI Configuration](/chatbot/builder/sidebar#ai-configuration) menu in the [sidebar](/chatbot/builder/sidebar). This allows you to define global settings that will be applied to all AI blocks in your bot.
## Configurations for AI Model Response Source
When you set the Response Source to "AI Model", you can configure the following settings:
* **Prompt**: The message or query that the AI will use to generate a response. You can use variables to make the prompt dynamic.
* **Store response in variable**: You can store the AI response in a variable to use it in other blocks.
* **Instructions**: Additional instructions for the AI to follow when generating a response. For example, you can specify its personality, tone, or style, or provide specific context for the response.
* **Model**: The AI model to use for generating responses.
* **Max Length**: Maximum number of tokens to generate, shared between the prompt and the response. One token is roughly 4 characters.
* **Temperature**: Randomness of the AI's responses. A higher temperature value will result in more diverse and creative responses, while a lower value will produce more focused and deterministic responses.
* **Top P**: Controls diversity via nucleus sampling: 0.5 means half of all likelihood-weighted options are considered.
* **Frequency Penalty**: How much to penalize new tokens based on their existing frequency in the text so far. Decreases the model's likelihood to repeat the same line verbatim.
* **Presence Penalty**: How much to penalize new tokens based on whether they appear in the text so far. Increases the model's likelihood to talk about new topics.
## How to set up the AI block to respond from the knowledge base?
Here's a high level overview of how the AI generates responses using the knowledge base:
* The user inputs a question or query, which is saved in a variable of your choice.
* The stored input is passed to the AI which uses natural language processing (NLP) to understand the user's query and the context of the conversation.
* The AI searches the knowledge base for relevant information.
* The AI generates the response and displays it to the user.
To set up the AI block, follow these steps:
1. Add a Text input block to the canvas. We'll use this block to capture the user's input and store it in a variable so it can be passed to the AI block.
 2. Click on the Text block to open the editor. In the `Store answer in variable` field, enter a variable where the user's input will be stored. In this example, we'll create and use a variable called `user_query`.
2. Click on the Text block to open the editor. In the `Store answer in variable` field, enter a variable where the user's input will be stored. In this example, we'll create and use a variable called `user_query`.
 3. Next, drag and drop the AI Response block onto the canvas.
3. Next, drag and drop the AI Response block onto the canvas.
 4. Connect the Text input block to the AI block by dragging the connector from the Text block to the AI block.
4. Connect the Text input block to the AI block by dragging the connector from the Text block to the AI block.
 5. Click the AI Response block to open the editor. In the `Question` field, enter the variable where the user's input is stored. In step 2, we used the `user_query` variable, so we'll enter `{user_query}` in the Question field.
5. Click the AI Response block to open the editor. In the `Question` field, enter the variable where the user's input is stored. In step 2, we used the `user_query` variable, so we'll enter `{user_query}` in the Question field.
 6. Set up the global AI settings by going to the `AI Configuration` in the sidebar. You can define settings such as the AI model, instructions, language, and business name.
7. Lastly, set up the block connections accordingly. For example, a setup like below will allow the user to continually ask questions and receive responses from the AI.
6. Set up the global AI settings by going to the `AI Configuration` in the sidebar. You can define settings such as the AI model, instructions, language, and business name.
7. Lastly, set up the block connections accordingly. For example, a setup like below will allow the user to continually ask questions and receive responses from the AI.
 ---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/ai-agent/ai-settings.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# AI settings
To configure the agent's AI settings, click the `Settings` button in the sidebar and select `AI`.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/ai-agent/ai-settings.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# AI settings
To configure the agent's AI settings, click the `Settings` button in the sidebar and select `AI`.
 ## Available settings
### AI Model
The AI model that the agent will use to think, plan, and generate answers to the user queries.
Every model has different capabilities and costs. We recommend testing with different models in the [Playground](/ai-agent/playground) to see which one works best for your agent.
### Temperature
Controls randomness/creativity in the Agent's writing and decision-making.
Lower = more deterministic; Higher = more varied.
* **0.0-0.3 (Precise)**: Best for support, policy-bound replies, data extraction, or when strict adherence to facts and formats is required.
* **0.4-0.6 (Balanced)**: Good general setting for helpful responses with light creativity.
* **0.7-1.0 (Creative)**: Use for brainstorming, marketing copy, or when variety is desirable. Expect less consistency.
**Tips**
* If your Agent must follow exact steps (e.g., collecting parameters for an HTTP Request), keep temperature low.
* Raise temperature only where tone/creativity matters and accuracy isn't compromised.
### Instructions
Define the Agent's role, goals, guardrails, and style (often called the "system prompt").
Here's some of the things you can include in the instructions:
* **Role & purpose**: What the Agent is for and what success looks like.
* **Scope & boundaries**: What it should/shouldn't answer.
* **Tone & language**: Brand voice, formality level, and multilingual behavior (auto-detect language; reply in user's language).
* **Compliance & safety**: Any legal disclaimers, restricted topics, PII handling, and masking sensitive values.
* **Formatting**: Preferred reply structure (short summaries, bullet points, tables).
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/blocks/send/audio.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Audio Block
> Learn about the Audio block and how to set it up in the builder
The Audio block allows you to play an audio file to the user in the conversation. It can be used for various purposes, such as playing a welcome message, providing information, or playing music.
## Adding an audio file
To add an audio file, you can either upload an audio file directly or provide a link to a file hosted online. The supported audio formats are `MP3`, `WAV`, and `OGG`.
## Available settings
### AI Model
The AI model that the agent will use to think, plan, and generate answers to the user queries.
Every model has different capabilities and costs. We recommend testing with different models in the [Playground](/ai-agent/playground) to see which one works best for your agent.
### Temperature
Controls randomness/creativity in the Agent's writing and decision-making.
Lower = more deterministic; Higher = more varied.
* **0.0-0.3 (Precise)**: Best for support, policy-bound replies, data extraction, or when strict adherence to facts and formats is required.
* **0.4-0.6 (Balanced)**: Good general setting for helpful responses with light creativity.
* **0.7-1.0 (Creative)**: Use for brainstorming, marketing copy, or when variety is desirable. Expect less consistency.
**Tips**
* If your Agent must follow exact steps (e.g., collecting parameters for an HTTP Request), keep temperature low.
* Raise temperature only where tone/creativity matters and accuracy isn't compromised.
### Instructions
Define the Agent's role, goals, guardrails, and style (often called the "system prompt").
Here's some of the things you can include in the instructions:
* **Role & purpose**: What the Agent is for and what success looks like.
* **Scope & boundaries**: What it should/shouldn't answer.
* **Tone & language**: Brand voice, formality level, and multilingual behavior (auto-detect language; reply in user's language).
* **Compliance & safety**: Any legal disclaimers, restricted topics, PII handling, and masking sensitive values.
* **Formatting**: Preferred reply structure (short summaries, bullet points, tables).
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/blocks/send/audio.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Audio Block
> Learn about the Audio block and how to set it up in the builder
The Audio block allows you to play an audio file to the user in the conversation. It can be used for various purposes, such as playing a welcome message, providing information, or playing music.
## Adding an audio file
To add an audio file, you can either upload an audio file directly or provide a link to a file hosted online. The supported audio formats are `MP3`, `WAV`, and `OGG`.
 You can enable the `Autoplay` option to automatically play the audio file when the block is displayed to the user.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/knowledge-base/auto-sync-data-sources.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Auto-sync data sources
> Learn how to auto-sync data sources in the Knowledge Base.
Auto-syncing allows you to automatically sync your knowledge base sources at specified intervals, such as daily, weekly, or monthly, to fetch the latest data. This ensures that your knowledge base is always up to date with the latest information.
## How to enable auto-syncing
1. Go to the `Knowledge Base` page.
2. From the `Auto-sync` column, you can select an interval for each data source.
You can enable the `Autoplay` option to automatically play the audio file when the block is displayed to the user.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/knowledge-base/auto-sync-data-sources.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Auto-sync data sources
> Learn how to auto-sync data sources in the Knowledge Base.
Auto-syncing allows you to automatically sync your knowledge base sources at specified intervals, such as daily, weekly, or monthly, to fetch the latest data. This ensures that your knowledge base is always up to date with the latest information.
## How to enable auto-syncing
1. Go to the `Knowledge Base` page.
2. From the `Auto-sync` column, you can select an interval for each data source.
 3. Click on the auto-sync value for a specific source and choose an interval.
3. Click on the auto-sync value for a specific source and choose an interval.
 4. If you want to enable auto-syncing for multiple sources, you can select the sources and click the `Change auto-sync frequency` button to update all selected sources at once.
4. If you want to enable auto-syncing for multiple sources, you can select the sources and click the `Change auto-sync frequency` button to update all selected sources at once.
 ---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/variables/available-system-variables.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Available system variables
> List of all the system variables available and what they do.
Here are all the system variables that are available. If a variable is not present in your chatbot, you must [import it](/chatbot/builder/variables/import-system-variables).
`chat_id`
The unique identifier of the chat.
`user_id`
The unique identifier of the user.
`conversation_content`
The chat transcript (recent 25 messages).
`current_date`
The current date in UTC.
`current_time`
The current time in UTC.
`locale`
The user's browser locale, such as en-US, en-CA, fr-FR, pt-BR, etc.
`page_title`
The title of the page the user is currently on.
`page_url`
The URL of the page the user is currently on.
`timestamp`
The UNIX timestamp, which is the number of seconds since January 1, 1970 UTC.
`current_time`
The current time in UTC.
`current_date`
The current date in UTC.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/block-editor.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Block Editor
> Learn how to edit blocks in the Builder.
The Block Editor is where you can configure the settings of a block in the Builder.
The editor appears when you click a block that you've added to the canvas. Every block has its own unique settings that you can configure.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/variables/available-system-variables.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Available system variables
> List of all the system variables available and what they do.
Here are all the system variables that are available. If a variable is not present in your chatbot, you must [import it](/chatbot/builder/variables/import-system-variables).
`chat_id`
The unique identifier of the chat.
`user_id`
The unique identifier of the user.
`conversation_content`
The chat transcript (recent 25 messages).
`current_date`
The current date in UTC.
`current_time`
The current time in UTC.
`locale`
The user's browser locale, such as en-US, en-CA, fr-FR, pt-BR, etc.
`page_title`
The title of the page the user is currently on.
`page_url`
The URL of the page the user is currently on.
`timestamp`
The UNIX timestamp, which is the number of seconds since January 1, 1970 UTC.
`current_time`
The current time in UTC.
`current_date`
The current date in UTC.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/block-editor.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Block Editor
> Learn how to edit blocks in the Builder.
The Block Editor is where you can configure the settings of a block in the Builder.
The editor appears when you click a block that you've added to the canvas. Every block has its own unique settings that you can configure.
 ---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/web-widget/installation/bubble.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Bubble
> Learn how to add Chatling to your Bubble website
1. Go to your dashboard.
2. Click `Deploy` button in the sidebar menu.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/web-widget/installation/bubble.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Bubble
> Learn how to add Chatling to your Bubble website
1. Go to your dashboard.
2. Click `Deploy` button in the sidebar menu.
 8. On the side, click the gear icon to open Settings.
8. On the side, click the gear icon to open Settings.
 9. Go to `SEO / metatags`.
9. Go to `SEO / metatags`.
 10. Under the `SEO settings` section, paste the widget code in the header or body textbox.
10. Under the `SEO settings` section, paste the widget code in the header or body textbox.
 11. The settings will be saved automatically. Click the Preview icon to confirm that the widget has been added.
* Note that this method only works on paid plans. If you're on a free account, Bubble doesn't load the widget.
11. The settings will be saved automatically. Click the Preview icon to confirm that the widget has been added.
* Note that this method only works on paid plans. If you're on a free account, Bubble doesn't load the widget.
 ---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/blocks/inputs/buttons.md
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/ai-agent/actions/buttons.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Buttons
Displays a set of buttons in the chat, such as URL buttons to open a webpage or text buttons to send preset replies that keep the flow moving.
## Configuration
### `Action Name`
A short, specific identifier that tells the Agent what this action does (e.g. best\_sellers\_buttons, support\_button).
### `When to Use`
A detailed description of what the action does and when it must be used.
When applicable, you can specify one or more of the following:
* **Positive cues/phrases**: Example utterances and keywords that signal this action (include a few variations).
* **Preconditions**: What must be true before running.
* **Do not use when**: Explicit exclusions to avoid false triggers.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/blocks/inputs/buttons.md
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/ai-agent/actions/buttons.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Buttons
Displays a set of buttons in the chat, such as URL buttons to open a webpage or text buttons to send preset replies that keep the flow moving.
## Configuration
### `Action Name`
A short, specific identifier that tells the Agent what this action does (e.g. best\_sellers\_buttons, support\_button).
### `When to Use`
A detailed description of what the action does and when it must be used.
When applicable, you can specify one or more of the following:
* **Positive cues/phrases**: Example utterances and keywords that signal this action (include a few variations).
* **Preconditions**: What must be true before running.
* **Do not use when**: Explicit exclusions to avoid false triggers.
 ---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/ai-agent/actions/cal-booking.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Cal.com Booking Widget
The Cal.com Booking Widget action embeds your Cal.com scheduler directly inside the chat, so users can view real-time availability and book without leaving the conversation.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/ai-agent/actions/cal-booking.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Cal.com Booking Widget
The Cal.com Booking Widget action embeds your Cal.com scheduler directly inside the chat, so users can view real-time availability and book without leaving the conversation.
 ## Configuration
### `Action Name`
A short, specific identifier that tells the Agent what this action does (e.g. best\_sellers\_buttons, support\_button).
### `When to Use`
A detailed description of what the action does and when it must be used.
When applicable, you can specify one or more of the following:
* **Positive cues/phrases**: Example utterances and keywords that signal this action (include a few variations).
* **Preconditions**: What must be true before running.
* **Do not use when**: Explicit exclusions to avoid false triggers.
## Configuration
### `Action Name`
A short, specific identifier that tells the Agent what this action does (e.g. best\_sellers\_buttons, support\_button).
### `When to Use`
A detailed description of what the action does and when it must be used.
When applicable, you can specify one or more of the following:
* **Positive cues/phrases**: Example utterances and keywords that signal this action (include a few variations).
* **Preconditions**: What must be true before running.
* **Do not use when**: Explicit exclusions to avoid false triggers.
 ## Adding a carousel
To add a carousel, you can create multiple cards within the block editor. For each card, you can set an image, title, description, and buttons.
You can add as many cards as you like to the carousel. Users can swipe through the cards to view the content.
## Adding a carousel
To add a carousel, you can create multiple cards within the block editor. For each card, you can set an image, title, description, and buttons.
You can add as many cards as you like to the carousel. Users can swipe through the cards to view the content.
 ---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/whatsapp/change-language.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Change language
> A guide to change the language of system and error messages in your WhatsApp chatbot.
You can set the language that your chatbot or AI agent will use for system messages, errors, and various other messages.
The steps differ for AI Agents and Chatbots. We've created separate guides for each below.
## How to change the WhatsApp language for a Chatbot
1. From your chatbot's dashboard, click the `Settings` button under the Chatbot menu.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/whatsapp/change-language.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Change language
> A guide to change the language of system and error messages in your WhatsApp chatbot.
You can set the language that your chatbot or AI agent will use for system messages, errors, and various other messages.
The steps differ for AI Agents and Chatbots. We've created separate guides for each below.
## How to change the WhatsApp language for a Chatbot
1. From your chatbot's dashboard, click the `Settings` button under the Chatbot menu.
 3. Click `Save` to save the changes.
## How to change the WhatsApp language for an AI Agent
1. From your agent's dashboard, click the `Deploy` button in the sidebar.
3. Click `Save` to save the changes.
## How to change the WhatsApp language for an AI Agent
1. From your agent's dashboard, click the `Deploy` button in the sidebar.
 3. You will see the `Language` settings. Select the language you want to use.
3. You will see the `Language` settings. Select the language you want to use.
 4. Click `Save` to save the changes.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/api-reference/v2/ai-kb/chat.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Chat with Knowledge Base AI
> Chat with the AI using the knowledge base as the response source.
## Request parameters
### Path
4. Click `Save` to save the changes.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/api-reference/v2/ai-kb/chat.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Chat with Knowledge Base AI
> Chat with the AI using the knowledge base as the response source.
## Request parameters
### Path
 3. Choose `AI Agent` as the type.
3. Choose `AI Agent` as the type.
 4. Enter a name for your Agent and click the `Create agent` button.
4. Enter a name for your Agent and click the `Create agent` button.
 5. From your Agent's dashboard, click the `Deploy` button in the sidebar.
5. From your Agent's dashboard, click the `Deploy` button in the sidebar.
 7. A popup will appear to guide you through the process of connecting your WhatsApp Business account to Chatling.
7. A popup will appear to guide you through the process of connecting your WhatsApp Business account to Chatling.
 9. The Facebook authentication window will open. Sign in to your Facebook account and click the `Continue` button.
9. The Facebook authentication window will open. Sign in to your Facebook account and click the `Continue` button.
 4. Select `WhatsApp` as the platform.
4. Select `WhatsApp` as the platform.
 5. You can choose to create a chatbot from scratch or use a template. Templates help you get started quickly with pre-built flows.
6. Enter a name for your chatbot and click the `Create chatbot` button.
5. You can choose to create a chatbot from scratch or use a template. Templates help you get started quickly with pre-built flows.
6. Enter a name for your chatbot and click the `Create chatbot` button.
 7. A setup wizard will open to guide you through connecting your WhatsApp Business account.
7. A setup wizard will open to guide you through connecting your WhatsApp Business account.
 All contacts created by the chatbot are displayed in the `Contacts` page in your dashboard.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/general-settings/custom-domain.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Custom domain
> Learn how to add a custom domain to your chatbot.
You can use a custom subdomain for the chatbot widget and sharing link rather than the default one used by Chatling. This allows you to whitelabel your chatbots to maintain your brand identity or make them look like your team developed them.
## How to set a custom domain
1. Open the chatbot you want to set a custom subdomain for.
2. From the menu, click on `Settings` under the `Chatbot` section.
All contacts created by the chatbot are displayed in the `Contacts` page in your dashboard.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/general-settings/custom-domain.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Custom domain
> Learn how to add a custom domain to your chatbot.
You can use a custom subdomain for the chatbot widget and sharing link rather than the default one used by Chatling. This allows you to whitelabel your chatbots to maintain your brand identity or make them look like your team developed them.
## How to set a custom domain
1. Open the chatbot you want to set a custom subdomain for.
2. From the menu, click on `Settings` under the `Chatbot` section.
 4. Enter the custom domain you want to use for the chatbot, such as `sample.domain.com`, and click the `Save` button.
4. Enter the custom domain you want to use for the chatbot, such as `sample.domain.com`, and click the `Save` button.
 5. Add the DNS records displayed on the page to your domain provider to activate the custom domain.
5. Add the DNS records displayed on the page to your domain provider to activate the custom domain.
 6. Once you add the DNS records, it may take up to 24 hours for the changes to propagate. You can click the `Verify` button to check if the records are active.
7. Once completed and the status is `Active`, the chatbot widget and sharing link will use the custom domain.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/web-widget/installation/custom-website.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Custom Website
> Learn how to add Chatling to your website
You can easily add Chatling to your website by pasting the widget code to your website's header or body section.
1. Go to your dashboard.
2. Click `Deploy` button in the sidebar menu.
6. Once you add the DNS records, it may take up to 24 hours for the changes to propagate. You can click the `Verify` button to check if the records are active.
7. Once completed and the status is `Active`, the chatbot widget and sharing link will use the custom domain.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/web-widget/installation/custom-website.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Custom Website
> Learn how to add Chatling to your website
You can easily add Chatling to your website by pasting the widget code to your website's header or body section.
1. Go to your dashboard.
2. Click `Deploy` button in the sidebar menu.
 3. Find your phone number from the list and click on the settings icon next to it.
3. Find your phone number from the list and click on the settings icon next to it.
 4. From here, you can update the profile information for your WhatsApp Business account.
4. From here, you can update the profile information for your WhatsApp Business account.
 ---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/web-widget/customize.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Design your chatbot widget
> A guide on how to customize the appearance of your website widget and make it match your brand.

You can customize the appearance of your website chat widget to match your brand. Many aspects of the widget, such as the colors, icons, and other design elements can be customized to create a chatbot that fits seamlessly into your website.
## How to customize the widget
1. Go to your chatbot or AI agent's dashboard.
2. Click the `Deploy` button in the sidebar menu.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/web-widget/customize.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Design your chatbot widget
> A guide on how to customize the appearance of your website widget and make it match your brand.

You can customize the appearance of your website chat widget to match your brand. Many aspects of the widget, such as the colors, icons, and other design elements can be customized to create a chatbot that fits seamlessly into your website.
## How to customize the widget
1. Go to your chatbot or AI agent's dashboard.
2. Click the `Deploy` button in the sidebar menu.
 ---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/blocks/action/delete-contact.md
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/api-reference/v2/contacts/delete-contact.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Delete contact
> Delete a contact by its ID.
## Request parameters
### Path
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/blocks/action/delete-contact.md
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/api-reference/v2/contacts/delete-contact.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Delete contact
> Delete a contact by its ID.
## Request parameters
### Path
 ## How to delete data sources in bulk
To delete multiple data sources at once, click on the checkbox next to the data sources you want to delete. Then, click the `Bulk action` dropdown and select `Delete`.
## How to delete data sources in bulk
To delete multiple data sources at once, click on the checkbox next to the data sources you want to delete. Then, click the `Bulk action` dropdown and select `Delete`.
 ---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/api-reference/v2/knowledge-base/delete-source.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Delete data source
> Delete a data source from the knowledge base.
## Request parameters
### Path
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/api-reference/v2/knowledge-base/delete-source.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Delete data source
> Delete a data source from the knowledge base.
## Request parameters
### Path
 4. Click the `Delete` button.
4. Click the `Delete` button.
 5. Confirm the deletion by typing `delete permanently` in the text box and click \`Delete\`\`
5. Confirm the deletion by typing `delete permanently` in the text box and click \`Delete\`\`
 ---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/faq/difference-between-ai-agents-and-ai-chatbots.md
# What's the difference between AI Agents and AI Chatbots?
The main difference between an agent and a chatbot is how they handle conversations and tasks:
* **Chatbots** rely on prebuilt flows. This means their responses and actions follow a set, predefined path that you design in advance. They are great for handling straightforward, repetitive tasks where the conversation can be mapped out step by step.
* **AI Agents**, on the other hand, plan steps dynamically based on the context of the conversation and the instructions and actions you set. They do not require a rigid flow design. Instead, they can decide which tasks to carry out while interacting with users, making them more flexible and adaptive to complex or changing situations.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/whatsapp/disconnect-account.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Disconnect WhatsApp account
> Learn how to disconnect your WhatsApp account in Chatling.
The guide below will walk you through the process of disconnecting your WhatsApp account from your chatbot or AI agent in Chatling.
The steps differ for chatbots and AI agents. We've created separate guides for each below.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/faq/difference-between-ai-agents-and-ai-chatbots.md
# What's the difference between AI Agents and AI Chatbots?
The main difference between an agent and a chatbot is how they handle conversations and tasks:
* **Chatbots** rely on prebuilt flows. This means their responses and actions follow a set, predefined path that you design in advance. They are great for handling straightforward, repetitive tasks where the conversation can be mapped out step by step.
* **AI Agents**, on the other hand, plan steps dynamically based on the context of the conversation and the instructions and actions you set. They do not require a rigid flow design. Instead, they can decide which tasks to carry out while interacting with users, making them more flexible and adaptive to complex or changing situations.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/whatsapp/disconnect-account.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Disconnect WhatsApp account
> Learn how to disconnect your WhatsApp account in Chatling.
The guide below will walk you through the process of disconnecting your WhatsApp account from your chatbot or AI agent in Chatling.
The steps differ for chatbots and AI agents. We've created separate guides for each below.
 ---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/whatsapp/display-name-approval.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Display name approval
> Learn how to fix issues related to the display name approval for your WhatsApp account.
If you get an error message stating `WhatsApp provided number needs display name approval before messages can be sent`, it means you cannot use the WhatsApp bot until Facebook approves your display name.
This normally happens when you use the free WhatsApp number provided by Facebook when you first connect your WhatsApp account to Chatling.
To fix this issue, you must verify your business in Facebook before they approve your display name.
## How to verify your business in Facebook
1. Go to the [Security Center](https://business.facebook.com/latest/settings/security_center) in your Facebook Business Manager.
2. Under the `Business Verification` section, set the verification use case to `Setting up a WhatsApp Business account`.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/whatsapp/display-name-approval.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Display name approval
> Learn how to fix issues related to the display name approval for your WhatsApp account.
If you get an error message stating `WhatsApp provided number needs display name approval before messages can be sent`, it means you cannot use the WhatsApp bot until Facebook approves your display name.
This normally happens when you use the free WhatsApp number provided by Facebook when you first connect your WhatsApp account to Chatling.
To fix this issue, you must verify your business in Facebook before they approve your display name.
## How to verify your business in Facebook
1. Go to the [Security Center](https://business.facebook.com/latest/settings/security_center) in your Facebook Business Manager.
2. Under the `Business Verification` section, set the verification use case to `Setting up a WhatsApp Business account`.
 3. Click the `Start verification` button.
3. Click the `Start verification` button.
 4. Follow the on-screen instructions to verify your business.
5. Once you complete the process, your business will either be verified immediately or placed under review.
6. After your business is verified, Facebook will begin reviewing your display name. To view the status of the review:
* Go to [WhatsApp Manager](https://business.facebook.com/latest/whatsapp_manager/overview).
* Click `Phone numbers` in the left sidebar.
* You will see the status of the review under the display name as shown below.
4. Follow the on-screen instructions to verify your business.
5. Once you complete the process, your business will either be verified immediately or placed under review.
6. After your business is verified, Facebook will begin reviewing your display name. To view the status of the review:
* Go to [WhatsApp Manager](https://business.facebook.com/latest/whatsapp_manager/overview).
* Click `Phone numbers` in the left sidebar.
* You will see the status of the review under the display name as shown below.
 7. Once the review is complete, you'll receive an email notification from Facebook and you can begin using your WhatsApp bot to send and receive messages.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/web-widget/display-sources.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Display AI sources
> Learn how to enable sources for AI responses.
1. Open the widget designer. To learn how to access it, see [this guide](/web-widget/customize#how-to-customize-the-widget).
2. Go to `Configure`.
7. Once the review is complete, you'll receive an email notification from Facebook and you can begin using your WhatsApp bot to send and receive messages.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/web-widget/display-sources.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Display AI sources
> Learn how to enable sources for AI responses.
1. Open the widget designer. To learn how to access it, see [this guide](/web-widget/customize#how-to-customize-the-widget).
2. Go to `Configure`.
 Here's how it appears in the chatbot:
Here's how it appears in the chatbot:
 ---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/web-widget/download-chat-transcripts.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Download transcripts
> A guide to enabling chat transcript downloads for end-users.
If you'd like your chatbot users to have the option to download chat transcripts, you can turn on this feature in the chatbot's appearance settings.
## How to allow end-users to download chat transcripts
1. Open your chatbot's dashboard.
2. Go to the widget designer. To learn how to access it, see [this guide](/web-widget/customize).
3. Click `Configure` from the sidebar.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/web-widget/download-chat-transcripts.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Download transcripts
> A guide to enabling chat transcript downloads for end-users.
If you'd like your chatbot users to have the option to download chat transcripts, you can turn on this feature in the chatbot's appearance settings.
## How to allow end-users to download chat transcripts
1. Open your chatbot's dashboard.
2. Go to the widget designer. To learn how to access it, see [this guide](/web-widget/customize).
3. Click `Configure` from the sidebar.
 4. Enable `Allow users to download chat transcripts`.
4. Enable `Allow users to download chat transcripts`.
 5. Click `Save`.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/api-reference/v2/chatbots/duplicate-chatbot.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Duplicate chatbot
## Request parameters
### Path
5. Click `Save`.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/api-reference/v2/chatbots/duplicate-chatbot.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Duplicate chatbot
## Request parameters
### Path
 2. Click on the ellipsis `...` icon next to the chatbot or agent you want to duplicate.
2. Click on the ellipsis `...` icon next to the chatbot or agent you want to duplicate.
 3. Select the `Duplicate` option from the dropdown menu.
3. Select the `Duplicate` option from the dropdown menu.
 ---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/api-reference/v2/usage/email-credits.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Email Credits
> Get the email credits usage for the project.
## Response
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/api-reference/v2/usage/email-credits.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Email Credits
> Get the email credits usage for the project.
## Response
 The Email block has the following configuration options:
* **Store email in variable**: The variable where the user's email address will be stored.
* **Input required**: Determine whether the user must provide an email address to proceed. If this option is disabled, a Skip button will appear, allowing users to skip the input.
* **Disallowed domains**: Specify a list of email domains that are not allowed. Users will not be able to enter email addresses associated with these domains.
* **[Quick replies](/chatbot/builder/block-options/quick-replies)**
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/knowledge-base/exclude-webpage-sections.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Exclude webpage sections
> Learn how to exclude certain sections of a webpage when adding a data source.
Websites often contain a lot of information that may not be relevant to the AI. When you add webpages to the knowledge base, you can exclude certain sections of the page from being crawled and indexed by the AI.
This can be useful for removing irrelevant information as well as preventing unnecessary characters from being counted towards your plan's limit.
## How to exclude sections of a webpage
1. Go to the `Knowledge Base`.
2. Click the `New Data Source` or `Add new` button.
The Email block has the following configuration options:
* **Store email in variable**: The variable where the user's email address will be stored.
* **Input required**: Determine whether the user must provide an email address to proceed. If this option is disabled, a Skip button will appear, allowing users to skip the input.
* **Disallowed domains**: Specify a list of email domains that are not allowed. Users will not be able to enter email addresses associated with these domains.
* **[Quick replies](/chatbot/builder/block-options/quick-replies)**
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/knowledge-base/exclude-webpage-sections.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Exclude webpage sections
> Learn how to exclude certain sections of a webpage when adding a data source.
Websites often contain a lot of information that may not be relevant to the AI. When you add webpages to the knowledge base, you can exclude certain sections of the page from being crawled and indexed by the AI.
This can be useful for removing irrelevant information as well as preventing unnecessary characters from being counted towards your plan's limit.
## How to exclude sections of a webpage
1. Go to the `Knowledge Base`.
2. Click the `New Data Source` or `Add new` button.
 5. You can exclude sections by entering the HTML classes or IDs of the elements you want to exclude. You must press Enter after each class or ID to add it to the list.
You can also select the HTML tags you want to remove, such as `header` or `footer`.
5. You can exclude sections by entering the HTML classes or IDs of the elements you want to exclude. You must press Enter after each class or ID to add it to the list.
You can also select the HTML tags you want to remove, such as `header` or `footer`.
 You can now go ahead with entering the website, sitemap, or list of URLs that you want to add to the knowledge base. The crawler will exclude the sections you specified.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/ai-agent/actions/tutorials/fetch-and-email-order-confirmation.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# 1. Fetch and Email Order Confirmation
In this tutorial, you'll build a simple but real-world flow that (1) fetches order data from an API via the [HTTP Request action](/ai-agent/actions/http-request), and (2) sends an email confirmation to the user with the [Send Email action](/ai-agent/actions/send-email).
By the end, your agent will automatically collect the user's email and order number, call your API to verify and fetch the order, and deliver a personalized confirmation email.
You can now go ahead with entering the website, sitemap, or list of URLs that you want to add to the knowledge base. The crawler will exclude the sections you specified.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/ai-agent/actions/tutorials/fetch-and-email-order-confirmation.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# 1. Fetch and Email Order Confirmation
In this tutorial, you'll build a simple but real-world flow that (1) fetches order data from an API via the [HTTP Request action](/ai-agent/actions/http-request), and (2) sends an email confirmation to the user with the [Send Email action](/ai-agent/actions/send-email).
By the end, your agent will automatically collect the user's email and order number, call your API to verify and fetch the order, and deliver a personalized confirmation email.
 **Request**: Configure the request by defining the API URL, method, payload, and headers that will be used to fetch the user's order.
For this tutorial, we'll use a dummy API that returns an order. However, in a real app, you'd point the HTTP Request to your own or third-party API, include auth (e.g., Bearer token), and the relevant payload such as the user's email and order number.
**Request**: Configure the request by defining the API URL, method, payload, and headers that will be used to fetch the user's order.
For this tutorial, we'll use a dummy API that returns an order. However, in a real app, you'd point the HTTP Request to your own or third-party API, include auth (e.g., Bearer token), and the relevant payload such as the user's email and order number.
 4. Click the `Test Request` button to verify that the request runs successfully and that the agent receives a valid JSON response.
4. Click the `Test Request` button to verify that the request runs successfully and that the agent receives a valid JSON response.
 5. Click `Create action` to save the action.
6. Go back to the `Actions` page.
7. Click the `New` button and choose `Send Email`.
8. Set up the action as follows:
**Action name**: email\_order\_confirmation
**When to use**: Use this action to send the order confirmation to the user. First use the get\_order action to get the user's order, then use this action to email the order confirmation to the user.
**Frequency**: Whenever applicable
**Input parameters**: We'll add the following parameters that are required to send the email:
* `email`:
* Description: The email address where the order confirmation should be sent.
* Save to variable: email
* `order_number`:
* Description: The order number of the user's order.
* Save to variable: order\_number
* `order_details`:
* Description: The details of the order that you retrieve from the get\_order action. Format it as HTML with bullet points.
* Save to variable: order\_details
5. Click `Create action` to save the action.
6. Go back to the `Actions` page.
7. Click the `New` button and choose `Send Email`.
8. Set up the action as follows:
**Action name**: email\_order\_confirmation
**When to use**: Use this action to send the order confirmation to the user. First use the get\_order action to get the user's order, then use this action to email the order confirmation to the user.
**Frequency**: Whenever applicable
**Input parameters**: We'll add the following parameters that are required to send the email:
* `email`:
* Description: The email address where the order confirmation should be sent.
* Save to variable: email
* `order_number`:
* Description: The order number of the user's order.
* Save to variable: order\_number
* `order_details`:
* Description: The details of the order that you retrieve from the get\_order action. Format it as HTML with bullet points.
* Save to variable: order\_details
 **Email Setup**: configure the email as follows:
* Sender name: A name of your choice, for example `Apple`
* To: Type in `{{email}}` and press Enter to use the email address of the user.
* Subject: `Order confirmation for #{{order_number}}`
* Message:
```
Hi there!
As requested, here is your confirmation for order #{{order_number}}:
{{order_details}}
```
**Email Setup**: configure the email as follows:
* Sender name: A name of your choice, for example `Apple`
* To: Type in `{{email}}` and press Enter to use the email address of the user.
* Subject: `Order confirmation for #{{order_number}}`
* Message:
```
Hi there!
As requested, here is your confirmation for order #{{order_number}}:
{{order_details}}
```
 9. Click the `Create action` button to save the action.
## Test the actions
Now that you've set up the actions, it's time to test them.
From the `Actions` page, enable both the actions.
Go to the `Playground` page to start a chat with your agent. Ask the agent to email your order confirmation. It should fetch the order details from the API and email the order confirmation to the email address you specify.
Here's an example of how the agent would respond:
9. Click the `Create action` button to save the action.
## Test the actions
Now that you've set up the actions, it's time to test them.
From the `Actions` page, enable both the actions.
Go to the `Playground` page to start a chat with your agent. Ask the agent to email your order confirmation. It should fetch the order details from the API and email the order confirmation to the email address you specify.
Here's an example of how the agent would respond:
 2. Find and open a conversation where the AI has responded incorrectly.
3. Click the `Fine-tune this answer` button below the AI response you want to fix.
2. Find and open a conversation where the AI has responded incorrectly.
3. Click the `Fine-tune this answer` button below the AI response you want to fix.
 4. A dialog will appear where you can edit the AI's answer or replace it with a correct one.
4. A dialog will appear where you can edit the AI's answer or replace it with a correct one.
 5. Once done, click the `Finetune` button. The new answer will be added to the FAQ sources in the knowledge base and will be queued for processing.
Now, when the AI is asked a similar question, it will respond with the answer you provided.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/blocks/inputs/form.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Form Block
> Learn about the Form input block and how to set it up in the Builder.
The Form block is used to collect multiple pieces of information from users in a structured way. You can use this block to create forms for lead generation, user feedback, surveys, and more.
You can add multiple fields to the form and configure each field to collect different types of information, such as text, email, phone number, and more.
5. Once done, click the `Finetune` button. The new answer will be added to the FAQ sources in the knowledge base and will be queued for processing.
Now, when the AI is asked a similar question, it will respond with the answer you provided.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/blocks/inputs/form.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Form Block
> Learn about the Form input block and how to set it up in the Builder.
The Form block is used to collect multiple pieces of information from users in a structured way. You can use this block to create forms for lead generation, user feedback, surveys, and more.
You can add multiple fields to the form and configure each field to collect different types of information, such as text, email, phone number, and more.
 ## Configuration
The Form block has the following configuration options:
* **Fields**: Add and configure the fields you want to include in the form.
* **Label**: The label of the field to indicate what information is being collected.
* **Type**: Type of the field, such as Text, Email, Number, etc. This prevents users from entering invalid data.
* **Store user input in variable**: The variable where the user's response to the field will be stored.
## Configuration
The Form block has the following configuration options:
* **Fields**: Add and configure the fields you want to include in the form.
* **Label**: The label of the field to indicate what information is being collected.
* **Type**: Type of the field, such as Text, Email, Number, etc. This prevents users from entering invalid data.
* **Store user input in variable**: The variable where the user's response to the field will be stored.
 ---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/blocks/action/get-contact.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Get Contact Block
> Learn about the Get Contact block and how to set it up in the Builder.
The `Get Contact` block can be used to retrieve a contact's information.
The block consists of the following components:
* **Search**: Specify the field and value to use to look up the contact. You can enter a variable to search dynamically.
* **Contact details**: Define the properties to retrieve and the variables to store the values in.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/getting-started.md
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/ai-agent/getting-started.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Getting started with AI Agents
> Learn how to create your first AI agent in Chatling
What we'll be covering:
1. [Create an AI Agent](#1-create-an-ai-agent)
2. [Configure the AI settings](#2-configure-the-ai-settings)
3. [Populate the knowledge base](#3-populate-the-knowledge-base)
4. [Create AI actions](#4-create-ai-actions)
5. [Test your Agent](#5-test-your-agent)
6. [Deploy](#6-deploy-your-agent)
## 1. Create an AI Agent
1. Go to your account and open the "My agents" page. Click the `+ Create` or `New` button.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/blocks/action/get-contact.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Get Contact Block
> Learn about the Get Contact block and how to set it up in the Builder.
The `Get Contact` block can be used to retrieve a contact's information.
The block consists of the following components:
* **Search**: Specify the field and value to use to look up the contact. You can enter a variable to search dynamically.
* **Contact details**: Define the properties to retrieve and the variables to store the values in.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/getting-started.md
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/ai-agent/getting-started.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Getting started with AI Agents
> Learn how to create your first AI agent in Chatling
What we'll be covering:
1. [Create an AI Agent](#1-create-an-ai-agent)
2. [Configure the AI settings](#2-configure-the-ai-settings)
3. [Populate the knowledge base](#3-populate-the-knowledge-base)
4. [Create AI actions](#4-create-ai-actions)
5. [Test your Agent](#5-test-your-agent)
6. [Deploy](#6-deploy-your-agent)
## 1. Create an AI Agent
1. Go to your account and open the "My agents" page. Click the `+ Create` or `New` button.
 2. Select the `AI` menu.
2. Select the `AI` menu.
 3. Here you can configure the AI settings, such as:
* **AI Model**: The AI model that the Agent will use to generate responses.
* **Temperature**: Controls randomness of the agent's responses. A lower temperature will make the outputs more focused and deterministic, whereas a higher temperature will make the responses diverse and creative.
* **Instructions**: Define the agent's role, goals, guardrails, and style (often called the "system prompt"). There are templates available to help you get started. Click the `Browse templates` button to see the available templates.
3. Here you can configure the AI settings, such as:
* **AI Model**: The AI model that the Agent will use to generate responses.
* **Temperature**: Controls randomness of the agent's responses. A lower temperature will make the outputs more focused and deterministic, whereas a higher temperature will make the responses diverse and creative.
* **Instructions**: Define the agent's role, goals, guardrails, and style (often called the "system prompt"). There are templates available to help you get started. Click the `Browse templates` button to see the available templates.
 ## 3. Populate the knowledge base
The Knowledge Base is where you upload information the Agent uses to generate responses to user queries. You can upload information about your business, products, services, policies, and more.
You can add several types of data to the knowledge base, such as websites, documents, texts, and FAQs. You can also connect your Zendesk or Zoho account to import articles from your help center.
When a user asks a question, the Agent queries the knowledge base for relevant information and generates a response based on the data it finds.
## 3. Populate the knowledge base
The Knowledge Base is where you upload information the Agent uses to generate responses to user queries. You can upload information about your business, products, services, policies, and more.
You can add several types of data to the knowledge base, such as websites, documents, texts, and FAQs. You can also connect your Zendesk or Zoho account to import articles from your help center.
When a user asks a question, the Agent queries the knowledge base for relevant information and generates a response based on the data it finds.
 To add data to the knowledge base, click the `+ Add data source` button, then select the type of data you want to add.
To add data to the knowledge base, click the `+ Add data source` button, then select the type of data you want to add.
 ## 4. Create AI actions
Actions unlock the true power of AI Agents. Instead of only generating replies, the Agent can actively carry out tasks during a conversation.
This might involve saving details of potential leads, displaying booking widgets, interacting with external systems to fetch or store data, creating support tickets, and more.
1. Click the `Actions` menu from the sidebar.
2. Click `Create action`.
3. Select the type of action you want to create.
4. Configure the action according to your needs.
5. Click the `Create` button to save the action.
To learn more about actions, check out the [Actions](/ai-agent/actions/introduction) documentation.
## 5. Test your Agent
You can test your AI Agent in the Playground. It is your sandbox to experiment with your Agent in real time.
To open the Playground, click `Playground` from the sidebar menu.
You can tweak core settings—like AI model, enabled actions, temperature, and instructions—then chat with the Agent to see exactly how those changes affect behavior.
## 4. Create AI actions
Actions unlock the true power of AI Agents. Instead of only generating replies, the Agent can actively carry out tasks during a conversation.
This might involve saving details of potential leads, displaying booking widgets, interacting with external systems to fetch or store data, creating support tickets, and more.
1. Click the `Actions` menu from the sidebar.
2. Click `Create action`.
3. Select the type of action you want to create.
4. Configure the action according to your needs.
5. Click the `Create` button to save the action.
To learn more about actions, check out the [Actions](/ai-agent/actions/introduction) documentation.
## 5. Test your Agent
You can test your AI Agent in the Playground. It is your sandbox to experiment with your Agent in real time.
To open the Playground, click `Playground` from the sidebar menu.
You can tweak core settings—like AI model, enabled actions, temperature, and instructions—then chat with the Agent to see exactly how those changes affect behavior.
 You can also run side-by-side comparisons of up to 5 instances of your Agent, each with different settings, to quickly identify the configuration that performs best.
You can also run side-by-side comparisons of up to 5 instances of your Agent, each with different settings, to quickly identify the configuration that performs best.
 9. Enter a name for the tag, such as `Chatling`.
9. Enter a name for the tag, such as `Chatling`.
 10. Click on `Tag Configuration`.
10. Click on `Tag Configuration`.
 11. Select `Custom HTML`.
11. Select `Custom HTML`.
 12. Paste the widget code into the `HTML` field.
12. Paste the widget code into the `HTML` field.
 13. Click on `Triggering`.
13. Click on `Triggering`.
 14. Select `All Pages`.
14. Select `All Pages`.
 15. Click `Save`.
15. Click `Save`.
 ---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/faq/hide-chatbot-on-specific-pages.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# How to hide the chatbot on specific pages
> Learn how to set the visibility of your chatbot on specific pages.
Sometimes you may want to hide your chatbot on specific pages of your website. This could be for various reasons, such as maintaining a distraction-free environment on certain pages, or to comply with specific page requirements. Chatling provides a simple way to control the visibility of your chatbot by allowing you to specify URLs where the chatbot widget should not appear.
## How to hide the chatbot on specific pages
1. From the chatbot dashboard, go to `Settings`.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/faq/hide-chatbot-on-specific-pages.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# How to hide the chatbot on specific pages
> Learn how to set the visibility of your chatbot on specific pages.
Sometimes you may want to hide your chatbot on specific pages of your website. This could be for various reasons, such as maintaining a distraction-free environment on certain pages, or to comply with specific page requirements. Chatling provides a simple way to control the visibility of your chatbot by allowing you to specify URLs where the chatbot widget should not appear.
## How to hide the chatbot on specific pages
1. From the chatbot dashboard, go to `Settings`.
 3. Enter a name for the variable and click `Create`. The name must be alphanumeric and can include underscores, such as `first_name`, `firstName`, or `First Name`.
3. Enter a name for the variable and click `Create`. The name must be alphanumeric and can include underscores, such as `first_name`, `firstName`, or `First Name`.
 Note that variable names are case-sensitive. For example, `first name` and `First Name` are considered different variables.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/variables/how-to-use-variables.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# How to use variables
> A guide on how to use Variables in your chatbot
Variables can be used for capturing information, displaying dynamic content, and processing data in your chatbot.
## How to store data in variables
You can store data in variables using the `Store answer in variable` or a similar option that's available for certain blocks in the builder. This option appears in the [block editor](/chatbot/builder/block-editor).
Let's take the [Text input block](/chatbot/builder/blocks/inputs/text) as an example. This block allows users to enter text. To store the user's response in a variable, click the dropdown below the `Store answer in variable` option and select a variable.
Note that variable names are case-sensitive. For example, `first name` and `First Name` are considered different variables.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/variables/how-to-use-variables.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# How to use variables
> A guide on how to use Variables in your chatbot
Variables can be used for capturing information, displaying dynamic content, and processing data in your chatbot.
## How to store data in variables
You can store data in variables using the `Store answer in variable` or a similar option that's available for certain blocks in the builder. This option appears in the [block editor](/chatbot/builder/block-editor).
Let's take the [Text input block](/chatbot/builder/blocks/inputs/text) as an example. This block allows users to enter text. To store the user's response in a variable, click the dropdown below the `Store answer in variable` option and select a variable.
 ## How to display variables in messages
You can display variables in messages using the `{variableName}` syntax. The variable name should be enclosed in curly braces.
As an example, let's you have a variable called `first_name` and you want to greet the user by their name. Here's how to do it:
1. Add a [Text output block](/chatbot/builder/blocks/send/text) to your chatbot.
2. Click the block to open the editor.
3. Type `Hello, {first_name}!` in the message field.
## How to display variables in messages
You can display variables in messages using the `{variableName}` syntax. The variable name should be enclosed in curly braces.
As an example, let's you have a variable called `first_name` and you want to greet the user by their name. Here's how to do it:
1. Add a [Text output block](/chatbot/builder/blocks/send/text) to your chatbot.
2. Click the block to open the editor.
3. Type `Hello, {first_name}!` in the message field.
 4. When the chatbot displays this block, it will replace `{first_name}` with the value stored by the variable.
4. When the chatbot displays this block, it will replace `{first_name}` with the value stored by the variable.
 Note that the values stored are on a per-conversation basis. This means that the value of a variable is unique to each conversation and is not shared across different conversations.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/blocks/action/http-request.md
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/ai-agent/actions/http-request.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# HTTP Request
The HTTP Request action allows the AI Agent to connect to external APIs and services during the chat and perform an action.
The Agent can collect the needed inputs from the user, pull values from chat history, or use saved contact data—then send the request and use the result to respond or take the next step.
## Configuration
### `Action Name`
A short, specific identifier that tells the Agent what this action does (e.g. check\_order\_status, create\_support\_ticket).
### `When to Use`
A detailed description of what the action does and when it must be used.
When applicable, you can specify one or more of the following:
* **Positive cues/phrases**: Example utterances and keywords that signal this action (include a few variations).
* **Preconditions**: What must be true before running.
* **Do not use when**: Explicit exclusions to avoid false triggers.
### `Frequency`
Specify how often the Agent can invoke this action to avoid overusing it, e.g `Once per chat` or `Whenever applicable`.
### `Input parameters`
Define the parameters the Agent must gather before sending the request. The Agent can capture these from user input, existing chat context, or saved contact data.
For each parameter, you can specify the following:
* **Name**: The name of the parameter. Must start with a letter and contain only letters, numbers, and underscores.
* **Description** (optional): A description of the parameter to indicate what it is and if applicable, the formatting rules and min/max length.
* **Save to variable** (optional): The variable where the data can be saved. Applicable when you want to use the data in the HTTP request's parameters, such as URL, body, headers, etc.
### `Request`
Configure how the HTTP call is made.
* **Method**: GET, POST, PUT, PATCH, DELETE
* **URL**: Enter the request URL, such as an API endpoint.
* **Query Params** (optional): Key-value pairs appended to the URL.
* **Body** (optional): The request payload which can be passed as form data, form URL encoded, or raw JSON.
* **Headers** (optional): Data to be sent as the headers of the request, such as Content-Type and Authorization.
### `Test Request`
Run a live test with sample input values to confirm that it's working.
The request must succeed before the action can be created. A request is considered successful if it returns a 2xx status code and a valid JSON response.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/contacts/identify-users.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Identify users across multiple chats
When you save a contact, it's associated with the user and persists across multiple chat sessions. This information can be used to personalize the conversation, skip repetitive questions, and tailor the flow accordingly.
## How it works
The [Get Contact](/chatbot/builder/blocks/action/get-contact) block can be used to fetch the contact information associated with the current user.
The example below shows a flow that identifies the user and takes different actions based on whether their contact details exist.
Note that the values stored are on a per-conversation basis. This means that the value of a variable is unique to each conversation and is not shared across different conversations.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/blocks/action/http-request.md
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/ai-agent/actions/http-request.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# HTTP Request
The HTTP Request action allows the AI Agent to connect to external APIs and services during the chat and perform an action.
The Agent can collect the needed inputs from the user, pull values from chat history, or use saved contact data—then send the request and use the result to respond or take the next step.
## Configuration
### `Action Name`
A short, specific identifier that tells the Agent what this action does (e.g. check\_order\_status, create\_support\_ticket).
### `When to Use`
A detailed description of what the action does and when it must be used.
When applicable, you can specify one or more of the following:
* **Positive cues/phrases**: Example utterances and keywords that signal this action (include a few variations).
* **Preconditions**: What must be true before running.
* **Do not use when**: Explicit exclusions to avoid false triggers.
### `Frequency`
Specify how often the Agent can invoke this action to avoid overusing it, e.g `Once per chat` or `Whenever applicable`.
### `Input parameters`
Define the parameters the Agent must gather before sending the request. The Agent can capture these from user input, existing chat context, or saved contact data.
For each parameter, you can specify the following:
* **Name**: The name of the parameter. Must start with a letter and contain only letters, numbers, and underscores.
* **Description** (optional): A description of the parameter to indicate what it is and if applicable, the formatting rules and min/max length.
* **Save to variable** (optional): The variable where the data can be saved. Applicable when you want to use the data in the HTTP request's parameters, such as URL, body, headers, etc.
### `Request`
Configure how the HTTP call is made.
* **Method**: GET, POST, PUT, PATCH, DELETE
* **URL**: Enter the request URL, such as an API endpoint.
* **Query Params** (optional): Key-value pairs appended to the URL.
* **Body** (optional): The request payload which can be passed as form data, form URL encoded, or raw JSON.
* **Headers** (optional): Data to be sent as the headers of the request, such as Content-Type and Authorization.
### `Test Request`
Run a live test with sample input values to confirm that it's working.
The request must succeed before the action can be created. A request is considered successful if it returns a 2xx status code and a valid JSON response.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/contacts/identify-users.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Identify users across multiple chats
When you save a contact, it's associated with the user and persists across multiple chat sessions. This information can be used to personalize the conversation, skip repetitive questions, and tailor the flow accordingly.
## How it works
The [Get Contact](/chatbot/builder/blocks/action/get-contact) block can be used to fetch the contact information associated with the current user.
The example below shows a flow that identifies the user and takes different actions based on whether their contact details exist.
 Here's how the above flow works:
1. When the chat starts, the `Get Contact` block is executed to check if a contact exists for the current user.
Here's how the above flow works:
1. When the chat starts, the `Get Contact` block is executed to check if a contact exists for the current user.
 ---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/variables/import-system-variables.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Import system variables
> Learn how to import system variables that aren't available by default in your chatbot.
Not all system variables are available by default when you create a chatbot. If you require additional system variables that aren't available, you can import them from the `Variables` menu in the builder's [sidebar](/chatbot/builder/sidebar).
## How to import additional system variables
1. Go to the `Builder` in your chatbot.
2. Click the `Variables` menu in the sidebar.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/variables/import-system-variables.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Import system variables
> Learn how to import system variables that aren't available by default in your chatbot.
Not all system variables are available by default when you create a chatbot. If you require additional system variables that aren't available, you can import them from the `Variables` menu in the builder's [sidebar](/chatbot/builder/sidebar).
## How to import additional system variables
1. Go to the `Builder` in your chatbot.
2. Click the `Variables` menu in the sidebar.
 3. Click `Import system variables`.
3. Click `Import system variables`.
 4. A list is displayed with all the additional system variables that you can import. Select the ones you want to import.
4. A list is displayed with all the additional system variables that you can import. Select the ones you want to import.
 5. Click the `Import` button.
5. Click the `Import` button.
 6. The selected system variables are now available to use in your chatbot.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/ai/instructions.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Instructions
> A guide on what AI Instructions are and how to use them.
Instructions are a way to provide guidance to the AI on how to respond.
You can use instructions to tailor the AI's responses to your specific needs, such as providing more detailed responses, using a specific tone, have a specific personality, or avoiding certain topics.
Here are a few examples:
* Your name is "Joanne" and you are our customer support assistant. When referring to yourself, do not mention anything about being an AI assistant or AI model. Instead, refer to yourself as "Joanne".
* Keep your answers short and to the point, and do not provide unnecessary information.
* Use a friendly and casual tone when responding to users.
* You must act as a professional customer support agent. NEVER break character.
* When responding in English, use American English spelling and grammar.
* Promote special offers or promotions when appropriate. For example, if a customer asks about a product, you can mention that we have a store-wide promotion of 50% off.
* Limit your answers to a maximum of 5 sentences.
* You are a lead generation assistant for a Digital Marketing agency and you are communicating with a prospective customer.
* Do not discuss politics, religion, or any other sensitive topics.
## How to add instructions
The method for adding instructions depends on the [Response Source](/chatbot/builder/blocks/ai/ai-response#what-is-the-response-source) that you've set for the [AI Response](/chatbot/builder/blocks/ai/ai-response) block.
### Response Source: Knowledge Base
If you are using the Knowledge Base as the response source, you can add instructions using the [AI Configuration menu](/chatbot/builder/sidebar#ai-configuration) in the Builder's sidebar.
1. Click on the AI Configuration menu in the sidebar.
6. The selected system variables are now available to use in your chatbot.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/ai/instructions.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Instructions
> A guide on what AI Instructions are and how to use them.
Instructions are a way to provide guidance to the AI on how to respond.
You can use instructions to tailor the AI's responses to your specific needs, such as providing more detailed responses, using a specific tone, have a specific personality, or avoiding certain topics.
Here are a few examples:
* Your name is "Joanne" and you are our customer support assistant. When referring to yourself, do not mention anything about being an AI assistant or AI model. Instead, refer to yourself as "Joanne".
* Keep your answers short and to the point, and do not provide unnecessary information.
* Use a friendly and casual tone when responding to users.
* You must act as a professional customer support agent. NEVER break character.
* When responding in English, use American English spelling and grammar.
* Promote special offers or promotions when appropriate. For example, if a customer asks about a product, you can mention that we have a store-wide promotion of 50% off.
* Limit your answers to a maximum of 5 sentences.
* You are a lead generation assistant for a Digital Marketing agency and you are communicating with a prospective customer.
* Do not discuss politics, religion, or any other sensitive topics.
## How to add instructions
The method for adding instructions depends on the [Response Source](/chatbot/builder/blocks/ai/ai-response#what-is-the-response-source) that you've set for the [AI Response](/chatbot/builder/blocks/ai/ai-response) block.
### Response Source: Knowledge Base
If you are using the Knowledge Base as the response source, you can add instructions using the [AI Configuration menu](/chatbot/builder/sidebar#ai-configuration) in the Builder's sidebar.
1. Click on the AI Configuration menu in the sidebar.
 3. Click the `Add instruction` button and enter your instruction.
3. Click the `Add instruction` button and enter your instruction.
 4. To add more instructions, click the `New` button to create a new instruction.
### Response Source: AI Model
If you are using the AI Model as the response source, you can add instructions directly from the [AI Response block](/chatbot/builder/blocks/ai/ai-response).
1. Click the AI Response block on the canvas to open the block editor.
2. Under the `Instructions` section, you can add all your instructions. You can add multiple instructions in the same field, separated by a new line.
4. To add more instructions, click the `New` button to create a new instruction.
### Response Source: AI Model
If you are using the AI Model as the response source, you can add instructions directly from the [AI Response block](/chatbot/builder/blocks/ai/ai-response).
1. Click the AI Response block on the canvas to open the block editor.
2. Under the `Instructions` section, you can add all your instructions. You can add multiple instructions in the same field, separated by a new line.
 ---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/api-reference/v2/intro.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# API Introduction
> The Chatling API allows you to manage your chatbots programmatically.
Integrate Chatling into your application or interact with your chatbots programmatically using our API.
This documentation guides you through creating your API key, authenticating requests, and sending requests to the API.
## Generate your API key
To send requests to the API, you must include your API key. Here's how to create it:
1. Go to your Chatling account and open the Project Settings.
2. Click the API Keys tab.
3. Press the `New API key` button.
4. Enter a name for the key and press `Generate key`.
5. Copy the newly created key. For security purposes, the API key will be displayed once only. Note it down and store it in a secure place.
If you forget your API key, you must delete it and generate a new one.
## Authentication
Your API key acts as the Bearer token and must be supplied in the `Authorization` header of every request.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/api-reference/v2/intro.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# API Introduction
> The Chatling API allows you to manage your chatbots programmatically.
Integrate Chatling into your application or interact with your chatbots programmatically using our API.
This documentation guides you through creating your API key, authenticating requests, and sending requests to the API.
## Generate your API key
To send requests to the API, you must include your API key. Here's how to create it:
1. Go to your Chatling account and open the Project Settings.
2. Click the API Keys tab.
3. Press the `New API key` button.
4. Enter a name for the key and press `Generate key`.
5. Copy the newly created key. For security purposes, the API key will be displayed once only. Note it down and store it in a secure place.
If you forget your API key, you must delete it and generate a new one.
## Authentication
Your API key acts as the Bearer token and must be supplied in the `Authorization` header of every request.
 3. Enter the email address of the member you want to invite and select one or more roles to assign to them.
3. Enter the email address of the member you want to invite and select one or more roles to assign to them.
 4. Click **Send invite**.
The user will receive an email invitation to join the project. Once they accept the invitation, they will be added to the project with the assigned roles.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/api-reference/v2/usage/knowledge-base.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Knowledge Base
> Get the knowledge base usage for the project.
## Response
4. Click **Send invite**.
The user will receive an email invitation to join the project. Once they accept the invitation, they will be added to the project with the assigned roles.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/api-reference/v2/usage/knowledge-base.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Knowledge Base
> Get the knowledge base usage for the project.
## Response
 ---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/ai-agent/actions/lead-form.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Lead Form
Collect qualified leads right inside the conversation. The Lead Form action lets your AI Agent present a form in chat, collect user's information, and save them as a contact.
Any contacts saved by the AI agent will be displayed in the `Contacts` page in your dashboard.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/ai-agent/actions/lead-form.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Lead Form
Collect qualified leads right inside the conversation. The Lead Form action lets your AI Agent present a form in chat, collect user's information, and save them as a contact.
Any contacts saved by the AI agent will be displayed in the `Contacts` page in your dashboard.
 ## Configuration
Below are the configuration options for the Lead Form action:
### `Mandatory`
Determines whether the form submission is mandatory. When enabled, the user will be required to submit the form before they can continue.
If the option is disabled, an "X" button will be displayed in the form to allow the user to dismiss the form.
## Configuration
Below are the configuration options for the Lead Form action:
### `Mandatory`
Determines whether the form submission is mandatory. When enabled, the user will be required to submit the form before they can continue.
If the option is disabled, an "X" button will be displayed in the form to allow the user to dismiss the form.
 ### `Fields`
Add and configure the fields you want to include in the form. You can add multiple fields and specify whether they must be required.
### `Fields`
Add and configure the fields you want to include in the form. You can add multiple fields and specify whether they must be required.
 To reorder, grab the drag handle on the left of a field and move it up or down.
To reorder, grab the drag handle on the left of a field and move it up or down.
 ### `When to Use`
A detailed description of when the AI agent should use this action.
### `When to Use`
A detailed description of when the AI agent should use this action.
 ### `Customize Text`
You can customize the text to be displayed for the submit button and success message.
The success message is the message that is displayed after the form is submitted. It is optional and can be disabled.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/api-reference/v2/ai-kb/list-ai-languages.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# List AI languages
> Get a list of all the supported AI languages.
## Request parameters
### Path
### `Customize Text`
You can customize the text to be displayed for the submit button and success message.
The success message is the message that is displayed after the form is submitted. It is optional and can be disabled.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/api-reference/v2/ai-kb/list-ai-languages.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# List AI languages
> Get a list of all the supported AI languages.
## Request parameters
### Path
 ## Creating an intent
1. Open the Intents page.
2. Click the `New` button.
## Creating an intent
1. Open the Intents page.
2. Click the `New` button.
 3. Enter the details for the intent.
* **Name**: A clear, descriptive identifier (e.g., "Order Tracking", "Submit ticket").
* **Description**: Explains the user's goal or purpose this intent represents.
* **Sample phrases**: Examples of user messages that should trigger this intent. This helps the chatbot understand and match the intent.
3. Enter the details for the intent.
* **Name**: A clear, descriptive identifier (e.g., "Order Tracking", "Submit ticket").
* **Description**: Explains the user's goal or purpose this intent represents.
* **Sample phrases**: Examples of user messages that should trigger this intent. This helps the chatbot understand and match the intent.
 4. Click the `Create intent` button.
## Editing an intent
1. Open the Intents page to view all the existing intents.
2. Find and click on the intent you want to edit.
3. Make changes to the intent's details, such as name, description, and sample phrases.
4. Click the `Create intent` button.
## Editing an intent
1. Open the Intents page to view all the existing intents.
2. Find and click on the intent you want to edit.
3. Make changes to the intent's details, such as name, description, and sample phrases.
 4. Click the `Save` button to save your changes.
## Deleting intents
1. Open the Intents page to view all the existing intents.
2. Click the checkbox next to one or more intents you want to delete.
4. Click the `Save` button to save your changes.
## Deleting intents
1. Open the Intents page to view all the existing intents.
2. Click the checkbox next to one or more intents you want to delete.
 3. Click the `Delete` button in the top left.
3. Click the `Delete` button in the top left.
 ---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/missing-topics.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Got other questions?
If there are any topics you'd like to see covered in the documentation, please let us know! We're always looking to improve our documentation and make it as helpful as possible for our users.
Please reach out to us at [support@chatling.ai](mailto:support@chatling.ai) with your suggestions and any questions you have.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/blocks/inputs/number.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Number Block
> Learn about the Number input block and how to set it up in the Builder.
The Number block is used to collect numerical input from users. You can use this block to ask users for numbers, such as quantities, prices, or percentages.
## Configuration
The Number block has the following configuration options:
* **Store answer in variable**: The variable where the user's input will be stored.
* **Input required**: Whether the user's input is mandatory. If disabled, a Skip button will appear, allowing users to skip the input.
* **Date type**: The type of number the block will accept. You can choose from the following options:
* \*\*Number (Integer/Decimal): Accepts any number, including whole numbers and decimals.
* **Integer**: Accepts only whole numbers.
* **Min**: The minimum value the user can input.
* **Max**: The maximum value the user can input.
* **[Quick replies](/chatbot/builder/block-options/quick-replies)**
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/missing-topics.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Got other questions?
If there are any topics you'd like to see covered in the documentation, please let us know! We're always looking to improve our documentation and make it as helpful as possible for our users.
Please reach out to us at [support@chatling.ai](mailto:support@chatling.ai) with your suggestions and any questions you have.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/blocks/inputs/number.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Number Block
> Learn about the Number input block and how to set it up in the Builder.
The Number block is used to collect numerical input from users. You can use this block to ask users for numbers, such as quantities, prices, or percentages.
## Configuration
The Number block has the following configuration options:
* **Store answer in variable**: The variable where the user's input will be stored.
* **Input required**: Whether the user's input is mandatory. If disabled, a Skip button will appear, allowing users to skip the input.
* **Date type**: The type of number the block will accept. You can choose from the following options:
* \*\*Number (Integer/Decimal): Accepts any number, including whole numbers and decimals.
* **Integer**: Accepts only whole numbers.
* **Min**: The minimum value the user can input.
* **Max**: The maximum value the user can input.
* **[Quick replies](/chatbot/builder/block-options/quick-replies)**
 ---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/web-widget/operating-hours.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Operating hours
> Schedule the chatbot to be visible at certain times.
You can set the operating hours for your chatbot to define when it should be available to users. This is useful if you want to limit the chatbot's availability to certain times of the day or week, e.g during business hours or off-hours.
When outside of the operating hours, your chatbot will be automatically hidden, ensuring it's only live when you want it to be.
## Set operating hours
1. From your chatbot's dashboard, go to the **Settings** page.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/web-widget/operating-hours.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Operating hours
> Schedule the chatbot to be visible at certain times.
You can set the operating hours for your chatbot to define when it should be available to users. This is useful if you want to limit the chatbot's availability to certain times of the day or week, e.g during business hours or off-hours.
When outside of the operating hours, your chatbot will be automatically hidden, ensuring it's only live when you want it to be.
## Set operating hours
1. From your chatbot's dashboard, go to the **Settings** page.
 3. Under the `Operating hours` section, click the `Set operating hours` button.
3. Under the `Operating hours` section, click the `Set operating hours` button.
 4. Select the days and times when the chatbot should be visible. **Note that the timezone is UTC.**
To keep the chatbot visible throughout the day, leave the start and end times empty.
4. Select the days and times when the chatbot should be visible. **Note that the timezone is UTC.**
To keep the chatbot visible throughout the day, leave the start and end times empty.
 5. Click the `Add` button to add the schedule.
6. Click the `Save` button to save the changes.
Once you define the operating hours, the chatbot will be visible during the specified times and hidden outside of these hours.
## Edit existing operating hours
To edit the operating hours, you have to delete one or more schedules that you want to edit and then add the new schedules.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/whatsapp/overview.md
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/web-widget/installation/overview.md
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/team-members/overview.md
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/knowledge-base/overview.md
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/contacts/overview.md
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/blocks/trigger/overview.md
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/blocks/overview.md
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/blocks/hubspot/overview.md
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/blocks/condition/overview.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Overview
> Learn about the condition blocks and how to use them
Condition blocks are used to create conditional logic in your bot. You can use it to check if a certain condition is met and then perform different actions based on the result.
Similar to an "if-else" statement in programming, condition blocks evaluate a condition and executes different paths based on whether the condition is true or false.
5. Click the `Add` button to add the schedule.
6. Click the `Save` button to save the changes.
Once you define the operating hours, the chatbot will be visible during the specified times and hidden outside of these hours.
## Edit existing operating hours
To edit the operating hours, you have to delete one or more schedules that you want to edit and then add the new schedules.
---
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/whatsapp/overview.md
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/web-widget/installation/overview.md
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/team-members/overview.md
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/knowledge-base/overview.md
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/contacts/overview.md
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/blocks/trigger/overview.md
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/blocks/overview.md
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/blocks/hubspot/overview.md
# Source: https://docs.chatling.ai/chatbot/builder/blocks/condition/overview.md
> ## Documentation Index
> Fetch the complete documentation index at: https://docs.chatling.ai/llms.txt
> Use this file to discover all available pages before exploring further.
# Overview
> Learn about the condition blocks and how to use them
Condition blocks are used to create conditional logic in your bot. You can use it to check if a certain condition is met and then perform different actions based on the result.
Similar to an "if-else" statement in programming, condition blocks evaluate a condition and executes different paths based on whether the condition is true or false.
 ## Types of condition blocks
There are two types of condition blocks available in Chatling:
* [**Variable**](./variable): Compares a variable with a value or another variable.
* **Language**: Checks if the user's language matches a specific language. Useful for creating multilingual bots.
## How do condition blocks work?
Condition blocks consist of two main parts:
* **Conditions**: The conditions that the block will evaluate. You can use variables, languages, comparison operators, and logical operators to create complex conditions.
* **Paths**: The paths that the block will follow based on the result of the conditions. Every condition you add will have a corresponding path that the block will follow if the condition is true.
## Types of condition blocks
There are two types of condition blocks available in Chatling:
* [**Variable**](./variable): Compares a variable with a value or another variable.
* **Language**: Checks if the user's language matches a specific language. Useful for creating multilingual bots.
## How do condition blocks work?
Condition blocks consist of two main parts:
* **Conditions**: The conditions that the block will evaluate. You can use variables, languages, comparison operators, and logical operators to create complex conditions.
* **Paths**: The paths that the block will follow based on the result of the conditions. Every condition you add will have a corresponding path that the block will follow if the condition is true.
 Here's an example of how a condition block works:
1. The block evaluates conditions in the order they are added.
2. If a condition is true, the block follows the path associated with that condition.
3. If none of the conditions are true, the block follows the "Else" path.
## The Else condition
The `Else` condition is executed if none of the other conditions are met. You can use it to define a fallback path that the block will follow if none of the other conditions are true.
## Comparison operators
Conditions support a variety of comparison operators that you can use to compare values. Here are some of the operators you can use:
* **Equals**: Checks if the variable is equal to the value.
* **Not equals**: Checks if the variable is not equal to the value.
* **Contains**: Checks if the variable contains the value.
* **Not contains**: Checks if the variable does not contain the value.
* **Greater than or equals**: Checks if the variable is greater than or equal to the value.
* **Less than**: Checks if the variable is less than the value.
* **Less than or equals**: Checks if the variable is less than or equal to the value.
* **Starts with**: Checks if the variable starts with the value.
* **Ends with**: Checks if the variable ends with the value.
* **Is empty**: Checks if the variable is empty.
* **Is not empty**: Checks if the variable is not empty.
## Group and child conditions
Conditions are grouped together to create complex logic using logical operators like "AND" and "OR". Every group contains one or more conditions that are evaluated together.
Here's an example of how a condition block works:
1. The block evaluates conditions in the order they are added.
2. If a condition is true, the block follows the path associated with that condition.
3. If none of the conditions are true, the block follows the "Else" path.
## The Else condition
The `Else` condition is executed if none of the other conditions are met. You can use it to define a fallback path that the block will follow if none of the other conditions are true.
## Comparison operators
Conditions support a variety of comparison operators that you can use to compare values. Here are some of the operators you can use:
* **Equals**: Checks if the variable is equal to the value.
* **Not equals**: Checks if the variable is not equal to the value.
* **Contains**: Checks if the variable contains the value.
* **Not contains**: Checks if the variable does not contain the value.
* **Greater than or equals**: Checks if the variable is greater than or equal to the value.
* **Less than**: Checks if the variable is less than the value.
* **Less than or equals**: Checks if the variable is less than or equal to the value.
* **Starts with**: Checks if the variable starts with the value.
* **Ends with**: Checks if the variable ends with the value.
* **Is empty**: Checks if the variable is empty.
* **Is not empty**: Checks if the variable is not empty.
## Group and child conditions
Conditions are grouped together to create complex logic using logical operators like "AND" and "OR". Every group contains one or more conditions that are evaluated together.
 Conditions within a group are evaluated together to determine if the group is true or false. You can use logical operators such as "AND" and "OR" to combine conditions within a group.
For example, you can create a group with two conditions and set it to "AND" to require both conditions to be true for the group to be true. On the other hand, you can set it to "OR" to require only one of the conditions to be true for the group to be true.
By default, condition blocks have one group with one condition. To add additional groups, click the `Add group condition` button.
## Logical operators
Logical operators are used to combine conditions within a group. You can choose from the following logical operators:
* **AND**: Requires all conditions in the group to be true for the group to be true.
* **OR**: Requires at least one condition in the group to be true for the group to be true.
Conditions within a group are evaluated together to determine if the group is true or false. You can use logical operators such as "AND" and "OR" to combine conditions within a group.
For example, you can create a group with two conditions and set it to "AND" to require both conditions to be true for the group to be true. On the other hand, you can set it to "OR" to require only one of the conditions to be true for the group to be true.
By default, condition blocks have one group with one condition. To add additional groups, click the `Add group condition` button.
## Logical operators
Logical operators are used to combine conditions within a group. You can choose from the following logical operators:
* **AND**: Requires all conditions in the group to be true for the group to be true.
* **OR**: Requires at least one condition in the group to be true for the group to be true.